The development of peptide ligands that target helix 69 rRNA of bacterial ribosomes
- PMID: 27492196
- PMCID: PMC4992606
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmc.2016.07.050
The development of peptide ligands that target helix 69 rRNA of bacterial ribosomes
Abstract
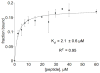
Antibiotic resistance prevents successful treatment of common bacterial infections, making it clear that new target locations and drugs are required to resolve this ongoing challenge. The bacterial ribosome is a common target for antibacterials due to its essential contribution to cell viability. The focus of this work is a region of the ribosome called helix 69 (H69), which was recently identified as a secondary target site for aminoglycoside antibiotics. H69 has key roles in essential ribosomal processes such as subunit association, ribosome recycling, and tRNA selection. Conserved across phylogeny, bacterial H69 also contains two pseudouridines and one 3-methylpseudouridine. Phage display revealed a heptameric peptide sequence that targeted H69. Using solid-phase synthesis, peptide variants with higher affinity and improved selectivity to modified H69 were generated. Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry was used to determine relative apparent dissociation constants of the RNA-peptide complexes.
Keywords: Helix 69; Ligand binding; Peptide; Pseudouridine; Ribosomal RNA.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Chemical probing for examining the structure of modified RNAs and ligand binding to RNA.Methods. 2019 Mar 1;156:110-120. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2018.10.015. Epub 2018 Nov 2. Methods. 2019. PMID: 30391513
-
Selection of heptapeptides that bind helix 69 of bacterial 23S ribosomal RNA.Bioorg Med Chem. 2013 Mar 1;21(5):1240-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2012.12.048. Epub 2013 Jan 10. Bioorg Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23375098 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosomal intersubunit bridge B2a is involved in factor-dependent translation initiation and translational processivity.J Mol Biol. 2009 Jan 16;385(2):405-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.10.065. Epub 2008 Nov 5. J Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19007789
-
Pseudouridines and pseudouridine synthases of the ribosome.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2001;66:147-59. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2001.66.147. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2001. PMID: 12762017 Review.
-
The 30S ribosomal P site: a function of 16S rRNA.FEBS Lett. 2005 Feb 7;579(4):855-8. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2004.11.026. FEBS Lett. 2005. PMID: 15680962 Review.
Cited by
-
Peptides Targeting RNA m6 A Methylations Influence the Viability of Cancer Cells.ChemMedChem. 2023 Feb 14;18(4):e202200549. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202200549. Epub 2023 Jan 23. ChemMedChem. 2023. PMID: 36567478 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Florey HW. Acta Med Scand. 1947;128:495–504.
-
- Hermann T. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2005;15:355–366. - PubMed
-
- Carter AP, Clemons WM, Brodersen DE, Morgan-Warren RJ, Wimberly BT, Ramakrishnan V. Nature. 2000;407:340–348. - PubMed
- Ban N, Nissen P, Hansen J, Moore PB, Steitz TA. Science. 2000;289:905–920. - PubMed
- Davidovich C, Bashan A, Yonath A. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:20665–20670. - PMC - PubMed
- Yusupov MM, Yusupova GZ, Baucom A, Lieberman K, Earnest TN, Cate JH, Noller HF. Science. 2001;292:883–896. - PubMed
-
- Bowen WS, Van Dyke N, Murgola EJ, Lodmell JS, Hill WE. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:2934–2943. - PubMed
- Rodriguez-Fonseca C, Phan H, Long KS, Porse BT, Kirillov SV, Amils R, Garrett RA. RNA. 2000;6:744–754. - PMC - PubMed
- Bulkley D, Johnson F, Steitz TA. J Mol Biol. 2012;416:571–578. - PMC - PubMed
- Wimberly BT, Brodersen DE, Clemons WM, Jr, Morgan-Warren RJ, Carter AP, Vonrhein C, Hartsch T, Ramakrishnan V. Nature. 2000;407:327–339. - PubMed
- Brodersen DE, Clemens WM, Jr, Carter AP, Morgan-Warren RJ, Wimberly BT, Ramakrishnan V. Cell. 2000;103:1143–1154. - PubMed
- Borovinskaya MA, Shoji S, Holton JM, Fredrick K, Cate JH. ACS Chem Biol. 2007;2:545–552. - PMC - PubMed
- Alacaraz LA, del Alamo M, Barrera FN, Mateu MG, Neira JL. Biophys J. 2007;93:1264–1276. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

