Interleukin-1β effect on the endogenous ADP-ribosylation and phosphorylation of eukaryotic elongation factor 2
- PMID: 27510652
- PMCID: PMC5101336
- DOI: 10.1007/s10616-016-9990-1
Interleukin-1β effect on the endogenous ADP-ribosylation and phosphorylation of eukaryotic elongation factor 2
Abstract
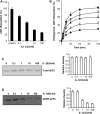
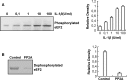
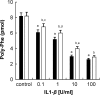
Eukaryotic elongation factor 2 (eEF2) plays an important role in eukaryotic polypeptide chain elongation. Adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-ribosylation is a post-translational modification reaction that catalyzes the transfer of ADP-ribose group to eEF2 and this causes the inhibition of protein synthesis. Indeed, in the absence of diptheria toxin, endogenous ADP-ribosylation can occur. eEF2 is phosphorylated by eEF2 kinase which prevents binding to ribosomes thus inhibiting its activity. Increase in endogenous ADP-ribosylation level approximately 70-75 % was observed in IL-1β treated HUVECs. Moreover, a 70 % rise of phosphorylation of eEF2 was measured. Alteration of endogenous ADP-ribosylation of eEF2 activity was related with cellular mono-ADP-ribosyltransferases (ADPrT). Increment of endogenous ADP-ribosylation on eEF2 did not seem to occur as a direct effect of IL-1β; it arises from the activation of ADPrT. This 2.5 fold increase was abolished by ADPrT inhibitors. Due to these post-translational modifications, global protein synthesis is inhibited. After dephosphorylation of phospho-eEF2, around 20 % increase in protein synthesis was observed. In conclusion, systemic IL-1β has an important role in the regulation of global protein synthesis.
Keywords: Diphtheria toxin; Endogenous ADP-ribosylation; Eukaryotic elongation factor 2; Interleukin-1β; Phosphorylation; Protein synthesis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of oxidative stress on in vivo ADP-ribosylation of eukaryotic elongation factor 2.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005 Jan;37(1):91-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2004.05.016. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15381153
-
Endogenous ADP-ribosylation for eukaryotic elongation factor 2: evidence of two different sites and reactions.Cell Biochem Funct. 2006 Jul-Aug;24(4):369-80. doi: 10.1002/cbf.1265. Cell Biochem Funct. 2006. PMID: 16142694
-
The role of the diphthamide-containing loop within eukaryotic elongation factor 2 in ADP-ribosylation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A.Biochem J. 2008 Jul 1;413(1):163-74. doi: 10.1042/BJ20071083. Biochem J. 2008. PMID: 18373493
-
A role of intracellular mono-ADP-ribosylation in cancer biology.FEBS J. 2013 Aug;280(15):3551-62. doi: 10.1111/febs.12290. Epub 2013 May 10. FEBS J. 2013. PMID: 23590234 Review.
-
Eukaryotic elongation factor-2 (eEF2): its regulation and peptide chain elongation.Cell Biochem Funct. 2011 Apr;29(3):227-34. doi: 10.1002/cbf.1740. Epub 2011 Mar 10. Cell Biochem Funct. 2011. PMID: 21394738 Review.
References
-
- Argüelles S, Camandola S, Hutchison ER, Cutler RG, Ayala A, Mattson MP. Molecular control of the amount, subcellular location, and activity state of translation elongation factor 2 in neurons experiencing stress. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013;61:61–71. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.03.016. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Argüelles S, Camandola S, Cutler RG, Ayala A, Mattson MP. Elongation factor 2 diphthamide is critical for translation of two IRES-dependent protein targets, XIAP and FGF2, under oxidative stress conditions. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014;67:131–138. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.10.015. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

