Novel biomarkers of resistance of pancreatic cancer cells to oncolytic vesicular stomatitis virus
- PMID: 27533247
- PMCID: PMC5308675
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.11202
Novel biomarkers of resistance of pancreatic cancer cells to oncolytic vesicular stomatitis virus
Abstract
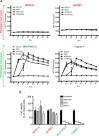
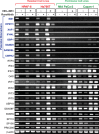
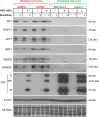
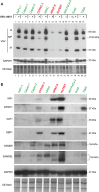
Vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) based recombinant viruses (such as VSV-ΔM51) are effective oncolytic viruses (OVs) against a majority of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cell lines. However, some PDAC cell lines are highly resistant to VSV-ΔM51. We recently showed that treatment of VSV-resistant PDAC cells with ruxolitinib (JAK1/2 inhibitor) or TPCA-1 (IKK-β inhibitor) breaks their resistance to VSV-ΔM51. Here we compared the global effect of ruxolitinib or TPCA-1 treatment on cellular gene expression in PDAC cell lines highly resistant to VSV-ΔM51. Our study identified a distinct subset of 22 interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs) downregulated by both ruxolitinib and TPCA-1. Further RNA and protein analyses demonstrated that 4 of these genes (MX1, EPSTI1, XAF1, and GBP1) are constitutively co-expressed in VSV-resistant, but not in VSV-permissive PDACs, thus serving as potential biomarkers to predict OV therapy success. Moreover, shRNA-mediated knockdown of one of such ISG, MX1, showed a positive effect on VSV-ΔM51 replication in resistant PDAC cells, suggesting that at least some of the identified ISGs contribute to resistance of PDACs to VSV-ΔM51. As certain oncogene and tumor suppressor gene variants are often associated with increased tropism of OVs to cancer cells, we also analyzed genomic DNA in a set of PDAC cell lines for frequently occurring cancer associated mutations. While no clear correlation was found between such mutations and resistance of PDACs to VSV-ΔM51, the analysis generated valuable genotypic data for future studies.
Keywords: biomarker of resistance; interferon-stimulated gene; oncolytic virus; pancreatic cancer; vesicular stomatitis virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Breaking resistance of pancreatic cancer cells to an attenuated vesicular stomatitis virus through a novel activity of IKK inhibitor TPCA-1.Virology. 2015 Nov;485:340-54. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2015.08.003. Epub 2015 Aug 29. Virology. 2015. PMID: 26331681 Free PMC article.
-
Intertumoral heterogeneity impacts oncolytic vesicular stomatitis virus efficacy in mouse pancreatic cancer cells.J Virol. 2023 Sep 28;97(9):e0100523. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01005-23. Epub 2023 Sep 6. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 37671865 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells by vesicular stomatitis virus.Virology. 2015 Jan 1;474:163-73. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2014.10.026. Epub 2014 Nov 19. Virology. 2015. PMID: 25463614 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding the Spectrum of Pancreatic Cancers Responsive to Vesicular Stomatitis Virus-Based Oncolytic Virotherapy: Challenges and Solutions.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 9;13(5):1171. doi: 10.3390/cancers13051171. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33803211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vesicular stomatitis virus as a flexible platform for oncolytic virotherapy against cancer.J Gen Virol. 2012 Dec;93(Pt 12):2529-2545. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.046672-0. Epub 2012 Oct 10. J Gen Virol. 2012. PMID: 23052398 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting IκappaB kinases for cancer therapy.Semin Cancer Biol. 2019 Jun;56:12-24. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2018.02.007. Epub 2018 Feb 24. Semin Cancer Biol. 2019. PMID: 29486318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combining Oncolytic Viruses and Small Molecule Therapeutics: Mutual Benefits.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jul 6;13(14):3386. doi: 10.3390/cancers13143386. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34298601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overexpression of Smac by an Armed Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Overcomes Tumor Resistance.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2019 Jun 4;14:188-195. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2019.05.006. eCollection 2019 Sep 27. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2019. PMID: 31312717 Free PMC article.
-
Epsti1 Regulates the Inflammatory Stage of Early Muscle Regeneration through STAT1-VCP Interaction.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Jun 24;20(9):3530-3543. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.94675. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38993551 Free PMC article.
-
Prospective insight into the role of benzyl propylene glycoside as a modulator of the cGAS-STING signaling pathway in the management of nonalcoholic fatty pancreas animal model.Biol Res. 2023 Mar 13;56(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s40659-023-00423-8. Biol Res. 2023. PMID: 36915161 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Donina S, Strele I, Proboka G, Auzins J, Alberts P, Jonsson B, Venskus D, Muceniece A. Adapted ECHO-7 virus Rigvir immunotherapy (oncolytic virotherapy) prolongs survival in melanoma patients after surgical excision of the tumour in a retrospective study. Melanoma Res. 2015;25:421–426. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang SX. Turning killer into cure - the story of oncolytic herpes simplex viruses. Discovery Med. 2015;20:303–309. - PubMed
-
- Garber K. China approves world's first oncolytic virus therapy for cancer treatment. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98:298–300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

