Gentiana scabra Reduces SR-A Expression and Oxidized-LDL Uptake in Human Macrophages
- PMID: 27471359
- PMCID: PMC4963422
- DOI: 10.6515/acs20150416a
Gentiana scabra Reduces SR-A Expression and Oxidized-LDL Uptake in Human Macrophages
Abstract
Background: Macrophages can imbibe low-density lipoprotein (LDL) through scavenger receptors to become foam cells, which is critical in the initiation and progression of atherosclerosis. Mounting evidence suggests that the anti-inflammatory nature of Chinese herbs have the capacity to halt the complex mechanisms underlying atherosclerosis. This study examined the effects of Chinese herbs on foam cell formation.
Methods: Chinese herbs were obtained from the Sun Ten pharmaceutic company. Using oxidized LDL (OxLDL) uptake and a cell toxicity assay, we screened more than 30 types of Chinese herbs. Western blotting was used to determine expressions of scavenger receptors (SRs) and extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK) activities.
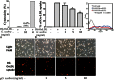
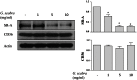
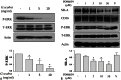
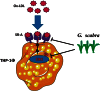
Results: We found that Gentiana scabra reduced oxidized LDL uptake effectively in THP-1 macrophages (p < 0.05 vs. OxLDL treated control). Moreover, treatment with Gentiana scabra in THP-1 macrophages resulted in decreased expression of scavenger receptor- A (SR-A) (p < 0.05 vs. control). Molecular investigation revealed that Gentiana scabra inhibited SR-A protein expression, possibly by regulating ERK signaling pathways (p < 0.05 vs. control).
Conclusions: By regulating SR-A expression, Gentiana scabra reduced oxidized LDL uptake in human macrophages. These results support the potential use of Gentiana scabra in treating atherosclerosis.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Foam cells; Gentiana scabra; Macrophage; Oxidized LDL.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PKCδ signalling regulates SR-A and CD36 expression and foam cell formation.Cardiovasc Res. 2012 Aug 1;95(3):346-55. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvs189. Epub 2012 Jun 11. Cardiovasc Res. 2012. PMID: 22687273
-
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate Reduces Scavenger Receptor A Expression and Foam Cell Formation in Human Macrophages.J Agric Food Chem. 2017 Apr 19;65(15):3141-3150. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b05832. Epub 2017 Apr 10. J Agric Food Chem. 2017. PMID: 28367625
-
Synergically increased expression of CD36, CLA-1 and CD68, but not of SR-A and LOX-1, with the progression to foam cells from macrophages.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2002;9(1):57-64. doi: 10.5551/jat.9.57. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2002. PMID: 12238639
-
Postprandial lipoproteins and the molecular regulation of vascular homeostasis.Prog Lipid Res. 2013 Oct;52(4):446-64. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2013.06.001. Epub 2013 Jun 15. Prog Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23774609 Review.
-
Foam cells in atherosclerosis.Clin Chim Acta. 2013 Sep 23;424:245-52. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.06.006. Epub 2013 Jun 16. Clin Chim Acta. 2013. PMID: 23782937 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring global research trends in Chinese medicine for atherosclerosis: a bibliometric study 2012-2023.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Jun 17;11:1400130. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1400130. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 38952541 Free PMC article.
-
Shen-Yuan-Dan Capsule Inhibiting Inflammatory Reaction by Regulating Insulin Receptor Substrate 1/PI3K/Akt/NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Apoliprotein E Knockout Mice Fed with a High-Fat Diet.Acta Cardiol Sin. 2017 May;33(3):285-291. doi: 10.6515/acs20160901b. Acta Cardiol Sin. 2017. PMID: 28559659 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
