SNVSniffer: an integrated caller for germline and somatic single-nucleotide and indel mutations
- PMID: 27489955
- PMCID: PMC4977481
- DOI: 10.1186/s12918-016-0300-5
SNVSniffer: an integrated caller for germline and somatic single-nucleotide and indel mutations
Abstract
Background: Various approaches to calling single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) or insertion-or-deletion (indel) mutations have been developed based on next-generation sequencing (NGS). However, most of them are dedicated to a particular type of mutation, e.g. germline SNVs in normal cells, somatic SNVs in cancer/tumor cells, or indels only. In the literature, efficient and integrated callers for both germline and somatic SNVs/indels have not yet been extensively investigated.
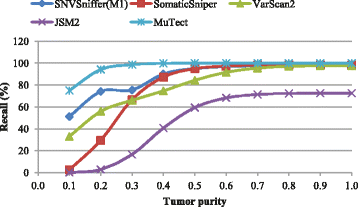
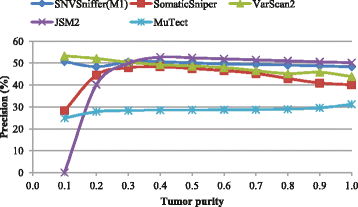
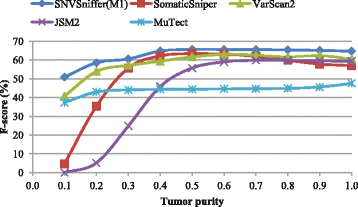
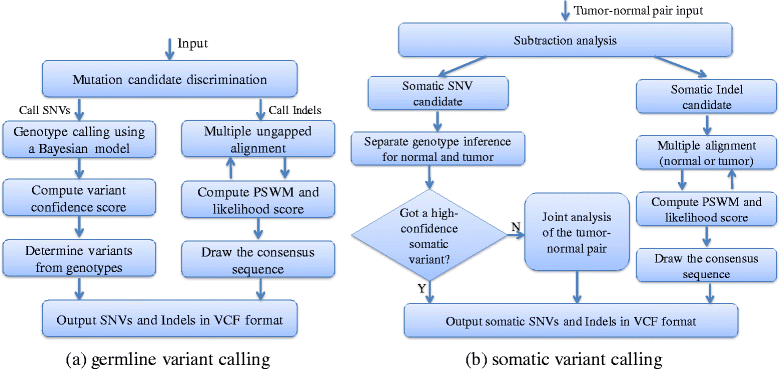
Results: We present SNVSniffer, an efficient and integrated caller identifying both germline and somatic SNVs/indels from NGS data. In this algorithm, we propose the use of Bayesian probabilistic models to identify SNVs and investigate a multiple ungapped alignment approach to call indels. For germline variant calling, we model allele counts per site to follow a multinomial conditional distribution. For somatic variant calling, we rely on paired tumor-normal pairs from identical individuals and introduce a hybrid subtraction and joint sample analysis approach by modeling tumor-normal allele counts per site to follow a joint multinomial conditional distribution. A comprehensive performance evaluation has been conducted using a diversity of variant calling benchmarks. For germline variant calling, SNVSniffer demonstrates highly competitive accuracy with superior speed in comparison with the state-of-the-art FaSD, GATK and SAMtools. For somatic variant calling, our algorithm achieves comparable or even better accuracy, at fast speed, than the leading VarScan2, SomaticSniper, JointSNVMix2 and MuTect.
Conclusions: SNVSniffers demonstrates the feasibility to develop integrated solutions to fast and efficient identification of germline and somatic variants. Nonetheless, accurate discovery of genetic variations is critical yet challenging, and still requires substantially more research efforts being devoted. SNVSniffer and synthetic samples are publicly available at http://snvsniffer.sourceforge.net .
Keywords: Bayesian model; Indel calling; SNP calling; Somatic SNV calling.
Figures
Similar articles
-
INDELseek: detection of complex insertions and deletions from next-generation sequencing data.BMC Genomics. 2017 Jan 5;18(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3449-9. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28056804 Free PMC article.
-
Benchmarking variant callers in next-generation and third-generation sequencing analysis.Brief Bioinform. 2021 May 20;22(3):bbaa148. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbaa148. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 32698196
-
A method to reduce ancestry related germline false positives in tumor only somatic variant calling.BMC Med Genomics. 2017 Oct 19;10(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s12920-017-0296-8. BMC Med Genomics. 2017. PMID: 29052513 Free PMC article.
-
A review of somatic single nucleotide variant calling algorithms for next-generation sequencing data.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2018 Feb 6;16:15-24. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2018.01.003. eCollection 2018. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2018. PMID: 29552334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Best practices for variant calling in clinical sequencing.Genome Med. 2020 Oct 26;12(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s13073-020-00791-w. Genome Med. 2020. PMID: 33106175 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Calling Variants in the Clinic: Informed Variant Calling Decisions Based on Biological, Clinical, and Laboratory Variables.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019 Apr 8;17:561-569. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2019.04.002. eCollection 2019. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019. PMID: 31049166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Validation of genetic variants from NGS data using deep convolutional neural networks.BMC Bioinformatics. 2023 Apr 20;24(1):158. doi: 10.1186/s12859-023-05255-7. BMC Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 37081386 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive benchmarking of SNV callers for highly admixed tumor data.PLoS One. 2017 Oct 11;12(10):e0186175. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186175. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29020110 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Outline of Whole Exome Sequencing Data Analysis Tools Available in Clinical Oncology.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Nov 4;11(11):1725. doi: 10.3390/cancers11111725. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31690036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic diversity affects the accuracy of bacterial single-nucleotide polymorphism-calling pipelines.Gigascience. 2020 Feb 1;9(2):giaa007. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giaa007. Gigascience. 2020. PMID: 32025702 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous