Benzimidazole derivative small-molecule 991 enhances AMPK activity and glucose uptake induced by AICAR or contraction in skeletal muscle
- PMID: 27577855
- PMCID: PMC5241553
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00237.2016
Benzimidazole derivative small-molecule 991 enhances AMPK activity and glucose uptake induced by AICAR or contraction in skeletal muscle
Abstract
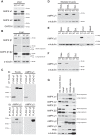
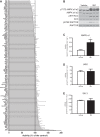
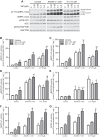
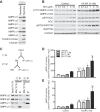
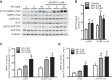
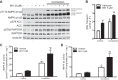
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) plays diverse roles and coordinates complex metabolic pathways for maintenance of energy homeostasis. This could be explained by the fact that AMPK exists as multiple heterotrimer complexes comprising a catalytic α-subunit (α1 and α2) and regulatory β (β1 and β2)- and γ (γ1, γ2, γ3)-subunits, which are uniquely distributed across different cell types. There has been keen interest in developing specific and isoform-selective AMPK-activating drugs for therapeutic use and also as research tools. Moreover, establishing ways of enhancing cellular AMPK activity would be beneficial for both purposes. Here, we investigated if a recently described potent AMPK activator called 991, in combination with the commonly used activator 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide riboside or contraction, further enhances AMPK activity and glucose transport in mouse skeletal muscle ex vivo. Given that the γ3-subunit is exclusively expressed in skeletal muscle and has been implicated in contraction-induced glucose transport, we measured the activity of AMPKγ3 as well as ubiquitously expressed γ1-containing complexes. We initially validated the specificity of the antibodies for the assessment of isoform-specific AMPK activity using AMPK-deficient mouse models. We observed that a low dose of 991 (5 μM) stimulated a modest or negligible activity of both γ1- and γ3-containing AMPK complexes. Strikingly, dual treatment with 991 and 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide riboside or 991 and contraction profoundly enhanced AMPKγ1/γ3 complex activation and glucose transport compared with any of the single treatments. The study demonstrates the utility of a dual activator approach to achieve a greater activation of AMPK and downstream physiological responses in various cell types, including skeletal muscle.
Keywords: 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide riboside; 991; A769662; AMP-activated protein kinase; LKB1; compound 13; ex229.
Copyright © 2016 the American Physiological Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Direct small molecule ADaM-site AMPK activators reveal an AMPKγ3-independent mechanism for blood glucose lowering.Mol Metab. 2021 Sep;51:101259. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2021.101259. Epub 2021 May 23. Mol Metab. 2021. PMID: 34033941 Free PMC article.
-
A small-molecule benzimidazole derivative that potently activates AMPK to increase glucose transport in skeletal muscle: comparison with effects of contraction and other AMPK activators.Biochem J. 2014 Jun 15;460(3):363-75. doi: 10.1042/BJ20131673. Biochem J. 2014. PMID: 24665903
-
PT-1 selectively activates AMPK-γ1 complexes in mouse skeletal muscle, but activates all three γ subunit complexes in cultured human cells by inhibiting the respiratory chain.Biochem J. 2015 May 1;467(3):461-72. doi: 10.1042/BJ20141142. Biochem J. 2015. PMID: 25695398 Free PMC article.
-
AMP-activated protein kinase and muscle glucose uptake.Acta Physiol Scand. 2003 Aug;178(4):337-45. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-201X.2003.01168.x. Acta Physiol Scand. 2003. PMID: 12864738 Review.
-
Targeting the AMP-activated protein kinase for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.Curr Drug Targets Immune Endocr Metabol Disord. 2002 Jul;2(2):119-27. Curr Drug Targets Immune Endocr Metabol Disord. 2002. PMID: 12476786 Review.
Cited by
-
Direct small molecule ADaM-site AMPK activators reveal an AMPKγ3-independent mechanism for blood glucose lowering.Mol Metab. 2021 Sep;51:101259. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2021.101259. Epub 2021 May 23. Mol Metab. 2021. PMID: 34033941 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial AMP-Activated Kinase α1 Phosphorylates eNOS on Thr495 and Decreases Endothelial NO Formation.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Sep 13;19(9):2753. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092753. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30217073 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic energy sensor AMPfret deciphers adenylate-dependent AMPK activation mechanism.Nat Commun. 2019 Mar 4;10(1):1038. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08938-z. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 30833561 Free PMC article.
-
A769662 Inhibits Insulin-Stimulated Akt Activation in Human Macrovascular Endothelial Cells Independent of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 5;19(12):3886. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123886. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30563079 Free PMC article.
-
AMPKα2 is a skeletal muscle stem cell intrinsic regulator of myonuclear accretion.iScience. 2023 Oct 26;26(12):108343. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108343. eCollection 2023 Dec 15. iScience. 2023. PMID: 38077152 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alessi DR, Sakamoto K, Bayascas JR. LKB1-dependent signaling pathways. Annu Rev Biochem 75: 137–163, 2006. - PubMed
-
- Barnes BR, Marklund S, Steiler TL, Walter M, Hjalm G, Amarger V, Mahlapuu M, Leng Y, Johansson C, Galuska D, Lindgren K, Abrink M, Stapleton D, Zierath JR, Andersson L. The 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase gamma3 isoform has a key role in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in glycolytic skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem 279: 38441–38447, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Calabrese MF, Rajamohan F, Harris MS, Caspers NL, Magyar R, Withka JM, Wang H, Borzilleri KA, Sahasrabudhe PV, Hoth LR, Geoghegan KF, Han S, Brown J, Subashi TA, Reyes AR, Frisbie RK, Ward J, Miller RA, Landro JA, Londregan AT, Carpino PA, Cabral S, Smith AC, Conn EL, Cameron KO, Qiu X, Kurumbail RG. Structural basis for AMPK activation: natural and synthetic ligands regulate kinase activity from opposite poles by different molecular mechanisms. Structure 22: 1161–1172, 2014. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

