Knockdown of the M2 Isoform of Pyruvate Kinase (PKM2) with shRNA Enhances the Effect of Docetaxel in Human NSCLC Cell Lines In Vitro
- PMID: 27593857
- PMCID: PMC5011261
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.6.1312
Knockdown of the M2 Isoform of Pyruvate Kinase (PKM2) with shRNA Enhances the Effect of Docetaxel in Human NSCLC Cell Lines In Vitro
Abstract
Purpose: The aim of our study was to explore the relationships between the M2 isoform of pyruvate kinase (PKM2) and the sensitivity of human non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells to docetaxel in vitro.
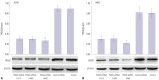
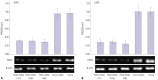
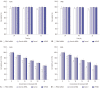
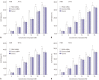
Materials and methods: With the method of plasmid transfection, we silenced the expression of PKM2 successfully in A549 and H460 cells. Western blotting and real-time PCR were applied to detect PKM2 expression at protein and gene levels. Cell viability was examined by CCK8 assay. Cell cycle distribution and apoptosis were examined by flow cytometry. P21 and Bax were detected.
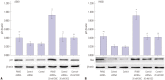
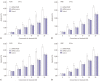
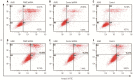
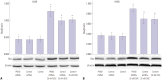
Results: Expression of PKM2 mRNA and protein were significantly decreased by shRNA targeting PKM2. Silencing of PKM2 increased docetaxel sensitivity of human NSCLC A549 and H460 cells in a collaborative manner, resulting in strong suppression of cell viability. The results of flow cytometric assays suggested that knockdown of PKM2 or docetaxel treatment, whether used singly or in combination, blocked the cells in the G2/M phase, which is in consistent with the effect of the two on the expression of p21. Cells with PKM2 silencing were more likely to be induced into apoptosis by docetaxel although knockdown of PKM2 alone can't induce apoptosis significantly, which is in consistent with the effect of the two on Bax expression.
Conclusion: The results suggest that PKM2 knockdown could serve as a chemosensitizer to docetaxel in non-small lung cancer cells through targeting PKM2, leading to inhibition of cell viability, increase of cell arrest of G2/M phase and apoptosis.
Keywords: The M2 isoform of pyruvate kinase; apoptosis; cell cycle; chemotherapy; docetaxel; non-small cell lung cancer; shRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting pyruvate kinase M2 contributes to radiosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo.Cancer Lett. 2015 Jan 28;356(2 Pt B):985-93. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.11.016. Epub 2014 Nov 13. Cancer Lett. 2015. PMID: 25444918
-
Subcellular compartmentalization of PKM2 identifies anti-PKM2 therapy response in vitro and in vivo mouse model of human non-small-cell lung cancer.PLoS One. 2019 May 23;14(5):e0217131. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0217131. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31120964 Free PMC article.
-
Docetaxel inhibits the proliferation of non-small-cell lung cancer cells via upregulation of microRNA-7 expression.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Aug 1;8(8):9072-80. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26464649 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation and function of pyruvate kinase M2 in cancer.Cancer Lett. 2013 Oct 10;339(2):153-8. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.06.008. Epub 2013 Jun 18. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 23791887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The molecular mechanisms of LncRNA-correlated PKM2 in cancer metabolism.Biosci Rep. 2019 Nov 29;39(11):BSR20192453. doi: 10.1042/BSR20192453. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31654067 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A highly expressed mRNA signature for predicting survival in patients with stage I/II non-small-cell lung cancer after operation.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 12;11(1):5855. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85246-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33712694 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating Glycolysis to Improve Cancer Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 30;24(3):2606. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032606. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of pyruvate kinase M2 in anticancer therapeutic treatments.Oncol Lett. 2019 Dec;18(6):5663-5672. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10948. Epub 2019 Oct 2. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31788038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Metabolic Remodelling in Lung Cancer and Its Putative Consequence in Therapy Response.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1219:311-333. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-34025-4_16. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32130706 Review.
-
The effects of hypoxia on mitochondrial function and metabolism in gastric cancer cells.Transl Cancer Res. 2021 Feb;10(2):817-826. doi: 10.21037/tcr-20-2598. Transl Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 35116412 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Warburg O. On the origin of cancer cells. Science. 1956;123:309–314. - PubMed
-
- Mazurek S. Pyruvate kinase type M2: a key regulator of the metabolic budget system in tumor cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011;43:969–980. - PubMed
-
- Yeh CS, Wang JY, Chung FY, Lee SC, Huang MY, Kuo CW, et al. Significance of the glycolytic pathway and glycolysis related-genes in tumorigenesis of human colorectal cancers. Oncol Rep. 2008;19:81–91. - PubMed
-
- Gumińska M, Ignacak J, Kedryna T, Stachurska MB. Tumor-specific pyruvate kinase isoenzyme M2 involved in biochemical strategy of energy generation in neoplastic cells. Acta Biochim Pol. 1997;44:711–724. - PubMed
-
- Hacker HJ, Steinberg P, Bannasch P. Pyruvate kinase isoenzyme shift from L-type to M2-type is a late event in hepatocarcinogenesis induced in rats by a choline-deficient/DL-ethionine-supplemented diet. Carcinogenesis. 1998;19:99–107. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

