Human Sirtuin 2 Localization, Transient Interactions, and Impact on the Proteome Point to Its Role in Intracellular Trafficking
- PMID: 27503897
- PMCID: PMC5054338
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M116.061333
Human Sirtuin 2 Localization, Transient Interactions, and Impact on the Proteome Point to Its Role in Intracellular Trafficking
Abstract
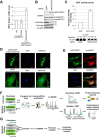
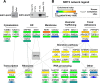
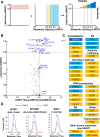
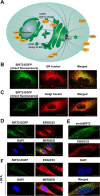
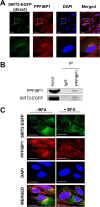
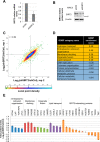
Human sirtuin 2 (SIRT2) is an NAD+-dependent deacetylase that primarily functions in the cytoplasm, where it can regulate α-tubulin acetylation levels. SIRT2 is linked to cancer progression, neurodegeneration, and infection with bacteria or viruses. However, the current knowledge about its interactions and the means through which it exerts its functions has remained limited. Here, we aimed to gain a better understanding of its cellular functions by characterizing SIRT2 subcellular localization, the identity and relative stability of its protein interactions, and its impact on the proteome of primary human fibroblasts. To assess the relative stability of SIRT2 interactions, we used immunoaffinity purification in conjunction with both label-free and metabolic labeling quantitative mass spectrometry. In addition to the expected associations with cytoskeleton proteins, including its known substrate TUBA1A, our results reveal that SIRT2 specifically interacts with proteins functioning in membrane trafficking, secretory processes, and transcriptional regulation. By quantifying their relative stability, we found most interactions to be transient, indicating a dynamic SIRT2 environment. We discover that SIRT2 localizes to the ER-Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC), and that this recruitment requires an intact ER-Golgi trafficking pathway. Further expanding these findings, we used microscopy and interaction assays to establish the interaction and coregulation of SIRT2 with liprin-β1 scaffolding protein (PPFiBP1), a protein with roles in focal adhesions disassembly. As SIRT2 functions may be accomplished via interactions, enzymatic activity, and transcriptional regulation, we next assessed the impact of SIRT2 levels on the cellular proteome. SIRT2 knockdown led to changes in the levels of proteins functioning in membrane trafficking, including some of its interaction partners. Altogether, our study expands the knowledge of SIRT2 cytoplasmic functions to define a previously unrecognized involvement in intracellular trafficking pathways, which may contribute to its roles in cellular homeostasis and human diseases.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SIRT2 deacetylates GRASP55 to facilitate post-mitotic Golgi assembly.J Cell Sci. 2019 Nov 1;132(21):jcs232389. doi: 10.1242/jcs.232389. J Cell Sci. 2019. PMID: 31604796 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation Of Microtubule Acetylation By The Interplay Of TPPP/p25, SIRT2 And New Anticancer Agents With Anti-SIRT2 Potency.Sci Rep. 2017 Dec 6;7(1):17070. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17381-3. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29213065 Free PMC article.
-
Active nuclear import of the deacetylase Sirtuin-2 is controlled by its C-terminus and importins.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 10;10(1):2034. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58397-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32042025 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Roles of SIRT2 in Regulating Physiological and Pathological Signal Transduction.Genet Res (Camb). 2022 Aug 29;2022:9282484. doi: 10.1155/2022/9282484. eCollection 2022. Genet Res (Camb). 2022. PMID: 36101744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SIRT2: Controversy and multiple roles in disease and physiology.Ageing Res Rev. 2019 Nov;55:100961. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2019.100961. Epub 2019 Sep 7. Ageing Res Rev. 2019. PMID: 31505260 Review.
Cited by
-
SIRT2 expression exhibits potential to serve as a biomarker for disease surveillance and prognosis in the management of cervical cancer patients.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Mar;99(11):e18668. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018668. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32176025 Free PMC article.
-
CoCl2 -triggered pseudohypoxic stress induces proteasomal degradation of SIRT4 via polyubiquitination of lysines K78 and K299.FEBS Open Bio. 2023 Dec;13(12):2187-2199. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13715. Epub 2023 Oct 12. FEBS Open Bio. 2023. PMID: 37803520 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Validation of a Novel Histone Acetylation-Related Gene Signature for Predicting the Prognosis of Ovarian Cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Feb 18;10:793425. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.793425. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35252174 Free PMC article.
-
RTN4B-mediated suppression of Sirtuin 2 activity ameliorates β-amyloid pathology and cognitive impairment in Alzheimer's disease mouse model.Aging Cell. 2020 Aug;19(8):e13194. doi: 10.1111/acel.13194. Epub 2020 Jul 23. Aging Cell. 2020. PMID: 32700357 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT2 deacetylates GRASP55 to facilitate post-mitotic Golgi assembly.J Cell Sci. 2019 Nov 1;132(21):jcs232389. doi: 10.1242/jcs.232389. J Cell Sci. 2019. PMID: 31604796 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Frye R. A. (2000) Phylogenetic classification of prokaryotic and eukaryotic Sir2-like proteins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 273, 793–798 - PubMed
-
- Liszt G., Ford E., Kurtev M., and Guarente L. (2005) Mouse Sir2 homolog SIRT6 is a nuclear ADP-ribosyltransferase. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 21313–21320 - PubMed
-
- Haigis M. C., Mostoslavsky R., Haigis K. M., Fahie K., Christodoulou D. C., Murphy A. J., Valenzuela D. M., Yancopoulos G. D., Karow M., Blander G., Wolberger C., Prolla T. A., Weindruch R., Alt F. W., and Guarente L. (2006) SIRT4 inhibits glutamate dehydrogenase and opposes the effects of calorie restriction in pancreatic beta cells. Cell 126, 941–954 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

