Activation of AKT pathway by Nrf2/PDGFA feedback loop contributes to HCC progression
- PMID: 27588483
- PMCID: PMC5323163
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.11700
Activation of AKT pathway by Nrf2/PDGFA feedback loop contributes to HCC progression
Abstract
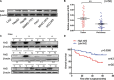
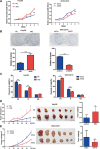
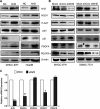
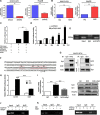
Nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a master transcription factor in the antioxidant response, has been found to be ubiquitously expressed in various cancer cells and in the regulation tumor proliferation, invasion, and chemoresistance activities. The regulatory roles of Nrf2 in controlling Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) progression remain unclear. In this study, we demonstrated that Nrf2 was significantly elevated in HCC cells and tissues and was correlated with poor prognosis of HCCs. Consistently, Nrf2 significantly promoted HCC cell growth both in vitro and in vivo. Further investigation suggested a novel association of Nrf2 with Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-A (PDGFA). Nrf2 promoted PDGFA transcription by recruiting specificity protein 1 (Sp1) to its promoter, resulting in increased activation of the AKT/p21 pathway and cell cycle progression of HCC cells. As a feedback loop, PDGFA enhanced Nrf2 expression and activation in an AKT dependent manner. In line with these findings, expression of Nrf2 and PDGFA were positively correlated in HCC tissues. Taken together, this study uncovers a novel mechanism of the Nrf2/PDGFA regulatory loop that is crucial for AKT-dependent HCC progression, and thereby provides potential targets for HCC therapy.
Keywords: AKT; Nrf2; PDGFA; hepatocellular carcinoma; tumorigenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Hepatocellular Carcinoma Induction by Aberrant NRF2 Activation-Mediated Transcription Networks: Interaction of NRF2-KEAP1 Controls the Fate of Hepatocarcinogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 29;21(15):5378. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155378. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32751080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GSTZ1 deficiency promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation via activation of the KEAP1/NRF2 pathway.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Oct 30;38(1):438. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1459-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31666108 Free PMC article.
-
STK17B promotes carcinogenesis and metastasis via AKT/GSK-3β/Snail signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Feb 14;9(2):236. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0262-1. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 29445189 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of brachyury contributes to tumor metastasis by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2014 Dec 14;33(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s13046-014-0105-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25499255 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear factor erythroid 2 (NF-E2)-related factor 2 (Nrf2) in autophagy-induced hepatocellular carcinoma.Clin Chim Acta. 2020 Jul;506:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2020.02.028. Epub 2020 Feb 25. Clin Chim Acta. 2020. PMID: 32109431 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Hepatocellular Carcinoma Induction by Aberrant NRF2 Activation-Mediated Transcription Networks: Interaction of NRF2-KEAP1 Controls the Fate of Hepatocarcinogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 29;21(15):5378. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155378. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32751080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of polyphenols in overcoming cancer drug resistance: a comprehensive review.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022 Jan 3;27(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s11658-021-00301-9. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022. PMID: 34979906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative stress indicated by elevated expression of Nrf2 and 8-OHdG promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression.Med Oncol. 2017 Apr;34(4):57. doi: 10.1007/s12032-017-0914-5. Epub 2017 Mar 9. Med Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28281193
-
Prospect of Circular RNA in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Novel Potential Biomarker and Therapeutic Target.Front Oncol. 2018 Aug 23;8:332. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00332. eCollection 2018. Front Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30191143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Demethylation of the NRF2 Promoter Protects Against Carcinogenesis Induced by Nano-SiO2.Front Genet. 2020 Jul 28;11:818. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00818. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32849814 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tang ZY, Ye SL, Liu YK, Qin LX, Sun HC, Ye QH, Wang L, Zhou J, Qiu SJ, Li Y, Ji XN, Liu H, Xia JL, et al. A decade's studies on metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2004;130:187–196. - PubMed
-
- Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2012;379:1245–1255. - PubMed
-
- Mitsuishi Y, Taguchi K, Kawatani Y, Shibata T, Nukiwa T, Aburatani H, Yamamoto M, Motohashi H. Nrf2 redirects glucose and glutamine into anabolic pathways in metabolic reprogramming. Cancer Cell. 2012;22:66–79. - PubMed
-
- Zipper LM, Mulcahy RT. The Keap1 BTB/POZ dimerization function is required to sequester Nrf2 in cytoplasm. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:36544–36552. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

