Hypoxia enhances the malignant nature of bladder cancer cells and concomitantly antagonizes protein O-glycosylation extension
- PMID: 27542232
- PMCID: PMC5325352
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.11257
Hypoxia enhances the malignant nature of bladder cancer cells and concomitantly antagonizes protein O-glycosylation extension
Abstract
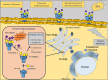
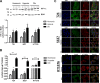
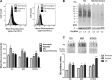
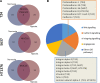
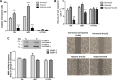
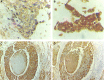
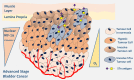
Invasive bladder tumours express the cell-surface Sialyl-Tn (STn) antigen, which stems from a premature stop in protein O-glycosylation. The STn antigen favours invasion, immune escape, and possibly chemotherapy resistance, making it attractive for target therapeutics. However, the events leading to such deregulation in protein glycosylation are mostly unknown. Since hypoxia is a salient feature of advanced stage tumours, we searched into how it influences bladder cancer cells glycophenotype, with emphasis on STn expression. Therefore, three bladder cancer cell lines with distinct genetic and molecular backgrounds (T24, 5637 and HT1376) were submitted to hypoxia. To disclose HIF-1α-mediated events, experiments were also conducted in the presence of Deferoxamine Mesilate (Dfx), an inhibitor of HIF-1α proteasomal degradation. In both conditions all cell lines overexpressed HIF-1α and its transcriptionally-regulated protein CA-IX. This was accompanied by increased lactate biosynthesis, denoting a shift toward anaerobic metabolism. Concomitantly, T24 and 5637 cells acquired a more motile phenotype, consistent with their more mesenchymal characteristics. Moreover, hypoxia promoted STn antigen overexpression in all cell lines and enhanced the migration and invasion of those presenting more mesenchymal characteristics, in an HIF-1α-dependent manner. These effects were reversed by reoxygenation, demonstrating that oxygen affects O-glycan extension. Glycoproteomics studies highlighted that STn was mainly present in integrins and cadherins, suggesting a possible role for this glycan in adhesion, cell motility and invasion. The association between HIF-1α and STn overexpressions and tumour invasion was further confirmed in bladder cancer patient samples. In conclusion, STn overexpression may, in part, result from a HIF-1α mediated cell-survival strategy to adapt to the hypoxic challenge, favouring cell invasion. In addition, targeting STn-expressing glycoproteins may offer potential to treat tumour hypoxic niches harbouring more malignant cells.
Keywords: bladder cancer; glycosylation; hypoxia; invasion; sialyl-Tn.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeted O-glycoproteomics explored increased sialylation and identified MUC16 as a poor prognosis biomarker in advanced-stage bladder tumours.Mol Oncol. 2017 Aug;11(8):895-912. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12035. Epub 2017 Mar 2. Mol Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28156048 Free PMC article.
-
Carbonic anhydrase IX is a marker of hypoxia and correlates with higher Gleason scores and ISUP grading in prostate cancer.Diagn Pathol. 2016 May 25;11(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s13000-016-0495-1. Diagn Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27225200 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia regulates the expression and localization of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein α by hypoxia inducible factor-1α in bladder transitional carcinoma cells.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Aug;12(2):2121-7. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3563. Epub 2015 Mar 27. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 25824695
-
Is the hypoxia-inducible factor pathway important in gastric cancer?Eur J Cancer. 2005 Dec;41(18):2792-805. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2005.09.008. Epub 2005 Nov 14. Eur J Cancer. 2005. PMID: 16290133 Review.
-
Role of glycosylation in hypoxia-driven cell migration and invasion.Cell Adh Migr. 2019 Dec;13(1):13-22. doi: 10.1080/19336918.2018.1491234. Epub 2018 Aug 19. Cell Adh Migr. 2019. PMID: 30015560 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bladder cancer cell lines adapt their aggressiveness profile to oxygen tension.Oncol Lett. 2022 May 20;24(1):220. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13341. eCollection 2022 Jul. Oncol Lett. 2022. PMID: 35720486 Free PMC article.
-
A Golgi-associated redox switch regulates catalytic activation and cooperative functioning of ST6Gal-I with B4GalT-I.Redox Biol. 2019 Jun;24:101182. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101182. Epub 2019 Apr 4. Redox Biol. 2019. PMID: 30959459 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review on the Implications of O-linked Glycan Branching and Truncating Enzymes on Cancer Progression and Metastasis.Cells. 2020 Feb 14;9(2):446. doi: 10.3390/cells9020446. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32075174 Free PMC article.
-
A Robust Hypoxia Risk Score Predicts the Clinical Outcomes and Tumor Microenvironment Immune Characters in Bladder Cancer.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 13;12:725223. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.725223. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34484235 Free PMC article.
-
Glycoproteogenomics: Setting the Course for Next-generation Cancer Neoantigen Discovery for Cancer Vaccines.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2021 Feb;19(1):25-43. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2021.03.005. Epub 2021 Jun 9. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2021. PMID: 34118464 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:E359–386. - PubMed
-
- Stenzl A, Cowan NC, De Santis M, Kuczyk MA, Merseburger AS, Ribal MJ, Sherif A, Witjes JA, European Association of U Treatment of muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer: update of the EAU guidelines. Eur Urol. 2011;59:1009–1018. - PubMed
-
- Wilson WR, Hay MP. Targeting hypoxia in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11:393–410. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

