Dual Therapeutic Action of a Neutralizing Anti-FGF2 Aptamer in Bone Disease and Bone Cancer Pain
- PMID: 27506449
- PMCID: PMC5154475
- DOI: 10.1038/mt.2016.158
Dual Therapeutic Action of a Neutralizing Anti-FGF2 Aptamer in Bone Disease and Bone Cancer Pain
Abstract
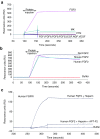
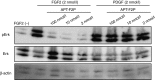
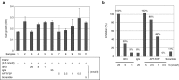
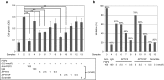
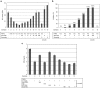
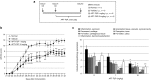
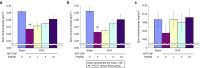
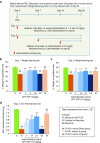
Fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) plays a crucial role in bone remodeling and disease progression. However, the potential of FGF2 antagonists for treatment of patients with bone diseases has not yet been explored. Therefore, we generated a novel RNA aptamer, APT-F2, specific for human FGF2 and characterized its properties in vitro and in vivo. APT-F2 blocked binding of FGF2 to each of its four cellular receptors, inhibited FGF2-induced downstream signaling and cells proliferation, and restored osteoblast differentiation blocked by FGF2. APT-F2P, a PEGylated form of APT-F2, effectively blocked the bone disruption in mouse and rat models of arthritis and osteoporosis. Treatment with APT-F2P also exerted a strong analgesic effect, equivalent to morphine, in a mouse model of bone cancer pain. These findings demonstrated dual therapeutic action of APT-F2P in bone diseases and pain, providing a promising approach to the treatment of bone diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The FGF2 aptamer inhibits the growth of FGF2-FGFR pathway driven lung cancer cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Sep 10;503(3):1330-1334. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.07.044. Epub 2018 Jul 11. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 30005872
-
FGF2 Stimulates COUP-TFII Expression via the MEK1/2 Pathway to Inhibit Osteoblast Differentiation in C3H10T1/2 Cells.PLoS One. 2016 Jul 12;11(7):e0159234. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159234. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27404388 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast growth factor 2-induced cytoplasmic asparaginyl-tRNA synthetase promotes survival of osteoblasts by regulating anti-apoptotic PI3K/Akt signaling.Bone. 2009 Nov;45(5):994-1003. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2009.07.018. Epub 2009 Jul 23. Bone. 2009. PMID: 19631775
-
Multiple Therapeutic Applications of RBM-007, an Anti-FGF2 Aptamer.Cells. 2021 Jun 28;10(7):1617. doi: 10.3390/cells10071617. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34203430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-FGF2 approaches as a strategy to compensate resistance to anti-VEGF therapy: long-pentraxin 3 as a novel antiangiogenic FGF2-antagonist.Eur Cytokine Netw. 2009 Dec;20(4):225-34. doi: 10.1684/ecn.2009.0175. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2009. PMID: 20167562 Review.
Cited by
-
Safety and tolerability of intravitreal umedaptanib pegol (anti-FGF2) for neovascular age-related macular degeneration (nAMD): a phase 1, open-label study.Eye (Lond). 2024 Apr;38(6):1149-1154. doi: 10.1038/s41433-023-02849-6. Epub 2023 Dec 1. Eye (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38040965 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Neuropathogenicity of non-viable Borrelia burgdorferi ex vivo.Sci Rep. 2022 Jan 13;12(1):688. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-03837-0. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35027599 Free PMC article.
-
Specific inhibition of FGF5-induced cell proliferation by RNA aptamers.Sci Rep. 2021 Feb 3;11(1):2976. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-82350-w. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33536494 Free PMC article.
-
New developments in the biology of fibroblast growth factors.WIREs Mech Dis. 2022 Jul;14(4):e1549. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.1549. Epub 2022 Feb 9. WIREs Mech Dis. 2022. PMID: 35142107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in Research on the Role of FGF in the Formation and Treatment of Corneal Neovascularization.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Feb 25;11:111. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00111. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32158390 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Marie, PJ, Miraoui, H and Sévère, N (2012). FGF/FGFR signaling in bone formation: progress and perspectives. Growth Factors 30: 117–123. - PubMed
-
- Okada-Ban, M, Thiery, JP and Jouanneau, J (2000). Fibroblast growth factor-2. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 32: 263–267. - PubMed
-
- Bolander, ME (1992). Regulation of fracture repair by growth factors. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 200: 165–170. - PubMed
-
- Mignatti, P, Morimoto, T and Rifkin, DB (1992). Basic fibroblast growth factor, a protein devoid of secretory signal sequence, is released by cells via a pathway independent of the endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi complex. J Cell Physiol 151: 81–93. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

