Inhibition of never in mitosis A (NIMA)-related kinase-4 reduces survivin expression and sensitizes cancer cells to TRAIL-induced cell death
- PMID: 27602754
- PMCID: PMC5323206
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.11781
Inhibition of never in mitosis A (NIMA)-related kinase-4 reduces survivin expression and sensitizes cancer cells to TRAIL-induced cell death
Abstract
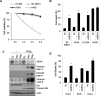
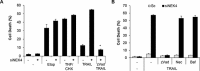
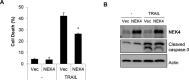
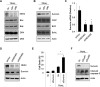
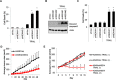
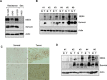
The tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) preferentially induces apoptosis in cancer cells. However, many tumors are resistant to TRAIL-induced apoptosis, and resistance mechanisms are not fully understood. To identify novel regulatory molecules of TRAIL resistance, we screened a siRNA library targeting the human kinome, and NEK4 (NIMA-related kinase-4) was identified. Knockdown of NEK4 sensitized TRAIL-resistant cancer cells and in vivo xenografts to cell death. In contrast, over expression of NEK4 suppressed TRAIL-induced cell death in TRAIL-sensitive cancer cells. In addition, loss of NEK4 resulted in decrease of the anti-apoptotic protein survivin, but an increase in apoptotic cell death. Interestingly, NEK4 was highly upregulated in tumor tissues derived from patients with lung cancer and colon cancer. These results suggest that inhibition of NEK4 sensitizes cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by regulation of survivin expression.
Keywords: NEK4; TRAIL; cancer; survivin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
2-methoxy-5-amino-N-hydroxybenzamide sensitizes colon cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by regulating death receptor 5 and survivin expression.Mol Cancer Ther. 2011 Oct;10(10):1969-81. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0316. Epub 2011 Aug 4. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011. PMID: 21817114
-
Aspirin sensitizes cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by reducing survivin levels.Clin Cancer Res. 2008 May 15;14(10):3168-76. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-4362. Clin Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18483385
-
HIF-2α dictates the susceptibility of pancreatic cancer cells to TRAIL by regulating survivin expression.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 27;8(26):42887-42900. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17157. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28476028 Free PMC article.
-
Lessons from TRAIL-resistance mechanisms in colorectal cancer cells: paving the road to patient-tailored therapy.Drug Resist Updat. 2004 Dec;7(6):345-58. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2004.11.002. Epub 2005 Jan 8. Drug Resist Updat. 2004. PMID: 15790545 Review.
-
Survivin as a Potential Target for Cancer Therapy.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16(15):6187-91. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2015.16.15.6187. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015. PMID: 26434815 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Senescence-Related Subtypes, the Development of a Prognosis Model, and Characterization of Immune Infiltration and Gut Microbiota in Colorectal Cancer.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 May 26;9:916565. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.916565. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35721059 Free PMC article.
-
NEK4 kinase regulates EMT to promote lung cancer metastasis.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Dec;22(12):5877-5887. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13857. Epub 2018 Sep 24. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30247800 Free PMC article.
-
In depth analysis of kinase cross screening data to identify chemical starting points for inhibition of the Nek family of kinases.Medchemcomm. 2017 Dec 8;9(1):44-66. doi: 10.1039/c7md00510e. eCollection 2018 Jan 1. Medchemcomm. 2017. PMID: 30108900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NEK5 interacts with LonP1 and its kinase activity is essential for the regulation of mitochondrial functions and mtDNA maintenance.FEBS Open Bio. 2021 Mar;11(3):546-563. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13108. Epub 2021 Feb 24. FEBS Open Bio. 2021. PMID: 33547867 Free PMC article.
-
NEK Family Review and Correlations with Patient Survival Outcomes in Various Cancer Types.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Mar 30;15(7):2067. doi: 10.3390/cancers15072067. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37046733 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yaacoub K, Pedeux R, Tarte K, Guillaudeux T. Role of the tumor microenvironment in regulating apoptosis and cancer progression. Cancer Lett. 2016;378:150–159. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

