Ca2+ signals, cell membrane disintegration, and activation of TMEM16F during necroptosis
- PMID: 27535660
- PMCID: PMC11107605
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-016-2338-3
Ca2+ signals, cell membrane disintegration, and activation of TMEM16F during necroptosis
Abstract
Activated receptor-interacting protein kinase 3 (RIPK3) and mixed lineage kinase domain like (MLKL) are essential components of the necroptotic pathway. Phosphorylated MLKL (pMLKL) is thought to induce membrane leakage, leading to cell swelling and disintegration of the cell membrane. However, the molecular identity of the necroptotic membrane pore remains unclear, and the role of pMLKL for membrane permeabilization is currently disputed. We observed earlier that the phospholipid scramblase and ion channel TMEM16F/anoctamin 6 cause large membrane currents, cell swelling, and cell death when activated by a strong increase in intracellular Ca2+. We, therefore, asked whether TMEM16F is also central to necroptotic cell death and other cellular events during necroptosis. Necroptosis was induced by TNFα, smac mimetic, and Z-VAD (TSZ) in NIH3T3 fibroblasts and the four additional cell lines HT29, 16HBE, H441, and L929. Time-dependent changes in intracellular Ca2+, cell morphology, and membrane currents were recorded. TSZ induced a small and only transient oscillatory rise in intracellular Ca2+, which was paralleled by the activation of outwardly rectifying Cl- currents, which were typical for TMEM16F/ANO6. Ca2+ oscillations were due to Ca2+ release from endoplasmic reticulum, and were independent of extracellular Ca2+. The initial TSZ-induced cell swelling was followed by cell shrinkage. Using typical channel blockers and siRNA-knockdown, the Cl- currents were shown to be due to the activation of ANO6. However, the knockdown of ANO6 or inhibitors of ANO6 did not inhibit necroptotic cell death. The present data demonstrate the activation of ANO6 during necroptosis, which, however, is not essential for cell death.
Keywords: Anoctamin 6; Apoptosis; Cell death; Chloride channel; Necroptosis; TMEM16F.
Figures
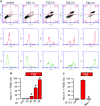
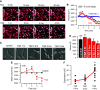
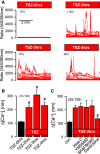
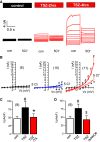
Similar articles
-
CFTR supports cell death through ROS-dependent activation of TMEM16F (anoctamin 6).Pflugers Arch. 2018 Feb;470(2):305-314. doi: 10.1007/s00424-017-2065-0. Epub 2017 Sep 5. Pflugers Arch. 2018. PMID: 28875346
-
Regulation of TMEM16A/ANO1 and TMEM16F/ANO6 ion currents and phospholipid scrambling by Ca2+ and plasma membrane lipid.J Physiol. 2018 Jan 15;596(2):217-229. doi: 10.1113/JP275175. Epub 2017 Dec 18. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29134661 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium-activated and apoptotic phospholipid scrambling induced by Ano6 can occur independently of Ano6 ion currents.Cell Death Dis. 2013 Apr 25;4(4):e611. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.135. Cell Death Dis. 2013. PMID: 23618909 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular functions of anoctamin 6 (TMEM16F): a chloride channel, cation channel, or phospholipid scramblase?Pflugers Arch. 2014 Mar;466(3):407-14. doi: 10.1007/s00424-013-1305-1. Epub 2013 Jun 8. Pflugers Arch. 2014. PMID: 23748496 Review.
-
Ion channels in regulated cell death.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 Jun;73(11-12):2387-403. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2208-z. Epub 2016 Apr 18. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27091155 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Viral infiltration of pancreatic islets in patients with COVID-19.Nat Commun. 2021 Jun 10;12(1):3534. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23886-3. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34112801 Free PMC article.
-
CFTR supports cell death through ROS-dependent activation of TMEM16F (anoctamin 6).Pflugers Arch. 2018 Feb;470(2):305-314. doi: 10.1007/s00424-017-2065-0. Epub 2017 Sep 5. Pflugers Arch. 2018. PMID: 28875346
-
Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species and Lytic Programmed Cell Death in Acute Inflammation.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023 Oct;39(10-12):708-727. doi: 10.1089/ars.2022.0209. Epub 2023 Aug 31. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023. PMID: 37450339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flipping the dogma - phosphatidylserine in non-apoptotic cell death.Cell Commun Signal. 2019 Oct 29;17(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s12964-019-0437-0. Cell Commun Signal. 2019. PMID: 31665027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Lck inhibitor, AMG-47a, blocks necroptosis and implicates RIPK1 in signalling downstream of MLKL.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Apr 1;13(4):291. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04740-w. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35365636 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lang F, Hoffmann EK. Role of ion transport in control of apoptotic cell death. Compr Physiol. 2012;2:2037–2061. - PubMed
-
- Planells-Cases R, Lutter D, Guyader C, Gerhards NM, Ullrich F, Elger DA, Kucukosmanoglu A, Xu G, Voss FK, Reincke SM, Stauber T, Blomen VA, Vis DJ, Wessels LF, Brummelkamp TR, Borst P, Rottenberg S, Jentsch TJ. Subunit composition of VRAC channels determines substrate specificity and cellular resistance to Pt-based anti-cancer drugs. EMBO J. 2015;34:2993–3008. doi: 10.15252/embj.201592409. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

