Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (HIF) as a Target for Novel Therapies in Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 27445820
- PMCID: PMC4921475
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00184
Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (HIF) as a Target for Novel Therapies in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
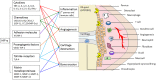
Hypoxia is an important micro-environmental characteristic of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Hypoxia-inducible factors (HIF) are key transcriptional factors that are highly expressed in RA synovium to regulate the adaptive responses to this hypoxic milieu. Accumulating evidence supports hypoxia and HIFs in regulating a number of important pathophysiological characteristics of RA, including synovial inflammation, angiogenesis, and cartilage destruction. Experimental and clinical data have confirmed the upregulation of both HIF-1α and HIF-2α in RA. This review will focus on the differential expression of HIFs within the synovial joint and its functional behavior in different cell types to regulate RA progression. Potential development of new therapeutic strategies targeting HIF-regulated pathways at sites of disease in RA will also be addressed.
Keywords: angiogenesis; cartilage degradation; hypoxia; hypoxia-inducible factor; inflammation; rheumatoid arthritis; synovitis; targeted therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Role of hypoxia-inducible factor in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016 Dec 18;48(6):1095-1099. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016. PMID: 27987521 Chinese.
-
Hypoxia inducible factor-1-alpha (HIF-1alpha) is related to both angiogenesis and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2009 Nov-Dec;27(6):945-51. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2009. PMID: 20149310
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-2α is an essential catabolic regulator of inflammatory rheumatoid arthritis.PLoS Biol. 2014 Jun 10;12(6):e1001881. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001881. eCollection 2014 Jun. PLoS Biol. 2014. PMID: 24914685 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 as regulator of angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis - therapeutic implications.Curr Med Chem. 2010;17(3):254-63. doi: 10.2174/092986710790149783. Curr Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20214567 Review.
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor: a potential therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis.Curr Drug Targets. 2013 Jun 1;14(6):700-7. doi: 10.2174/1389450111314060010. Curr Drug Targets. 2013. PMID: 23531111 Review.
Cited by
-
Rheumatoid arthritis and mitochondrial homeostasis: The crossroads of metabolism and immunity.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 23;9:1017650. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1017650. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36213670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-2 Alpha Regulates the Migration of Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes via Oxidative Stress-Induced CD70 Expression in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 20;23(4):2342. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042342. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216458 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT1 promotes tumor-like invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis via targeting TIMP1.Oncotarget. 2017 Oct 6;8(51):88965-88973. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21628. eCollection 2017 Oct 24. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29179491 Free PMC article.
-
New Insights into the Role of Synovial Fibroblasts Leading to Joint Destruction in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 8;24(6):5173. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065173. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting JAK-STAT Signalling Alters PsA Synovial Fibroblast Pro-Inflammatory and Metabolic Function.Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 24;12:672461. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.672461. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34248953 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abeles A. M., Pillinger M. H. (2006). The role of the synovial fibroblast in rheumatoid arthritis: cartilage destruction and the regulation of matrix metalloproteinases. Bull. NYU Hosp. Jt. Dis. 64, 20–24. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

