Cellular distribution of the fragile X mental retardation protein in the mouse brain
- PMID: 27539535
- PMCID: PMC5558202
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.24100
Cellular distribution of the fragile X mental retardation protein in the mouse brain
Abstract
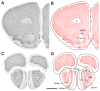
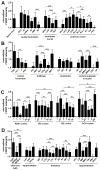
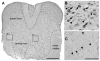
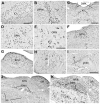
The fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP) plays an important role in normal brain development. Absence of FMRP results in abnormal neuronal morphologies in a selected manner throughout the brain, leading to intellectual deficits and sensory dysfunction in the fragile X syndrome (FXS). Despite FMRP importance for proper brain function, its overall expression pattern in the mammalian brain at the resolution of individual neuronal cell groups is not known. In this study we used FMR1 knockout and isogenic wildtype mice to systematically map the distribution of FMRP expression in the entire mouse brain. Using immunocytochemistry and cellular quantification analyses, we identified a large number of prominent cell groups expressing high levels of FMRP at the subcortical levels, in particular sensory and motor neurons in the brainstem and thalamus. In contrast, many cell groups in the midbrain and hypothalamus exhibit low FMRP levels. More important, we describe differential patterns of FMRP distribution in both cortical and subcortical brain regions. Almost all major brain areas contain high and low levels of FMRP cell groups adjacent to each other or between layers of the same cortical areas. These differential patterns indicate that FMRP expression appears to be specific to individual neuronal cell groups instead of being associated with all neurons in distinct brain regions, as previously considered. Taken together, these findings support the notion of FMRP differential neuronal regulation and strongly implicate the contribution of fundamental sensory and motor processing at subcortical levels to FXS pathology. J. Comp. Neurol. 525:818-849, 2017. © 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Keywords: RRID:AB_10805421; RRID:AB_1157880; RRID:AB_476743; cortical laminar heterogeneity; fragile X syndrome; sensory information processing; subcortical sensory systems; whole brain analyses.
© 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no identified conflict of interest.
Figures

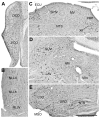
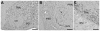
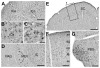
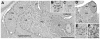
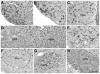
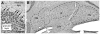

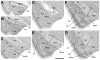
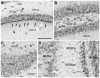
Similar articles
-
Deletion of Fmr1 in parvalbumin-expressing neurons results in dysregulated translation and selective behavioral deficits associated with fragile X syndrome.Mol Autism. 2022 Jun 29;13(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s13229-022-00509-2. Mol Autism. 2022. PMID: 35768828 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic mapping of fragile X granules in the mouse brain reveals a potential role for presynaptic FMRP in sensorimotor functions.J Comp Neurol. 2012 Nov 1;520(16):3687-706. doi: 10.1002/cne.23123. J Comp Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22522693 Free PMC article.
-
The role of reduced expression of fragile X mental retardation protein in neurons and increased expression in astrocytes in idiopathic and syndromic autism (duplications 15q11.2-q13).Autism Res. 2018 Oct;11(10):1316-1331. doi: 10.1002/aur.2003. Epub 2018 Aug 14. Autism Res. 2018. PMID: 30107092
-
The molecular biology of FMRP: new insights into fragile X syndrome.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2021 Apr;22(4):209-222. doi: 10.1038/s41583-021-00432-0. Epub 2021 Feb 19. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33608673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BDNF in fragile X syndrome.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Jan;76 Pt C:729-36. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.05.018. Epub 2013 May 29. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 23727436 Review.
Cited by
-
Region-Related Differences in Short-Term Synaptic Plasticity and Synaptotagmin-7 in the Male and Female Hippocampus of a Rat Model of Fragile X Syndrome.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 26;25(13):6975. doi: 10.3390/ijms25136975. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000085 Free PMC article.
-
Neural Correlates of Auditory Hypersensitivity in Fragile X Syndrome.Front Psychiatry. 2021 Oct 7;12:720752. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.720752. eCollection 2021. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34690832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamics of the fragile X mental retardation protein correlates with cellular and synaptic properties in primary auditory neurons following afferent deprivation.J Comp Neurol. 2021 Feb;529(3):481-500. doi: 10.1002/cne.24959. Epub 2020 Jun 27. J Comp Neurol. 2021. PMID: 32449186 Free PMC article.
-
Axonal localization of the fragile X family of RNA binding proteins is conserved across mammals.J Comp Neurol. 2020 Feb 15;528(3):502-519. doi: 10.1002/cne.24772. Epub 2019 Oct 10. J Comp Neurol. 2020. PMID: 31502255 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of Fmr1 from Forebrain Excitatory Neurons Triggers Abnormal Cellular, EEG, and Behavioral Phenotypes in the Auditory Cortex of a Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome.Cereb Cortex. 2020 Mar 14;30(3):969-988. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhz141. Cereb Cortex. 2020. PMID: 31364704 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abitbol M, Menini C, Delezoide AL, Rhyner T, Vekemans M, Mallet J. Nucleus basalis magnocellularis and hippocampus are the major sites of FMR-1 expression in the human fetal brain. Nat Genet. 1993;4:147–53. - PubMed
-
- Bakker CE, Verheij C, Willemsen R, Vanderhelm R, Oerlemans F, Vermey M, Bygrave A, Hoogeveen AT, Oostra BA, Reyniers E, DeBoulle K, Dhooge R, Cras P, Van Velzen N, Nagels G, Martin JJ, Dedeyn PP, Darby JK, Willems PJ. Fmr1 knockout mice: a model to study fragile X mental retardation. The Dutch-Belgian Fragile X Consortium. Cell. 1994;78:23–33. - PubMed
-
- Bakker CE, de Diego Otero Y, Bontekoe C, Raghoe P, Luteijn T, Hoogeveen AT, Oostra BA, Willemsen R. Immunocytochemical and biochemical characterization of FMRP, FXR1P, and FXR2P in the mouse. Exp Cell Res. 2000;258:162–70. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

