MiR-148a Functions as a Tumor Suppressor by Targeting CCK-BR via Inactivating STAT3 and Akt in Human Gastric Cancer
- PMID: 27518872
- PMCID: PMC4982598
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158961
MiR-148a Functions as a Tumor Suppressor by Targeting CCK-BR via Inactivating STAT3 and Akt in Human Gastric Cancer
Abstract
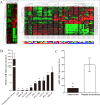
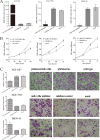
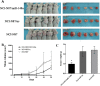
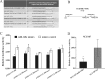
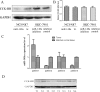
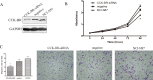
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have been widely accepted as a class of gene expression regulators which post-translationally regulate protein expression. These small noncoding RNAs have been proved closely involved in the modulation of various pathobiological processes in cancer. In this research, we demonstrated that miR-148a expression was significantly down-regulated in gastric cancer tissues in comparison with the matched normal mucosal tissues, and its expression was statistically associated with lymph node metastasis. Ectopic expression of miR-148a inhibited tumor cell proliferation and migration in vitro, and inhibited tumor formation in vivo. Subsequently, we identified cholecystokinin B receptor (CCK-BR) as a direct target of miR-148a using western blot and luciferase activity assay. More importantly, siRNA-induced knockdown of CCK-BR elicited similar anti-oncogenic effects (decreased proliferation and migration) as those induced by enforced miR-148a expression. We also found that miR-148a-mediated anti-cancer effects are dependent on the inhibition of STAT3 and Akt activation, which subsequently regulates the pathways involved in cell proliferation and migration. Taken together, our results suggest that miR-148a serves as a tumor suppressor in human gastric carcinogenesis by targeting CCK-BR via inactivating STAT3 and Akt.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-148a suppresses tumor cell invasion and metastasis by downregulating ROCK1 in gastric cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2011 Dec 15;17(24):7574-83. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1714. Epub 2011 Oct 12. Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21994419
-
miR-215 promotes malignant progression of gastric cancer by targeting RUNX1.Oncotarget. 2016 Jan 26;7(4):4817-28. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6736. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26716895 Free PMC article.
-
Role of miR-647 in human gastric cancer suppression.Oncol Rep. 2017 Mar;37(3):1401-1411. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.5383. Epub 2017 Jan 17. Oncol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28098914 Free PMC article.
-
The role of miR-148a in gastric cancer.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2014 Sep;140(9):1451-6. doi: 10.1007/s00432-014-1649-8. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24659367 Review.
-
The emerging role of miR-506 in cancer.Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 20;7(38):62778-62788. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11294. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27542202 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-148a inhibits cell proliferation and cell cycle progression in lung adenocarcinoma via directly targeting transcription factor E2F3.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Dec;16(6):5400-5409. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6845. Epub 2018 Oct 11. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 30546419 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA-148a serves as a prognostic factor and suppresses migration and invasion through Wnt1 in non-small cell lung cancer.PLoS One. 2017 Feb 15;12(2):e0171751. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171751. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28199399 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-148a Acts as a Tumor Suppressor in Osteosarcoma via Targeting Rho-Associated Coiled-Coil Kinase.Oncol Res. 2017 Sep 21;25(8):1231-1243. doi: 10.3727/096504017X14850134190255. Epub 2017 Jan 23. Oncol Res. 2017. PMID: 28117029 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of signal transducer and activator of transcription factor 3 in tumor angiogenesis.Oncotarget. 2017 Aug 4;8(40):69139-69161. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19932. eCollection 2017 Sep 15. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28978186 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MEG3: an Oncogenic Long Non-coding RNA in Different Cancers.Pathol Oncol Res. 2019 Jul;25(3):859-874. doi: 10.1007/s12253-019-00614-3. Epub 2019 Feb 21. Pathol Oncol Res. 2019. PMID: 30793226 Review.
References
-
- Borkowski R, Du L, Zhao Z, McMillan E, Kosti A, Yang CR, et al. Genetic mutation of p53 and suppression of the miR-17 approximately 92 cluster are synthetic lethal in non-small cell lung cancer due to upregulation of vitamin D Signaling. Cancer research. 2015;75(4):666–75. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-1329 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

