The modulation of MiR-155 and MiR-23a manipulates Klebsiella pneumoniae Adhesion on Human pulmonary Epithelial cells via Integrin α5β1 Signaling
- PMID: 27534887
- PMCID: PMC4989230
- DOI: 10.1038/srep31918
The modulation of MiR-155 and MiR-23a manipulates Klebsiella pneumoniae Adhesion on Human pulmonary Epithelial cells via Integrin α5β1 Signaling
Abstract
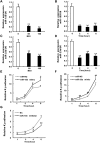
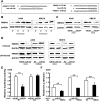
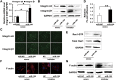
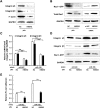
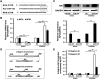
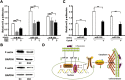
Micro-RNAs (miRNAs) critically regulate several host defense mechanisms, but their roles in the bacteria-epithelium interplay remain unclear. Our results displayed that the expression of miR-155 and miR-23a were down-regulated in K. pneumoniae-infected pulmonary epithelial cells. The elevated bacterial adhesion on A549 cells followed the enhancement of the cellular levels of these two miRNAs. Meanwhile, a mechanistic study demonstrated that miR-155 promoted integrin α5β1 function and resulted in the increased actin polymerization. Moreover, a non-histone nuclear protein, high mobility group nucleosomal-binding domain 2 (HMGN2) served as the potential target of miR-155 and miR-23a to regulate the integrin α5β1 expression and K. pneumoniae adhesion. Furthermore, the expression of a known integrin transcription suppressor-Nuclear Factor-I (NFI) was also repressed by miR-155, which paralleled with its chromatin location in the promoter regions of integrin α5 and β1. These results uncover novel links between miRNAs and integrin function to regulate bacterial adhesion, indicating a potential mechanism of host cell autonomous immune response to K. pneumoniae infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High mobility group nucleosomal binding 2 reduces integrin α5/β1-mediated adhesion of Klebsiella pneumoniae on human pulmonary epithelial cells via nuclear factor I.Microbiol Immunol. 2020 Dec;64(12):825-834. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12855. Epub 2020 Oct 29. Microbiol Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33034909
-
Knockdown of HMGN2 increases the internalization of Klebsiella pneumoniae by respiratory epithelial cells through the regulation of α5β1 integrin expression.Int J Mol Med. 2016 Sep;38(3):737-46. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2690. Epub 2016 Jul 25. Int J Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27460641 Free PMC article.
-
ADAM15 suppresses cell motility by driving integrin alpha5beta1 cell surface expression via Erk inactivation.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008;40(10):2164-73. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2008.02.021. Epub 2008 Feb 26. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18387333
-
Positive expression of E-cadherin suppresses cell adhesion to fibronectin via reduction of alpha5beta1 integrin in human breast carcinoma cells.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2006 Dec;132(12):795-803. doi: 10.1007/s00432-006-0128-2. Epub 2006 Jul 5. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2006. PMID: 16821070
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
Cited by
-
The current landscape of microRNAs (miRNAs) in bacterial pneumonia: opportunities and challenges.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022 Aug 19;27(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s11658-022-00368-y. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022. PMID: 35986232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Roles of Integrin α5β1 in Human Cancer.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Dec 31;13:13329-13344. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S273803. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 33408483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The regulatory effect of acetylation of HMGN2 and H3K27 on pyocyanin-induced autophagy in macrophages by affecting Ulk1 transcription.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Aug;25(15):7524-7537. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16788. Epub 2021 Jul 18. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34278675 Free PMC article.
-
Role of MicroRNA in the Lung's Innate Immune Response.J Innate Immun. 2017;9(3):243-249. doi: 10.1159/000452669. Epub 2016 Dec 3. J Innate Immun. 2017. PMID: 27915347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-155 regulates casein kinase 1 gamma 2: a potential pathogenetic role in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Blood Cancer J. 2017 Sep 8;7(9):e606. doi: 10.1038/bcj.2017.80. Blood Cancer J. 2017. PMID: 28885613 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

