Amplification of TGFβ Induced ITGB6 Gene Transcription May Promote Pulmonary Fibrosis
- PMID: 27494713
- PMCID: PMC4975449
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158047
Amplification of TGFβ Induced ITGB6 Gene Transcription May Promote Pulmonary Fibrosis
Abstract
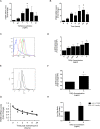
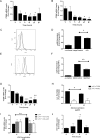
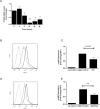
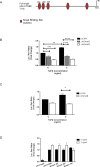
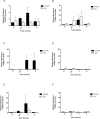
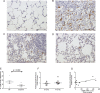
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a devastating, progressive disease with poor survival rates and limited treatment options. Upregulation of αvβ6 integrins within the alveolar epithelial cells is a characteristic feature of IPF and correlates with poor patient survival. The pro-fibrotic cytokine TGFβ1 can upregulate αvβ6 integrin expression but the molecular mechanisms driving this effect have not previously been elucidated. We confirm that stimulation with exogenous TGFβ1 increases expression of the integrin β6 subunit gene (ITGB6) and αvβ6 integrin cell surface expression in a time- and concentration-dependent manner. TGFβ1-induced ITGB6 expression occurs via transcriptional activation of the ITGB6 gene, but does not result from effects on ITGB6 mRNA stability. Basal expression of ITGB6 in, and αvβ6 integrins on, lung epithelial cells occurs via homeostatic αvβ6-mediated TGFβ1 activation in the absence of exogenous stimulation, and can be amplified by TGFβ1 activation. Fundamentally, we show for the first time that TGFβ1-induced ITGB6 expression occurs via canonical Smad signalling since dominant negative constructs directed against Smad3 and 4 inhibit ITGB6 transcriptional activity. Furthermore, disruption of a Smad binding site at -798 in the ITGB6 promoter abolishes TGFβ1-induced ITGB6 transcriptional activity. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation we demonstrate that TGFβ1 stimulation of lung epithelial cells results in direct binding of Smad3, and Smad4, to the ITGB6 gene promoter within this region. Finally, using an adenoviral TGFβ1 over-expression model of pulmonary fibrosis we demonstrate that Smad3 is crucial for TGFβ1-induced αvβ6 integrin expression within the alveolar epithelium in vivo. Together, these data confirm that a homeostatic, autocrine loop of αvβ6 integrin activated TGFβ1-induced ITGB6 gene expression regulates epithelial basal αvβ6 integrin expression, and demonstrates that this occurs via Smad-dependent transcriptional regulation at a single Smad binding site in the promoter of the β6 subunit gene. Active TGFβ1 amplifies this pathway both in vitro and in vivo, which may promote fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reduced Ets Domain-containing Protein Elk1 Promotes Pulmonary Fibrosis via Increased Integrin αvβ6 Expression.J Biol Chem. 2016 Apr 29;291(18):9540-53. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.692368. Epub 2016 Feb 9. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26861876 Free PMC article.
-
Influenza promotes collagen deposition via αvβ6 integrin-mediated transforming growth factor β activation.J Biol Chem. 2014 Dec 19;289(51):35246-63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.582262. Epub 2014 Oct 22. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25339175 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin αvβ6 contributes to the development of intestinal fibrosis via the FAK/AKT signaling pathway.Exp Cell Res. 2022 Feb 15;411(2):113003. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.113003. Epub 2021 Dec 31. Exp Cell Res. 2022. PMID: 34979108
-
Exploring the role of ITGB6: fibrosis, cancer, and other diseases.Apoptosis. 2024 Jun;29(5-6):570-585. doi: 10.1007/s10495-023-01921-6. Epub 2023 Dec 21. Apoptosis. 2024. PMID: 38127283 Review.
-
The ITGB6 gene: its role in experimental and clinical biology.Gene. 2020 Dec;763S:100023. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.100023. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Gene. 2020. PMID: 34493369 Review.
Cited by
-
Hox5 genes direct elastin network formation during alveologenesis by regulating myofibroblast adhesion.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Nov 6;115(45):E10605-E10614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1807067115. Epub 2018 Oct 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30348760 Free PMC article.
-
Lysyl oxidase like 2 is increased in asthma and contributes to asthmatic airway remodelling.Eur Respir J. 2022 Jul 7;60(1):2004361. doi: 10.1183/13993003.04361-2020. Print 2022 Jul. Eur Respir J. 2022. PMID: 34996828 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of β-catenin signaling attenuates arteriovenous fistula thickening in mice by suppressing myofibroblasts.Mol Med. 2022 Jan 21;28(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s10020-022-00436-1. Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35062862 Free PMC article.
-
Demystifying pulmonary fibrosis.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020 Sep 1;319(3):L554-L559. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00365.2020. Epub 2020 Aug 5. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32755321 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
miR-542-5p Attenuates Fibroblast Activation by Targeting Integrin α6 in Silica-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 22;19(12):3717. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123717. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30467286 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- G0901226/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G1100564/1/NC3RS_/National Centre for the Replacement, Refinement and Reduction of Animals in Research/United Kingdom
- NC/K500501/1/NC3RS_/National Centre for the Replacement, Refinement and Reduction of Animals in Research/United Kingdom
- MRF_MRF-091-0004-RG-TATLE/MRF/MRF/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

