Genomic Alteration in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC) Cell Lines Inferred from Karyotyping, Molecular Cytogenetics, and Array Comparative Genomic Hybridization
- PMID: 27501229
- PMCID: PMC4976893
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160901
Genomic Alteration in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC) Cell Lines Inferred from Karyotyping, Molecular Cytogenetics, and Array Comparative Genomic Hybridization
Abstract
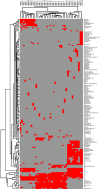
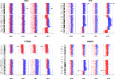
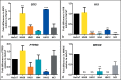
Genomic alteration in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) was studied in two cell line pairs (HN30-HN31 and HN4-HN12) using conventional C-banding, multiplex fluorescence in situ hybridization (M-FISH), and array comparative genomic hybridization (array CGH). HN30 and HN4 were derived from primary lesions in the pharynx and base of tongue, respectively, and HN31 and HN12 were derived from lymph-node metastatic lesions belonging to the same patients. Gain of chromosome 1, 7, and 11 were shared in almost all cell lines. Hierarchical clustering revealed that HN31 was closely related to HN4, which shared eight chromosome alteration cases. Large C-positive heterochromatins were found in the centromeric region of chromosome 9 in HN31 and HN4, which suggests complex structural amplification of the repetitive sequence. Array CGH revealed amplification of 7p22.3p11.2, 8q11.23q12.1, and 14q32.33 in all cell lines involved with tumorigenesis and inflammation genes. The amplification of 2p21 (SIX3), 11p15.5 (H19), and 11q21q22.3 (MAML2, PGR, TRPC6, and MMP family) regions, and deletion of 9p23 (PTPRD) and 16q23.1 (WWOX) regions were identified in HN31 and HN12. Interestingly, partial loss of PTPRD (9p23) and WWOX (16q23.1) genes was identified in HN31 and HN12, and the level of gene expression tended to be the down-regulation of PTPRD, with no detectable expression of the WWOX gene. This suggests that the scarcity of PTPRD and WWOX genes might have played an important role in progression of HNSCC, and could be considered as a target for cancer therapy or a biomarker in molecular pathology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
(Cyto)genomic and epigenetic characterization of BICR 10 cell line and three new established primary human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cultures.Genes Genomics. 2019 Oct;41(10):1207-1221. doi: 10.1007/s13258-019-00850-6. Epub 2019 Jul 18. Genes Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31321735
-
Molecular cytogenetic analysis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: By comparative genomic hybridization, spectral karyotyping, and expression array analysis.Head Neck. 2002 Sep;24(9):874-87. doi: 10.1002/hed.10122. Head Neck. 2002. PMID: 12211052
-
Molecular cytogenetic characterization of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and refinement of 3q amplification.Cancer Res. 2001 Jun 1;61(11):4506-13. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11389082
-
[Progresses on the methods of tumor chromosome aberration analysis].Yi Chuan. 2008 Dec;30(12):1529-35. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1005.2008.01529. Yi Chuan. 2008. PMID: 19073565 Review. Chinese.
-
Chromosomal imbalances in oral squamous cell carcinoma: examination of 31 cell lines and review of the literature.Oral Oncol. 2008 Apr;44(4):369-82. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2007.05.003. Epub 2007 Aug 2. Oral Oncol. 2008. PMID: 17681875 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of N-Terminal Tags on De Novo Vimentin Intermediate Filament Assembly.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 6;23(11):6349. doi: 10.3390/ijms23116349. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35683030 Free PMC article.
-
(Cyto)genomic and epigenetic characterization of BICR 10 cell line and three new established primary human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cultures.Genes Genomics. 2019 Oct;41(10):1207-1221. doi: 10.1007/s13258-019-00850-6. Epub 2019 Jul 18. Genes Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31321735
-
Senolytic-Mediated Elimination of Head and Neck Tumor Cells Induced Into Senescence by Cisplatin.Mol Pharmacol. 2022 Mar;101(3):168-180. doi: 10.1124/molpharm.121.000354. Epub 2021 Dec 14. Mol Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34907000 Free PMC article.
-
PTPRT and PTPRD Deleterious Mutations and Deletion Predict Bevacizumab Resistance in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Patients.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Sep 6;10(9):314. doi: 10.3390/cancers10090314. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30200630 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors suppress aggressiveness of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma via histone acetylation-independent blockade of the EGFR-Arf1 axis.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Feb 18;38(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1080-8. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30777099 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

