How Polyomaviruses Exploit the ERAD Machinery to Cause Infection
- PMID: 27589785
- PMCID: PMC5035956
- DOI: 10.3390/v8090242
How Polyomaviruses Exploit the ERAD Machinery to Cause Infection
Abstract
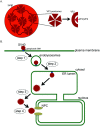
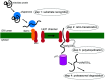
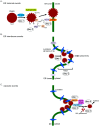
To infect cells, polyomavirus (PyV) traffics from the cell surface to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) where it hijacks elements of the ER-associated degradation (ERAD) machinery to penetrate the ER membrane and reach the cytosol. From the cytosol, the virus transports to the nucleus, enabling transcription and replication of the viral genome that leads to lytic infection or cellular transformation. How PyV exploits the ERAD machinery to cross the ER membrane and access the cytosol, a decisive infection step, remains enigmatic. However, recent studies have slowly unraveled many aspects of this process. These emerging insights should advance our efforts to develop more effective therapies against PyV-induced human diseases.
Keywords: ERAD; SV40; membrane penetration; polyomavirus; protein aggregation.
Conflict of interest statement
This work is funded by the National Institutes of Health (RO1 AI064296-10 and RO1 GM113722). None of the authors have a conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A nucleotide exchange factor promotes endoplasmic reticulum-to-cytosol membrane penetration of the nonenveloped virus simian virus 40.J Virol. 2015 Apr;89(8):4069-79. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03552-14. Epub 2015 Feb 4. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25653441 Free PMC article.
-
The endoplasmic reticulum membrane J protein C18 executes a distinct role in promoting simian virus 40 membrane penetration.J Virol. 2015 Apr;89(8):4058-68. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03574-14. Epub 2015 Jan 28. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25631089 Free PMC article.
-
ERdj5 Reductase Cooperates with Protein Disulfide Isomerase To Promote Simian Virus 40 Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane Translocation.J Virol. 2015 Sep;89(17):8897-908. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00941-15. Epub 2015 Jun 17. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26085143 Free PMC article.
-
A bacterial toxin and a nonenveloped virus hijack ER-to-cytosol membrane translocation pathways to cause disease.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2015;50(6):477-88. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2015.1085826. Epub 2015 Sep 11. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 26362261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SV40 Hijacks Cellular Transport, Membrane Penetration, and Disassembly Machineries to Promote Infection.Viruses. 2019 Oct 5;11(10):917. doi: 10.3390/v11100917. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31590347 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TBK1 is part of a galectin 8 dependent membrane damage recognition complex and drives autophagy upon Adenovirus endosomal escape.PLoS Pathog. 2022 Jul 20;18(7):e1010736. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010736. eCollection 2022 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 35857795 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress: New insights into the pathogenesis and treatment of retinal degenerative diseases.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2020 Nov;79:100860. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2020.100860. Epub 2020 Apr 6. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2020. PMID: 32272207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How non-enveloped viruses hijack host machineries to cause infection.Adv Virus Res. 2019;104:97-122. doi: 10.1016/bs.aivir.2019.05.002. Epub 2019 Jul 2. Adv Virus Res. 2019. PMID: 31439154 Free PMC article.
-
A plant reovirus hijacks the DNAJB12-Hsc70 chaperone complex to promote viral spread in its planthopper vector.Mol Plant Pathol. 2022 Jun;23(6):805-818. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13152. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Mol Plant Pathol. 2022. PMID: 34668642 Free PMC article.
-
A Transcriptomics Approach Reveals Putative Interaction of Candidatus Liberibacter Solanacearum with the Endoplasmic Reticulum of Its Psyllid Vector.Insects. 2019 Sep 2;10(9):279. doi: 10.3390/insects10090279. Insects. 2019. PMID: 31480697 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

