Serine/Arginine-Rich Splicing Factor 3 and Heterogeneous Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein A1 Regulate Alternative RNA Splicing and Gene Expression of Human Papillomavirus 18 through Two Functionally Distinguishable cis Elements
- PMID: 27489271
- PMCID: PMC5044842
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00965-16
Serine/Arginine-Rich Splicing Factor 3 and Heterogeneous Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein A1 Regulate Alternative RNA Splicing and Gene Expression of Human Papillomavirus 18 through Two Functionally Distinguishable cis Elements
Abstract
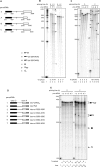
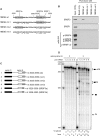
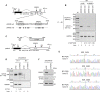
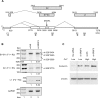
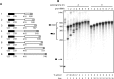
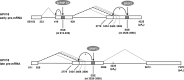
Human papillomavirus 18 (HPV18) is the second most common oncogenic HPV type associated with cervical, anogenital, and oropharyngeal cancers. Like other oncogenic HPVs, HPV18 encodes two major (one early and one late) polycistronic pre-mRNAs that are regulated by alternative RNA splicing to produce a repertoire of viral transcripts for the expression of individual viral genes. However, RNA cis-regulatory elements and trans-acting factors contributing to HPV18 alternative RNA splicing remain unknown. In this study, an exonic splicing enhancer (ESE) in the nucleotide (nt) 3520 to 3550 region in the HPV18 genome was identified and characterized for promotion of HPV18 929^3434 splicing and E1^E4 production through interaction with SRSF3, a host oncogenic splicing factor differentially expressed in epithelial cells and keratinocytes. Introduction of point mutations in the SRSF3-binding site or knockdown of SRSF3 expression in cells reduces 929^3434 splicing and E1^E4 production but activates other, minor 929^3465 and 929^3506 splicing. Knockdown of SRSF3 expression also enhances the expression of E2 and L1 mRNAs. An exonic splicing silencer (ESS) in the HPV18 nt 612 to 639 region was identified as being inhibitory to the 233^416 splicing of HPV18 E6E7 pre-mRNAs via binding to hnRNP A1, a well-characterized, abundantly and ubiquitously expressed RNA-binding protein. Introduction of point mutations into the hnRNP A1-binding site or knockdown of hnRNP A1 expression promoted 233^416 splicing and reduced E6 expression. These data provide the first evidence that the alternative RNA splicing of HPV18 pre-mRNAs is subject to regulation by viral RNA cis elements and host trans-acting splicing factors.
Importance: Expression of HPV18 genes is regulated by alternative RNA splicing of viral polycistronic pre-mRNAs to produce a repertoire of viral early and late transcripts. RNA cis elements and trans-acting factors contributing to HPV18 alternative RNA splicing have been discovered in this study for the first time. The identified ESS at the E7 open reading frame (ORF) prevents HPV18 233^416 splicing in the E6 ORF through interaction with a host splicing factor, hnRNP A1, and regulates E6 and E7 expression of the early E6E7 polycistronic pre-mRNA. The identified ESE at the E1^E4 ORF promotes HPV18 929^3434 splicing of both viral early and late pre-mRNAs and E1^E4 production through interaction with SRSF3. This study provides important observations on how alternative RNA splicing of HPV18 pre-mRNAs is subject to regulation by viral RNA cis elements and host splicing factors and offers potential therapeutic targets to overcome HPV-related cancer.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Heterogeneous Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein A1 (hnRNP A1) and hnRNP A2 Inhibit Splicing to Human Papillomavirus 16 Splice Site SA409 through a UAG-Containing Sequence in the E7 Coding Region.J Virol. 2020 Sep 29;94(20):e01509-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01509-20. Print 2020 Sep 29. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32759322 Free PMC article.
-
Human Papillomavirus 16 Oncoprotein Expression Is Controlled by the Cellular Splicing Factor SRSF2 (SC35).J Virol. 2015 May;89(10):5276-87. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03434-14. Epub 2015 Feb 25. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25717103 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of an hnRNP A1-dependent splicing silencer in the human papillomavirus type 16 L1 coding region that prevents premature expression of the late L1 gene.J Virol. 2004 Oct;78(20):10888-905. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.20.10888-10905.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15452209 Free PMC article.
-
Role of viral splicing elements and cellular RNA binding proteins in regulation of HIV-1 alternative RNA splicing.Curr HIV Res. 2006 Jan;4(1):43-55. doi: 10.2174/157016206775197655. Curr HIV Res. 2006. PMID: 16454710 Review.
-
Control of human papillomavirus gene expression by alternative splicing.Virus Res. 2017 Mar 2;231:83-95. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.11.016. Epub 2016 Nov 17. Virus Res. 2017. PMID: 27867028 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Poison Exon Splicing Regulates a Coordinated Network of SR Protein Expression during Differentiation and Tumorigenesis.Mol Cell. 2020 Nov 19;80(4):648-665.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.10.019. Epub 2020 Nov 10. Mol Cell. 2020. PMID: 33176162 Free PMC article.
-
PRMT1 Modulates Alternative Splicing to Enhance HPV18 mRNA Stability and Promote the Establishment of Infection.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 26:2024.09.26.614592. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.26.614592. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39386465 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Human Papillomavirus Type 16 Circular RNA Is Barely Detectable for the Claimed Biological Activity.mBio. 2022 Feb 22;13(1):e0359421. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03594-21. Epub 2022 Jan 18. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35038914 Free PMC article.
-
Oncogenic SRSF3 in health and diseases.Int J Biol Sci. 2023 Jun 12;19(10):3057-3076. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.83368. eCollection 2023. Int J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37416784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The chromatin insulator CTCF regulates HPV18 transcript splicing and differentiation-dependent late gene expression.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Nov 4;17(11):e1010032. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010032. eCollection 2021 Nov. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 34735550 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

