Effects of Long-Term Environmental Enrichment on Anxiety, Memory, Hippocampal Plasticity and Overall Brain Gene Expression in C57BL6 Mice
- PMID: 27536216
- PMCID: PMC4971077
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2016.00062
Effects of Long-Term Environmental Enrichment on Anxiety, Memory, Hippocampal Plasticity and Overall Brain Gene Expression in C57BL6 Mice
Abstract
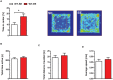
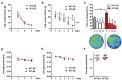
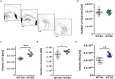
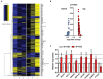
There is ample evidence that physical activity exerts positive effects on a variety of brain functions by facilitating neuroprotective processes and influencing neuroplasticity. Accordingly, numerous studies have shown that continuous exercise can successfully diminish or prevent the pathology of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease in transgenic mouse models. However, the long-term effect of physical activity on brain health of aging wild-type (WT) mice has not yet been studied in detail. Here, we show that prolonged physical and cognitive stimulation, mediated by an enriched environment (EE) paradigm for a duration of 11 months, leads to reduced anxiety and improved spatial reference memory in C57BL6 WT mice. While the number of CA1 pyramidal neurons remained unchanged between standard housed (SH) and EE mice, the number of dentate gyrus (DG) neurons, as well as the CA1 and DG volume were significantly increased in EE mice. A whole-brain deep sequencing transcriptome analysis, carried out to better understand the molecular mechanisms underlying the observed effects, revealed an up-regulation of a variety of genes upon EE, mainly associated with synaptic plasticity and transcription regulation. The present findings corroborate the impact of continuous physical activity as a potential prospective route in the prevention of age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative disorders.
Keywords: Morris water maze; deep sequencing; dentate gyrus; enriched environment; hippocampal plasticity; neurogenesis; physical activity; stereology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Lifelong environmental enrichment in the absence of exercise protects the brain from age-related cognitive decline.Neuropharmacology. 2019 Feb;145(Pt A):59-74. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.03.042. Epub 2018 Apr 7. Neuropharmacology. 2019. PMID: 29630903
-
Short-term exposure to enriched environment rescues chronic stress-induced impaired hippocampal synaptic plasticity, anxiety, and memory deficits.J Neurosci Res. 2017 Aug;95(8):1602-1610. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23992. Epub 2016 Nov 16. J Neurosci Res. 2017. PMID: 27862185
-
CAPS2 deficiency affects environmental enrichment-induced adult neurogenesis and differentiation/survival of newborn neurons in the hippocampal dentate gyrus.Neurosci Lett. 2017 Nov 20;661:121-125. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2017.09.047. Epub 2017 Sep 27. Neurosci Lett. 2017. PMID: 28963059
-
Environmental enrichment and brain repair: harnessing the therapeutic effects of cognitive stimulation and physical activity to enhance experience-dependent plasticity.Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2014 Feb;40(1):13-25. doi: 10.1111/nan.12102. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 24354721 Review.
-
Environmental enrichment effects on synaptic and cellular physiology of hippocampal neurons.Neuropharmacology. 2019 Feb;145(Pt A):3-12. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.04.007. Epub 2018 Apr 7. Neuropharmacology. 2019. PMID: 29634984 Review.
Cited by
-
Multisensory Stimulation Improves Cognition and Behavior in Adult Male Rats Born to LT4-treated Thyroidectomized Dams.Endocrinology. 2022 Sep 1;163(9):bqac105. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqac105. Endocrinology. 2022. PMID: 35914267 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental enrichment improves hippocampus-dependent spatial learning in female C57BL/6 mice in novel IntelliCage sweet reward-based behavioral tests.Front Behav Neurosci. 2023 Sep 18;17:1256744. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2023.1256744. eCollection 2023. Front Behav Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37791111 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-Sequencing Reveals Unique Transcriptional Signatures of Running and Running-Independent Environmental Enrichment in the Adult Mouse Dentate Gyrus.Front Mol Neurosci. 2018 Apr 13;11:126. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00126. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29706867 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a Fully Implantable Stimulator for Deep Brain Stimulation in Mice.Front Neurosci. 2020 Jul 21;14:726. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00726. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32792895 Free PMC article.
-
Short-term environmental enrichment, and not physical exercise, alleviate cognitive decline and anxiety from middle age onwards without affecting hippocampal gene expression.Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2019 Oct;19(5):1143-1169. doi: 10.3758/s13415-019-00743-x. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31463713
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

