Epidermal growth factor preserves myelin and promotes astrogliosis after intraventricular hemorrhage
- PMID: 27472419
- PMCID: PMC5026581
- DOI: 10.1002/glia.23037
Epidermal growth factor preserves myelin and promotes astrogliosis after intraventricular hemorrhage
Abstract
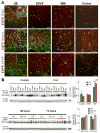
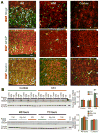
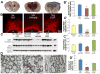
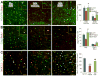
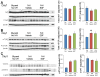
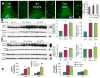
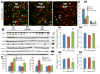
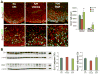
Intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) leads to reduced myelination and astrogliosis of the white matter in premature infants. No therapeutic strategy exists to minimize white matter injury in survivors with IVH. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) enhances myelination, astrogliosis, and neurologic recovery in animal models of white matter injury. Here, we hypothesized that recombinant human (rh) EGF treatment would enhance oligodendrocyte precursor cell (OPC) maturation, myelination, and neurological recovery in preterm rabbits with IVH. In addition, rhEGF would promote astrogliosis by inducing astroglial progenitor proliferation and GFAP transcription. We tested these hypotheses in a preterm rabbit model of IVH and evaluated autopsy samples from human preterm infants. We found that EGF and EGFR expression were more abundant in the ganglionic eminence relative to the cortical plate and white matter of human infants and that the development of IVH reduced EGF levels, but not EGFR expression. Accordingly, rhEGF treatment promoted proliferation and maturation of OPCs, preserved myelin in the white matter, and enhanced neurological recovery in rabbits with IVH. rhEGF treatment inhibited Notch signaling, which conceivably contributed to OPC maturation. rhEGF treatment contributed to astrogliosis by increasing astroglial proliferation and upregulating GFAP as well as Sox9 expression. Hence, IVH results in a decline in EGF expression; and rhEGF treatment preserves myelin, restores neurological recovery, and exacerbates astrogliosis by inducing proliferation of astrocytes and enhancing transcription of GFAP and Sox9 in pups with IVH. rhEGF treatment might improve the neurological outcome of premature infants with IVH. GLIA 2016;64:1987-2004.
Keywords: astrogliosis; epidermal growth factor; intraventricular hemorrhage; myelination; oligodendrocyte progenitor cells; premature infants.
© 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Nothing to report.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glycogen synthase kinase-3β inhibition enhances myelination in preterm newborns with intraventricular hemorrhage, but not recombinant Wnt3A.Neurobiol Dis. 2018 Oct;118:22-39. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2018.06.015. Epub 2018 Jun 22. Neurobiol Dis. 2018. PMID: 29940337 Free PMC article.
-
AMPA-Kainate Receptor Inhibition Promotes Neurologic Recovery in Premature Rabbits with Intraventricular Hemorrhage.J Neurosci. 2016 Mar 16;36(11):3363-77. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4329-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26985043 Free PMC article.
-
Hyaluronidase and Hyaluronan Oligosaccharides Promote Neurological Recovery after Intraventricular Hemorrhage.J Neurosci. 2016 Jan 20;36(3):872-89. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3297-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26791217 Free PMC article.
-
White matter injury in infants with intraventricular haemorrhage: mechanisms and therapies.Nat Rev Neurol. 2021 Apr;17(4):199-214. doi: 10.1038/s41582-020-00447-8. Epub 2021 Jan 27. Nat Rev Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33504979 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recovery of the brain after intraventricular hemorrhage.Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2022 Feb;27(1):101224. doi: 10.1016/j.siny.2021.101224. Epub 2021 Feb 26. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2022. PMID: 33888444 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Human Cord Blood-Derived Unrestricted Somatic Stem Cell Infusion Improves Neurobehavioral Outcome in a Rabbit Model of Intraventricular Hemorrhage.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019 Nov;8(11):1157-1169. doi: 10.1002/sctm.19-0082. Epub 2019 Jul 19. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31322326 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of Interneuron Neurogenesis in Premature Newborns and Reversal with Estrogen Treatment.J Neurosci. 2018 Jan 31;38(5):1100-1113. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1875-17.2017. Epub 2017 Dec 15. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29246927 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen Treatment Reverses Prematurity-Induced Disruption in Cortical Interneuron Population.J Neurosci. 2018 Aug 22;38(34):7378-7391. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0478-18.2018. Epub 2018 Jul 23. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30037831 Free PMC article.
-
Glycogen synthase kinase-3β inhibition enhances myelination in preterm newborns with intraventricular hemorrhage, but not recombinant Wnt3A.Neurobiol Dis. 2018 Oct;118:22-39. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2018.06.015. Epub 2018 Jun 22. Neurobiol Dis. 2018. PMID: 29940337 Free PMC article.
-
Nexilin Regulates Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cell Migration and Remyelination and Is Negatively Regulated by Protease-Activated Receptor 1/Ras-Proximate-1 Signaling Following Subarachnoid Hemorrhage.Front Neurol. 2018 Apr 25;9:282. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00282. eCollection 2018. Front Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29922213 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguirre A, Dupree JL, Mangin JM, Gallo V. A functional role for EGFR signaling in myelination and remyelination. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:990–1002. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

