Steroidogenic Factor 1 in the Ventromedial Nucleus of the Hypothalamus Regulates Age-Dependent Obesity
- PMID: 27598259
- PMCID: PMC5012732
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162352
Steroidogenic Factor 1 in the Ventromedial Nucleus of the Hypothalamus Regulates Age-Dependent Obesity
Abstract
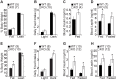
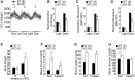
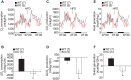
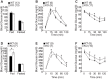
The ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus (VMH) is important for the regulation of whole body energy homeostasis and lesions in the VMH are reported to result in massive weight gain. The nuclear receptor steroidogenic factor 1 (SF-1) is a known VMH marker as it is exclusively expressed in the VMH region of the brain. SF-1 plays a critical role not only in the development of VMH but also in its physiological functions. In this study, we generated prenatal VMH-specific SF-1 KO mice and investigated age-dependent energy homeostasis regulation by SF-1. Deletion of SF-1 in the VMH resulted in dysregulated insulin and leptin homeostasis and late onset obesity due to increased food intake under normal chow and high fat diet conditions. In addition, SF-1 ablation was accompanied by a marked reduction in energy expenditure and physical activity and this effect was significantly pronounced in the aged mice. Taken together, our data indicates that SF-1 is a key component in the VMH-mediated regulation of energy homeostasis and implies that SF-1 plays a protective role against metabolic stressors including aging and high fat diet.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CPT1C in the ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus is necessary for brown fat thermogenesis activation in obesity.Mol Metab. 2019 Jan;19:75-85. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2018.10.010. Epub 2018 Nov 2. Mol Metab. 2019. PMID: 30448371 Free PMC article.
-
High-fat feeding promotes obesity via insulin receptor/PI3K-dependent inhibition of SF-1 VMH neurons.Nat Neurosci. 2011 Jun 5;14(7):911-8. doi: 10.1038/nn.2847. Nat Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21642975 Free PMC article.
-
Gsα Deficiency in the Ventromedial Hypothalamus Enhances Leptin Sensitivity and Improves Glucose Homeostasis in Mice on a High-Fat Diet.Endocrinology. 2016 Feb;157(2):600-10. doi: 10.1210/en.2015-1700. Epub 2015 Dec 15. Endocrinology. 2016. PMID: 26671183 Free PMC article.
-
SF-1 in the ventral medial hypothalamic nucleus: a key regulator of homeostasis.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2011 Apr 10;336(1-2):219-23. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2010.11.019. Epub 2010 Nov 24. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21111025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypothalamic and genetic obesity: an appraisal of the autonomic hypothesis and the endocrine hypothesis.Int J Obes. 1984;8 Suppl 1:119-37. Int J Obes. 1984. PMID: 6398803 Review.
Cited by
-
Estrogenic regulation of reproduction and energy homeostasis by a triumvirate of hypothalamic arcuate neurons.J Neuroendocrinol. 2022 Jun;34(6):e13145. doi: 10.1111/jne.13145. Epub 2022 May 17. J Neuroendocrinol. 2022. PMID: 35581942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypothalamic SLC7A14 accounts for aging-reduced lipolysis in white adipose tissue of male mice.Nat Commun. 2024 Sep 11;15(1):7948. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52059-1. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39261456 Free PMC article.
-
Nociceptin/orphanin FQ modulates energy homeostasis through inhibition of neurotransmission at VMN SF-1/ARC POMC synapses in a sex- and diet-dependent manner.Biol Sex Differ. 2019 Feb 12;10(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s13293-019-0220-3. Biol Sex Differ. 2019. PMID: 30755252 Free PMC article.
-
ADGRL1 is a glucose receptor involved in mediating energy and glucose homeostasis.Diabetologia. 2024 Jan;67(1):170-189. doi: 10.1007/s00125-023-06010-6. Epub 2023 Sep 15. Diabetologia. 2024. PMID: 37712955 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin Regulates Adrenal Steroidogenesis by Stabilizing SF-1 Activity.Sci Rep. 2018 Mar 22;8(1):5025. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-23298-2. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29567944 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parker KL. The roles of steroidogenic factor 1 in endocrine development and function. Molecular and cellular endocrinology. 1998;145(1–2):15–20. . - PubMed
-
- Shinoda K, Lei H, Yoshii H, Nomura M, Nagano M, Shiba H, et al. Developmental defects of the ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus and pituitary gonadotroph in the Ftz-F1 disrupted mice. Developmental dynamics: an official publication of the American Association of Anatomists. 1995;204(1):22–9. 10.1002/aja.1002040104 . - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

