The role of integrins in TGFβ activation in the tumour stroma
- PMID: 27515461
- PMCID: PMC5010607
- DOI: 10.1007/s00441-016-2474-y
The role of integrins in TGFβ activation in the tumour stroma
Abstract
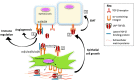
TGFβ1 is the most pleiotropic of all known cytokines and thus, to avoid uncontrolled TGFβ-activated processes, its activity is tightly regulated. Studies in fibrosis have led to the discovery that αv integrins are the major regulators of the local activation of latent TGFβ in our tissues. Since all cells can express one or more types of αv integrins, this raises the possibility that, in the complex milieu of a developing cancer, multiple cell types including both cancer cells and stromal cells activate TGFβ. In normal tissues, TGFβ1 is a tumour suppressor through its ability to suppress epithelial cell division, whereas in cancer, in which tumour cells develop genetic escape mechanisms to become resistant to TGFβ growth suppression, TGFβ signalling creates a tumour-permissive environment by activating fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transition, by promoting angiogenesis, by suppressing immune cell populations and by promoting the secretion of both matrix proteins and proteases. In addition, TGFβ drives epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) increasing the potential for metastasis. Since αv integrins activate TGFβ, they almost certainly drive TGFβ-dependent cancer progression. In this review, we discuss the data that are helping to develop this hypothesis and describe the evidence that αv integrins regulate the TGFβ promotion of cancer. Graphical Abstract Mechanisms of integrin-mediated transforming growth factor beta (TGFβ) activation and its effect on stromal processes. 1 Matrix-bound latent LAP-TGFβ1 binds αv integrins expressed by epithelial cells or fibroblasts (LAP latency-associated peptide). TGFβ1 becomes exposed. 2 Active TGFβ1 binds the TGFβ receptor in an autocrine or paracrine fashion. 3 TGFβ1 signalling increases integrin expression, LAP-TGFβ1 secretion and trans-differentiation of fibroblasts into contractile cells that secrete collagens and collagen cross-linking proteins. By contracting the matrix, latent TGFβ1 is stretched making the activation of latent TGFβ1 easier and creating a continuous cycle of TGFβ1 signalling. TGFβ1 promotes cancer progression by promoting angiogenesis, immune suppression and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT).
Keywords: Integrin; TGFβ; Tumour microenvironment; Tumour stroma; αvβ1, αvβ3, αvβ5, αvβ6, αvβ8.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Integrin-Mediated TGFβ Activation Modulates the Tumour Microenvironment.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Aug 21;11(9):1221. doi: 10.3390/cancers11091221. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31438626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
E-Cadherin and EpCAM expression by NSCLC tumour cells associate with normal fibroblast activation through a pathway initiated by integrin αvβ6 and maintained through TGFβ signalling.Oncogene. 2015 Feb 5;34(6):704-16. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.600. Epub 2014 Feb 3. Oncogene. 2015. PMID: 24488011
-
Integrin alpha8beta1 mediates adhesion to LAP-TGFbeta1.J Cell Sci. 2002 Dec 1;115(Pt 23):4641-8. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00145. J Cell Sci. 2002. PMID: 12415008
-
Expression and action of transforming growth factor beta (TGFbeta1, TGFbeta2, TGFbeta3) in normal bovine ovarian surface epithelium and implications for human ovarian cancer.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2001 Sep;182(2):145-55. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(01)00584-6. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2001. PMID: 11514049
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in fibrosis and repair. Transforming growth factor-β activation by epithelial cells and fibroblasts.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015 Mar;12 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S21-3. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201406-245MG. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015. PMID: 25830829 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrin Regulation of CAF Differentiation and Function.Cancers (Basel). 2019 May 24;11(5):715. doi: 10.3390/cancers11050715. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31137641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive analysis of integrin αvβ3/α6β1 in prognosis and immune escape of prostate cancer.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Oct 19;15(20):11369-11388. doi: 10.18632/aging.205131. Epub 2023 Oct 19. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 37862114 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond adhesion: emerging roles for integrins in control of the tumor microenvironment.F1000Res. 2017 Aug 31;6:1612. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.11877.1. eCollection 2017. F1000Res. 2017. PMID: 29026524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechano-therapeutics: Targeting Mechanical Signaling in Fibrosis and Tumor Stroma.Pharmacol Ther. 2020 Aug;212:107575. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107575. Epub 2020 May 11. Pharmacol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32437826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Collateral Damage Intended-Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts and Vasculature Are Potential Targets in Cancer Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Nov 7;18(11):2355. doi: 10.3390/ijms18112355. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29112161 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahmed N, Pansino F, Clyde R, Murthi P, Quinn MA, Rice GE, Agrez MV, Mok S, Baker MS. Overexpression of alpha(v)beta6 integrin in serous epithelial ovarian cancer regulates extracellular matrix degradation via the plasminogen activation cascade. Carcinogenesis. 2002;23:237–244. doi: 10.1093/carcin/23.2.237. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Allen MD, Thomas GJ, Clark S, Dawoud MM, Vallath S, Payne SJ, Gomm JJ, Dreger SA, Dickinson S, Edwards DR, Pennington CJ, Sestak I, Cuzick J, Marshall JF, Hart IR, Jones JL. Altered microenvironment promotes progression of preinvasive breast cancer: myoepithelial expression of alphavbeta6 integrin in DCIS identifies high-risk patients and predicts recurrence. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20:344–357. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-1504. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arnold TD, Ferrero GM, Qiu H, Phan IT, Akhurst RJ, Huang EJ, Reichardt LF. Defective retinal vascular endothelial cell development as a consequence of impaired integrin alphaVbeta8-mediated activation of transforming growth factor-beta. J Neurosci. 2012;32:1197–1206. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5648-11.2012. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

