In Silico Analysis of Microarray-Based Gene Expression Profiles Predicts Tumor Cell Response to Withanolides
- PMID: 27605335
- PMCID: PMC5007710
- DOI: 10.3390/microarrays1010044
In Silico Analysis of Microarray-Based Gene Expression Profiles Predicts Tumor Cell Response to Withanolides
Abstract
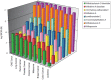
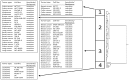
Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal (Indian ginseng, winter cherry, Solanaceae) is widely used in traditional medicine. Roots are either chewed or used to prepare beverages (aqueous decocts). The major secondary metabolites of Withania somnifera are the withanolides, which are C-28-steroidal lactone triterpenoids. Withania somnifera extracts exert chemopreventive and anticancer activities in vitro and in vivo. The aims of the present in silico study were, firstly, to investigate whether tumor cells develop cross-resistance between standard anticancer drugs and withanolides and, secondly, to elucidate the molecular determinants of sensitivity and resistance of tumor cells towards withanolides. Using IC50 concentrations of eight different withanolides (withaferin A, withaferin A diacetate, 3-azerininylwithaferin A, withafastuosin D diacetate, 4-B-hydroxy-withanolide E, isowithanololide E, withafastuosin E, and withaperuvin) and 19 established anticancer drugs, we analyzed the cross-resistance profile of 60 tumor cell lines. The cell lines revealed cross-resistance between the eight withanolides. Consistent cross-resistance between withanolides and nitrosoureas (carmustin, lomustin, and semimustin) was also observed. Then, we performed transcriptomic microarray-based COMPARE and hierarchical cluster analyses of mRNA expression to identify mRNA expression profiles predicting sensitivity or resistance towards withanolides. Genes from diverse functional groups were significantly associated with response of tumor cells to withaferin A diacetate, e.g. genes functioning in DNA damage and repair, stress response, cell growth regulation, extracellular matrix components, cell adhesion and cell migration, constituents of the ribosome, cytoskeletal organization and regulation, signal transduction, transcription factors, and others.
Keywords: cancer; drug development; medicinal food; microarray; natural products; pharmacogenomics.
Figures
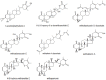
Similar articles
-
Extraction Optimization for Phenolic- and Withanolide-Rich Fractions from Withania somnifera Roots: Identification and Quantification of Withaferin A, 12-Deoxywithastromonolide, and Withanolide A in Plant Materials and Marketed Formulations Using a Reversed-Phase HPLC-Photodiode Array Detection Method.J AOAC Int. 2018 Nov 1;101(6):1773-1780. doi: 10.5740/jaoacint.18-0081. Epub 2018 Jun 26. J AOAC Int. 2018. PMID: 29945694
-
Withanolide A is inherently de novo biosynthesized in roots of the medicinal plant Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera).Physiol Plant. 2008 Jun;133(2):278-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3054.2008.01076.x. Epub 2008 Feb 26. Physiol Plant. 2008. PMID: 18312497
-
Metabolic characterization of Withania somnifera from different regions of India using NMR spectroscopy.Planta Med. 2011 Nov;77(17):1958-64. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1279997. Epub 2011 Jul 4. Planta Med. 2011. PMID: 21728148
-
Overview of the anticancer activity of withaferin A, an active constituent of the Indian ginseng Withania somnifera.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Jul;27(21):26025-26035. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09028-0. Epub 2020 May 13. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32405942 Review.
-
An updated review on phytochemistry and molecular targets of Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal (Ashwagandha).Front Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 29;14:1049334. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1049334. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37063285 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Efferth T., Kahl S., Paulus K., Adams M., Rauh R., Boechzelt H., Hao X., Kaina B., Bauer R. Phytochemistry and pharmacogenomics of natural products derived from traditional Chinese medicine and Chinese Materia Medica with activity against tumour cells. Mol. Cancer Therap. 2008;7:152–161. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-0073. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Li J.W.H., Vederas J.C. Drug discovery and natural products: End of an era or an endless frontier? Science. 2009;325:161–165. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

