Transcription Regulation of the Human Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase (hTERT) Gene
- PMID: 27548225
- PMCID: PMC4999838
- DOI: 10.3390/genes7080050
Transcription Regulation of the Human Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase (hTERT) Gene
Abstract
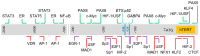
Embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells have the ability to maintain their telomere length via expression of an enzymatic complex called telomerase. Similarly, more than 85%-90% of cancer cells are found to upregulate the expression of telomerase, conferring them with the potential to proliferate indefinitely. Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase (TERT), the catalytic subunit of telomerase holoenzyme, is the rate-limiting factor in reconstituting telomerase activity in vivo. To date, the expression and function of the human Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase (hTERT) gene are known to be regulated at various molecular levels (including genetic, mRNA, protein and subcellular localization) by a number of diverse factors. Among these means of regulation, transcription modulation is the most important, as evident in its tight regulation in cancer cell survival as well as pluripotent stem cell maintenance and differentiation. Here, we discuss how hTERT gene transcription is regulated, mainly focusing on the contribution of trans-acting factors such as transcription factors and epigenetic modifiers, as well as genetic alterations in hTERT proximal promoter.
Keywords: mutation; promoter; telomerase; telomere; transcription regulation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Human telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter regulation in normal and malignant human ovarian epithelial cells.Cancer Res. 2001 Jul 15;61(14):5529-36. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11454703
-
Human telomerase reverse transcriptase regulates MMP expression independently of telomerase activity via NF-κB-dependent transcription.FASEB J. 2013 Nov;27(11):4375-83. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-230904. Epub 2013 Jul 24. FASEB J. 2013. PMID: 23884427
-
Opposing regulatory roles of E2F in human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) gene expression in human tumor and normal somatic cells.FASEB J. 2002 Dec;16(14):1943-5. doi: 10.1096/fj.02-0311fje. Epub 2002 Oct 4. FASEB J. 2002. PMID: 12368233
-
Human Specific Regulation of the Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase Gene.Genes (Basel). 2016 Jun 28;7(7):30. doi: 10.3390/genes7070030. Genes (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27367732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional regulation of the telomerase hTERT gene as a target for cellular and viral oncogenic mechanisms.Carcinogenesis. 2003 Jul;24(7):1167-76. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgg085. Epub 2003 May 22. Carcinogenesis. 2003. PMID: 12807729 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging mechanisms of telomerase reactivation in cancer.Trends Cancer. 2022 Aug;8(8):632-641. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2022.03.005. Epub 2022 May 12. Trends Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35568649 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complex context relationships between DNA methylation and accessibility, histone marks, and hTERT gene expression in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells: perspectives for all-trans retinoic acid in cancer therapy.Mol Oncol. 2020 Jun;14(6):1310-1326. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12681. Epub 2020 Apr 22. Mol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32239597 Free PMC article.
-
Fyn-mediated phosphorylation of Menin disrupts telomere maintenance in stem cells.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 19:2023.10.04.560876. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.04.560876. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 37873235 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Telomere associated gene expression as well as TERT protein level and telomerase activity are altered in the ovarian follicles of aged mice.Sci Rep. 2021 Jul 30;11(1):15569. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-95239-5. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34330985 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Telomere Homeostasis during Epstein-Barr virus Infection and Immortalization.Viruses. 2017 Aug 9;9(8):217. doi: 10.3390/v9080217. Viruses. 2017. PMID: 28792435 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

