The Role of the Endoscopist in the Stroke Unit
- PMID: 27588296
- PMCID: PMC4988254
- DOI: 10.1159/000443656
The Role of the Endoscopist in the Stroke Unit
Abstract
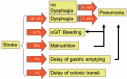
Background: Acute cerebral stroke is a common problem that is frequently associated with dysphagia resulting in an increased risk of aspiration pneumonia, complication, and mortality.
Methods: A literature review was carried out using the search terms 'stroke unit and endoscopy', 'stroke unit and dysphagia', and 'stroke unit and gastroenterology'.
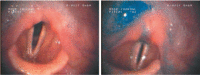
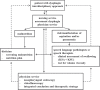
Results: Only few papers focus on the role of endoscopy in stroke units. One major role is the early detection of dysphagia by flexible endoscopic evaluation of swallowing (FEES). FEES appears to have a higher sensitivity and specificity compared to bedside tests and challenges videofluoroscopy. In contrast, other stroke-associated gastrointestinal complications requiring endoscopic diagnostic or therapeutic intervention, such as gastrointestinal bleeding, abdominal pain, or stasis, and the need to provide fluid and food via gastrostomy or jejunostomy are rarely seen in stroke units and become relevant during and after the rehabilitation phase.
Conclusion: FEES should involve an interdisciplinary team comprising neurologists, speech and language pathologists and/or therapists, as well as gastroenterologic endoscopists.
Keywords: Acute stroke; Dysphagia; Endoscopy Aspiration; Gastrostomy tube feeding; Stroke unit.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Speech-language pathologist-led fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing: functional outcomes for patients after stroke.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2014 Mar;23(3):e195-200. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2013.09.031. Epub 2013 Dec 19. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2014. PMID: 24361193
-
[FEES in the stroke unit: recommendations for implementation in the clinical routine].Nervenarzt. 2013 Jun;84(6):705-8. doi: 10.1007/s00115-013-3791-y. Nervenarzt. 2013. PMID: 23695003 Review. German.
-
Predictors of Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy Placement in Acute Ischemic Stroke.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2018 Nov;27(11):3200-3207. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2018.07.022. Epub 2018 Aug 29. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2018. PMID: 30172678
-
Prediction of outcome in neurogenic oropharyngeal dysphagia within 72 hours of acute stroke.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2012 Oct;21(7):569-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2011.01.004. Epub 2011 Jun 16. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2012. PMID: 21683618
-
Factors Associated With Gastrostomy Tube Removal in Patients With Dysphagia After Stroke: A Review of the Literature.Nutr Clin Pract. 2017 Apr;32(2):166-174. doi: 10.1177/0884533616661012. Nutr Clin Pract. 2017. PMID: 29927529 Review.
Cited by
-
Endoscopy Is Relatively Safe in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke and Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage.Dig Dis Sci. 2019 Jun;64(6):1588-1598. doi: 10.1007/s10620-018-5399-3. Epub 2018 Dec 5. Dig Dis Sci. 2019. PMID: 30519853
-
History of Fiberoptic Endoscopic Evaluation of Swallowing for Evaluation and Management of Pharyngeal Dysphagia: Changes over the Years.Dysphagia. 2017 Feb;32(1):27-38. doi: 10.1007/s00455-016-9775-x. Epub 2017 Jan 18. Dysphagia. 2017. PMID: 28101663 Review. No abstract available.
-
What is the value of fibre-endoscopic evaluation of swallowing (FEES) in neurological patients? A cross-sectional hospital-based registry study.BMJ Open. 2018 Mar 6;8(3):e019016. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-019016. BMJ Open. 2018. PMID: 29511010 Free PMC article.
-
Interventional and Interdisciplinary Endoscopy - Developments and Chances.Visc Med. 2016 Feb;32(1):6. doi: 10.1159/000444375. Epub 2016 Feb 16. Visc Med. 2016. PMID: 27588289 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Axelsson K, Norberg A, Asplund K. Eating after a stroke - towards an integrated view. Int J Nursing Stud. 1984;21:93–99. - PubMed
-
- Davalos A, Ricart W, Gonzalez-Huix F, et al. Effect of malnutrition after acute stroke on clinical outcome. Stroke. 1996;27:1028–1032. - PubMed
-
- Perry L, Love CP. Screening for dysphagia and aspiration in acute stroke: a systematic review. Dysphagia. 2001;16:7–18. - PubMed
-
- Meng NH, Wang TG, Lien IN, et al. Dysphagia in patients with brainstem stroke: incidence and outcome. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2000;79:170–175. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

