Pimasertib, a selective oral MEK1/2 inhibitor: absolute bioavailability, mass balance, elimination route, and metabolite profile in cancer patients
- PMID: 27483391
- PMCID: PMC5099557
- DOI: 10.1111/bcp.13078
Pimasertib, a selective oral MEK1/2 inhibitor: absolute bioavailability, mass balance, elimination route, and metabolite profile in cancer patients
Abstract
Aim: This trial (NCT: 01713036) investigated the absolute bioavailability, mass balance and metabolite profile of pimasertib in a new design combining these investigations in a single group of patients.
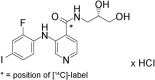
Methods: Six male patients with pathologically confirmed, locally advanced or metastatic solid tumours were enrolled. Exclusion criteria included Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status >1. In Part A of the trial, patients received a 60 mg oral dose of unlabelled pimasertib followed by an intravenous (i.v.) tracer dose of [14 C]pimasertib 2 μg (equalling 9 kBq) as a bolus injection, one hour after the oral dose, on Day 1. On Day 8, all patients received 60 mg pimasertib capsules spiked with 2.6 MBq of [14 C]pimasertib. Patients received 60 mg oral unlabelled pimasertib twice daily from Day 3 to Day 21 of Part A and in subsequent 21-day cycles in Part B.
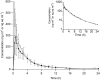
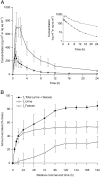
Results: Following i.v. administration, [14 C]pimasertib exhibited a geometric mean total body clearance of 45.7 l h-1 (geometric coefficient of variation [geometric CV]: 47.2%) and a volume of distribution of 229 l (geometric CV: 42.0%). Absolute bioavailability was 73%. The majority of the oral [14 C] dose (85.1%) was recovered in excreta. Total radioactivity was mainly excreted into urine (52.8%) and faeces (30.7%) with 78.9% of the [14 C] dose recovered as metabolites. Two major circulating metabolites were identified in plasma: a carboxylic acid (M445) and a phosphoethanolamine conjugate (M554). The safety profile was in line with the published pimasertib trials.
Conclusion: Pimasertib showed a favourable pharmacokinetic profile with high absolute bioavailability and a unique metabolic pathway (conjugation with phosphoethanolamine).
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01713036.
Keywords: 14C; absolute bioavailability; elimination route; mass balance; pimasertib.
© 2016 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Metabolism of the MEK1/2 Inhibitor Pimasertib Involves a Novel Conjugation with Phosphoethanolamine in Patients with Solid Tumors.Drug Metab Dispos. 2017 Feb;45(2):174-182. doi: 10.1124/dmd.116.072934. Epub 2016 Dec 1. Drug Metab Dispos. 2017. PMID: 27934635 Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacology of Pimasertib, A Selective MEK1/2 Inhibitor.Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2018 Aug;43(4):373-382. doi: 10.1007/s13318-018-0466-x. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2018. PMID: 29488172 Review.
-
Open-label, single-center, phase I trial to investigate the mass balance and absolute bioavailability of the highly selective oral MET inhibitor tepotinib in healthy volunteers.Invest New Drugs. 2020 Oct;38(5):1507-1519. doi: 10.1007/s10637-020-00926-1. Epub 2020 Mar 27. Invest New Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32221754 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phase I single dose, two-period and two-sequence cross-over trial to evaluate the relative bioavailability of two oral pimasertib formulations in advanced cancer patients.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2017 Apr;79(4):681-688. doi: 10.1007/s00280-017-3258-0. Epub 2017 Mar 13. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28289865 Clinical Trial.
-
Concomitant oral and intravenous pharmacokinetics of trametinib, a MEK inhibitor, in subjects with solid tumours.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2014 Sep;78(3):524-32. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12373. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24606567 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Metabolite Profiling in Anticancer Drug Development: A Systematic Review.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 Apr 9;14:1401-1444. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S221518. eCollection 2020. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020. PMID: 32308372 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic Cancer and Its Microenvironment-Recent Advances and Current Controversies.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 1;21(9):3218. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093218. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32370075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
C20orf24 promotes colorectal cancer progression by recruiting Rin1 to activate Rab5-mediated mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase signalling.Clin Transl Med. 2022 Apr;12(4):e796. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.796. Clin Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35389560 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Study of the mass balance, biotransformation and safety of [14C]SHR8554, a novel μ-opioid receptor injection, in healthy Chinese subjects.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 14;14:1231102. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1231102. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37781692 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Synthetic Approaches towards Small Molecule Reactivators of p53.Biomolecules. 2020 Apr 20;10(4):635. doi: 10.3390/biom10040635. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32326087 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Intellectual Property Organization . WO2006045514. 3‐arylamino pyridine derivatives. 2006. Available at https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2006045514&red... (last accessed 12 August 2015).
-
- World Intellectual Property Organization . WO2013178320. Solid state forms of n‐((s)‐2,3‐dihydroxy‐propyl)‐3‐(2‐fluoro‐4‐iodo‐phenylamino)‐isonicotinamide. 2013. Available at https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2013178320&red... (last accessed 12 August 2015).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

