eIF2β is critical for eIF5-mediated GDP-dissociation inhibitor activity and translational control
- PMID: 27458202
- PMCID: PMC5175340
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkw657
eIF2β is critical for eIF5-mediated GDP-dissociation inhibitor activity and translational control
Abstract
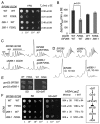
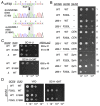
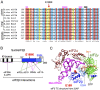
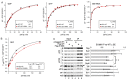
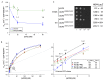
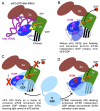
In protein synthesis translation factor eIF2 binds initiator tRNA to ribosomes and facilitates start codon selection. eIF2 GDP/GTP status is regulated by eIF5 (GAP and GDI functions) and eIF2B (GEF and GDF activities), while eIF2α phosphorylation in response to diverse signals is a major point of translational control. Here we characterize a growth suppressor mutation in eIF2β that prevents eIF5 GDI and alters cellular responses to reduced eIF2B activity, including control of GCN4 translation. By monitoring the binding of fluorescent nucleotides and initiator tRNA to purified eIF2 we show that the eIF2β mutation does not affect intrinsic eIF2 affinities for these ligands, neither does it interfere with eIF2 binding to 43S pre-initiation complex components. Instead we show that the eIF2β mutation prevents eIF5 GDI stabilizing nucleotide binding to eIF2, thereby altering the off-rate of GDP from eIF2•GDP/eIF5 complexes. This enables cells to grow with reduced eIF2B GEF activity but impairs activation of GCN4 targets in response to amino acid starvation. These findings provide support for the importance of eIF5 GDI activity in vivo and demonstrate that eIF2β acts in concert with eIF5 to prevent premature release of GDP from eIF2γ and thereby ensure tight control of protein synthesis initiation.
© The Author(s) 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
eIF2B promotes eIF5 dissociation from eIF2*GDP to facilitate guanine nucleotide exchange for translation initiation.Genes Dev. 2013 Dec 15;27(24):2696-707. doi: 10.1101/gad.231514.113. Genes Dev. 2013. PMID: 24352424 Free PMC article.
-
Direct binding of translation initiation factor eIF2gamma-G domain to its GTPase-activating and GDP-GTP exchange factors eIF5 and eIF2B epsilon.J Biol Chem. 2006 May 5;281(18):12636-44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M511700200. Epub 2006 Mar 7. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16522633
-
eIF5 has GDI activity necessary for translational control by eIF2 phosphorylation.Nature. 2010 May 20;465(7296):378-81. doi: 10.1038/nature09003. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20485439 Free PMC article.
-
A new function and complexity for protein translation initiation factor eIF2B.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(17):2660-5. doi: 10.4161/15384101.2014.948797. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 25486352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clues to the mechanism of action of eIF2B, the guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor for translation initiation.Biochem Soc Trans. 2008 Aug;36(Pt 4):658-64. doi: 10.1042/BST0360658. Biochem Soc Trans. 2008. PMID: 18631136 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantifying the Binding of Fluorescently Labeled Guanine Nucleotides and Initiator tRNA to Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 2.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2428:89-99. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1975-9_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35171475
-
Cyst stem cell lineage eIF5 non-autonomously prevents testicular germ cell tumor formation via eIF1A/eIF2γ-mediated pre-initiation complex.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Jul 26;13(1):351. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-03025-5. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35883200 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Synthesis Initiation in Eukaryotic Cells.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018 Dec 3;10(12):a033092. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a033092. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018. PMID: 29735639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
eIF2B and the Integrated Stress Response: A Structural and Mechanistic View.Biochemistry. 2020 Apr 7;59(13):1299-1308. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00132. Epub 2020 Mar 26. Biochemistry. 2020. PMID: 32200625 Free PMC article.
-
Fail-safe control of translation initiation by dissociation of eIF2α phosphorylated ternary complexes.Elife. 2017 Mar 18;6:e24542. doi: 10.7554/eLife.24542. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28315520 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hinnebusch A.G. The scanning mechanism of eukaryotic translation initiation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2014;83:779–812. - PubMed
-
- Kapp L.D., Lorsch J.R. GTP-dependent recognition of the methionine moiety on initiator tRNA by translation factor eIF2. J. Mol. Biol. 2004;335:923–936. - PubMed
-
- Algire M.A., Maag D., Lorsch J.R. Pi release from eIF2, not GTP hydrolysis, is the step controlled by start-site selection during eukaryotic translation initiation. Mol. Cell. 2005;20:251–262. - PubMed
-
- Pavitt G.D. eIF2B, a mediator of general and gene-specific translational control. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2005;33:1487–1492. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

