Is Alzheimer's disease a Type 3 Diabetes? A critical appraisal
- PMID: 27567931
- PMCID: PMC5344773
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.08.018
Is Alzheimer's disease a Type 3 Diabetes? A critical appraisal
Abstract
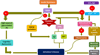
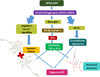
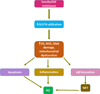
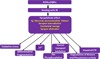
Recently researchers proposed the term 'Type-3-Diabetes' for Alzheimer's disease (ad) because of the shared molecular and cellular features among Type-1-Diabetes, Type-2-Diabetes and insulin resistance associated with memory deficits and cognitive decline in elderly individuals. Recent clinical and basic studies on patients with diabetes and AD revealed previously unreported cellular and pathological among diabetes, insulin resistance and AD. These studies are also strengthened by various basic biological studies that decipher the effects of insulin in the pathology of AD through cellular and molecular mechanisms. For instance, insulin is involved in the activation of glycogen synthase kinase 3β, which in turn causes phosphorylation of tau, which involved in the formation of neurofibrillary tangles. Interestingly, insulin also plays a crucial role in the formation amyloid plaques. In this review, we discussed significant shared mechanisms between AD and diabetes and we also provided therapeutic avenues for diabetes and AD. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled: Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Quality in Diabetes/Obesity and Critical Illness Spectrum of Diseases - edited by P. Hemachandra Reddy.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; BMI; GSK3β; MCI amyloid beta; Obesity; Tau; Type-3-Diabetes; diabetes.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

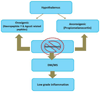
Similar articles
-
Diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer's disease: GSK-3β as a potential link.Behav Brain Res. 2018 Feb 26;339:57-65. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2017.11.015. Epub 2017 Nov 21. Behav Brain Res. 2018. PMID: 29158110 Review.
-
Insulin signaling: An opportunistic target to minify the risk of Alzheimer's disease.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2017 Sep;83:159-171. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2017.05.004. Epub 2017 May 30. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2017. PMID: 28624654 Review.
-
Neurons derived from sporadic Alzheimer's disease iPSCs reveal elevated TAU hyperphosphorylation, increased amyloid levels, and GSK3B activation.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2017 Dec 1;9(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s13195-017-0317-z. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 29191219 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting CCR3 to Reduce Amyloid-β Production, Tau Hyperphosphorylation, and Synaptic Loss in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Dec;54(10):7964-7978. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-0269-5. Epub 2016 Nov 23. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27878757
-
The participation of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 released by astrocytes in the pathology of Alzheimer's disease.Mol Brain. 2015 Dec 4;8(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s13041-015-0174-2. Mol Brain. 2015. PMID: 26637371 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Identification of repurposed drugs targeting significant long non-coding RNAs in the cross-talk between diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer's disease.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 31;12(1):18332. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-22822-9. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36316461 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Parkinson's Disease and Diabetes Mellitus: From Epidemiology, Pathophysiology and Prevention to Treatment.Aging Dis. 2022 Dec 1;13(6):1591-1605. doi: 10.14336/AD.2022.0325. eCollection 2022 Dec 1. Aging Dis. 2022. PMID: 36465171 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of Circadian Clocks Promotes Progression of Alzheimer's Disease in Diabetic Mice.Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Sep;58(9):4404-4412. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02425-7. Epub 2021 May 21. Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 34018152
-
Zonisamide Ameliorates Cognitive Impairment by Inhibiting ER Stress in a Mouse Model of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Front Aging Neurosci. 2020 Jul 9;12:192. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.00192. eCollection 2020. Front Aging Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32754028 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the common pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus via microarray data analysis.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Feb 27;15:1071391. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1071391. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36923118 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association Report. 2015.
-
- Pugazhenthi S, Qin L, Reddy PH. Common neurodegenerative pathways in obesity, diabetes, and Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.04.017. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kandimalla RJ, Prabhakar S, Binukumar BK, Wani WY, Gupta N, Sharma DR, Sunkaria A, Grover VK, Bhardwaj N, Jain K, Gill KD. Apo-Eepsilon4 allele in conjunction with Abeta42 and tau in CSF: biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2011;8:187–196. - PubMed
-
- Kandimalla RJ, Anand R, Veeramanikandan R, Wani WY, Prabhakar S, Grover VK, Bharadwaj N, Jain K, Gill KD. CSF ubiquitin as a specific biomarker in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2014;11:340–348. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

