Characterisation of a New Fungal Immunomodulatory Protein from Tiger Milk mushroom, Lignosus rhinocerotis
- PMID: 27460640
- PMCID: PMC4962085
- DOI: 10.1038/srep30010
Characterisation of a New Fungal Immunomodulatory Protein from Tiger Milk mushroom, Lignosus rhinocerotis
Abstract
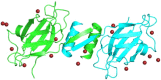
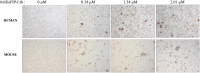
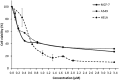
Lignosus rhinocerotis (Tiger milk mushroom) is an important folk medicine for indigenous peoples in Southeast Asia. We previously reported its de novo assembled 34.3 Mb genome encoding a repertoire of proteins including a putative bioactive fungal immunomodulatory protein. Here we report the cDNA of this new member (FIP-Lrh) with a homology range of 54-64% to FIPs from other mushroom species, the closest is with FIP-glu (LZ-8) (64%) from Ganoderma lucidum. The FIP-Lrh of 112 amino acids (12.59 kDa) has a relatively hydrophobic N-terminal. Its predicted 3-dimensional model has identical folding patterns to FIP-fve and contains a partially conserved and more positively charged carbohydrates binding pocket. Docking predictions of FIP-Lrh on 14 glycans commonly found on cellular surfaces showed the best binding energy of -3.98 kcal/mol to N-acetylgalactosamine and N-acetylglucosamine. Overexpression of a 14.9 kDa soluble 6xHisFIP-Lrh was achieved in pET-28a(+)/BL21 and the purified recombinant protein was sequence verified by LC-MS/MS (QTOF) analysis. The ability to haemagglutinate both mouse and human blood at concentration ≥0.34 μM, further demonstrated its lectin nature. In addition, the cytotoxic effect of 6xHisFIP-Lrh on MCF-7, HeLa and A549 cancer cell lines was detected at IC50 of 0.34 μM, 0.58 μM and 0.60 μM, respectively.
Figures
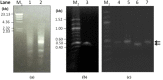
 ). The position of the splice sites (donor, GT and acceptor, AG) in the intron is in bold and underlined and was predicted using the SplicePort tool (
). The position of the splice sites (donor, GT and acceptor, AG) in the intron is in bold and underlined and was predicted using the SplicePort tool (
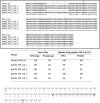
 ). A Neighbour-joining phylogram (with real Branch length, distance corrected) was generated using the Omega Clustal program with FIPs from the representatives of genera Lignosus, Ganoderma, Flammulina, Volvariella and Trametes.
). A Neighbour-joining phylogram (with real Branch length, distance corrected) was generated using the Omega Clustal program with FIPs from the representatives of genera Lignosus, Ganoderma, Flammulina, Volvariella and Trametes.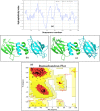

Similar articles
-
Recombinant Expression and Bioactivity Comparison of Four Typical Fungal Immunomodulatory Proteins from Three Main Ganoderma Species.BMC Biotechnol. 2018 Dec 14;18(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s12896-018-0488-0. BMC Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30547780 Free PMC article.
-
Shotgun proteomic analysis of tiger milk mushroom (Lignosus rhinocerotis) and the isolation of a cytotoxic fungal serine protease from its sclerotium.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Nov 4;174:437-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.08.042. Epub 2015 Aug 28. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26320692
-
Functional evaluation of a recombinant fungal immunomodulatory protein from L. rhinocerus produced in P. pastoris and E. coli host expression systems.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Apr;105(7):2799-2813. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11225-x. Epub 2021 Mar 25. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33763709
-
Ganoderma immunomodulatory proteins: mushrooming functional FIPs.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Apr;106(7):2367-2380. doi: 10.1007/s00253-022-11839-9. Epub 2022 Mar 29. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35348851 Review.
-
Recent status and prospects of the fungal immunomodulatory protein family.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2011 Dec;31(4):365-75. doi: 10.3109/07388551.2010.543967. Epub 2011 Jun 9. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21651437 Review.
Cited by
-
Safety assessment of the fungal immunomodulatory protein from Ganoderma microsporum (GMI) derived from engineered Pichia pastoris: Genetic toxicology, a 13-week oral gavage toxicity study, and an embryo-fetal developmental toxicity study in Sprague-Dawley rats.Toxicol Rep. 2022 May 26;9:1240-1254. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2022.05.013. eCollection 2022. Toxicol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36518484 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a Novel Anti-cancer Protein, FIP-bbo, from Botryobasidium botryosum and Protein Structure Analysis using Molecular Dynamic Simulation.Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 9;9(1):5818. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42104-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30967569 Free PMC article.
-
Mycopharmaceuticals and Nutraceuticals: Promising Agents to Improve Human Well-Being and Life Quality.J Fungi (Basel). 2021 Jun 24;7(7):503. doi: 10.3390/jof7070503. J Fungi (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34202552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recombinant Expression and Bioactivity Comparison of Four Typical Fungal Immunomodulatory Proteins from Three Main Ganoderma Species.BMC Biotechnol. 2018 Dec 14;18(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s12896-018-0488-0. BMC Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30547780 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo toxicity of bioreactor-grown biomass and exopolysaccharides from Malaysian tiger milk mushroom mycelium for potential future health applications.Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 29;11(1):23079. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-02486-7. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34845290 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lai W. H. et al. Molecular phylogenetic analysis of wild Tiger’s Milk Mushroom (Lignosus rhinocerus) collected from Pahang, Malaysia and its nutritional value and toxic metal content. Int. Food. Res. J. 20(5), 2301–2307 (2013).
-
- Jamil N. A. et al. LCMS-QTOF Determination of Lentinan-Like β-D-Glucan Content Isolated by Hot Water and Alkaline Solution from Tiger’s Milk Mushroom, Termite Mushroom, and Selected Local Market Mushrooms. J. Mycology 8 pp (2013).
-
- Lee S. S. & Chang Y. S. Ethnomycology. In: Jones E. B. G., Hyde K. D., Vikineswary S. (eds) Malaysian fungal diversity. Mushroom Research Centre, University of Malaya and Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment Malaysia, Kuala Lumpur, pp 307–317 (2007).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

