The Polyadenosine RNA-binding Protein, Zinc Finger Cys3His Protein 14 (ZC3H14), Regulates the Pre-mRNA Processing of a Key ATP Synthase Subunit mRNA
- PMID: 27563065
- PMCID: PMC5077184
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.754069
The Polyadenosine RNA-binding Protein, Zinc Finger Cys3His Protein 14 (ZC3H14), Regulates the Pre-mRNA Processing of a Key ATP Synthase Subunit mRNA
Abstract
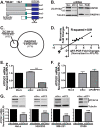
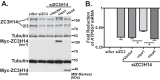
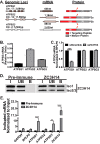
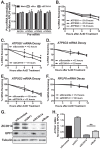
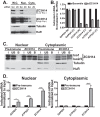
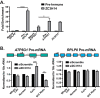
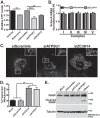
Polyadenosine RNA-binding proteins (Pabs) regulate multiple steps in gene expression. This protein family includes the well studied Pabs, PABPN1 and PABPC1, as well as the newly characterized Pab, zinc finger CCCH-type containing protein 14 (ZC3H14). Mutations in ZC3H14 are linked to a form of intellectual disability. To probe the function of ZC3H14, we performed a transcriptome-wide analysis of cells depleted of either ZC3H14 or the control Pab, PABPN1. Depletion of PABPN1 affected ∼17% of expressed transcripts, whereas ZC3H14 affected only ∼1% of expressed transcripts. To assess the function of ZC3H14 in modulating target mRNAs, we selected the gene encoding the ATP synthase F0 subunit C (ATP5G1) transcript. Knockdown of ZC3H14 significantly reduced ATP5G1 steady-state mRNA levels. Consistent with results suggesting that ATP5G1 turnover increases upon depletion of ZC3H14, double knockdown of ZC3H14 and the nonsense-mediated decay factor, UPF1, rescues ATP5G1 transcript levels. Furthermore, fractionation reveals an increase in the amount of ATP5G1 pre-mRNA that reaches the cytoplasm when ZC3H14 is depleted and that ZC3H14 binds to ATP5G1 pre-mRNA in the nucleus. These data support a role for ZC3H14 in ensuring proper nuclear processing and retention of ATP5G1 pre-mRNA. Consistent with the observation that ATP5G1 is a rate-limiting component for ATP synthase activity, knockdown of ZC3H14 decreases cellular ATP levels and causes mitochondrial fragmentation. These data suggest that ZC3H14 modulates pre-mRNA processing of select mRNA transcripts and plays a critical role in regulating cellular energy levels, observations that have broad implications for proper neuronal function.
Keywords: ATP synthase; MSUT2; Nab2; RNA; RNA processing; RNA splicing; RNA-binding protein; ZC3H14; post-transcriptional regulation.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The polyadenosine RNA-binding protein ZC3H14 interacts with the THO complex and coordinately regulates the processing of neuronal transcripts.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jul 27;46(13):6561-6575. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky446. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29912477 Free PMC article.
-
Splice variants of the human ZC3H14 gene generate multiple isoforms of a zinc finger polyadenosine RNA binding protein.Gene. 2009 Jun 15;439(1-2):71-8. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2009.02.022. Epub 2009 Mar 18. Gene. 2009. PMID: 19303045 Free PMC article.
-
New kid on the ID block: neural functions of the Nab2/ZC3H14 class of Cys₃His tandem zinc-finger polyadenosine RNA binding proteins.RNA Biol. 2012 May;9(5):555-62. doi: 10.4161/rna.20187. Epub 2012 May 1. RNA Biol. 2012. PMID: 22614829 Free PMC article.
-
The long and the short of it: the role of the zinc finger polyadenosine RNA binding protein, Nab2, in control of poly(A) tail length.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jun;1819(6):546-54. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.03.006. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22484098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Poly(A) RNA-binding proteins and polyadenosine RNA: new members and novel functions.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2014 Sep-Oct;5(5):601-22. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1233. Epub 2014 Apr 30. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2014. PMID: 24789627 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The polyadenosine RNA-binding protein ZC3H14 interacts with the THO complex and coordinately regulates the processing of neuronal transcripts.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jul 27;46(13):6561-6575. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky446. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29912477 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA-binding protein, ZC3H14, is required for proper poly(A) tail length control, expression of synaptic proteins, and brain function in mice.Hum Mol Genet. 2017 Oct 1;26(19):3663-3681. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx248. Hum Mol Genet. 2017. PMID: 28666327 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative proteomics reveals the dynamic proteome landscape of zebrafish embryos during the maternal-to-zygotic transition.iScience. 2024 May 8;27(6):109944. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109944. eCollection 2024 Jun 21. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38784018 Free PMC article.
-
Post-transcriptional regulation of Pabpn1 by the RNA binding protein HuR.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Sep 6;46(15):7643-7661. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky535. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29939290 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of inflammatory responses by dynamic subcellular localization of RNA-binding protein Arid5a.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Feb 6;115(6):E1214-E1220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1719921115. Epub 2018 Jan 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29358370 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Phillips T. (2008) Regulation of transcription and gene expression in eukaryotes. Nat. Education 1, 199
-
- Moore M. J. (2005) From birth to death: the complex lives of eukaryotic mRNAs. Science 309, 1514–1518 - PubMed
-
- Fasken M. B., and Corbett A. H. (2005) Process or perish: quality control in mRNA biogenesis. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 12, 482–488 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

