cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) complexes probed by complementary differential scanning fluorimetry and ion mobility-mass spectrometry
- PMID: 27444646
- PMCID: PMC5095912
- DOI: 10.1042/BCJ20160648
cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) complexes probed by complementary differential scanning fluorimetry and ion mobility-mass spectrometry
Abstract
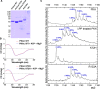
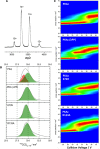
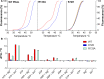
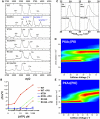
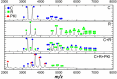
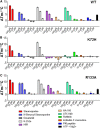
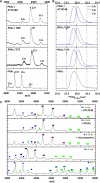
cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) is an archetypal biological signaling module and a model for understanding the regulation of protein kinases. In the present study, we combine biochemistry with differential scanning fluorimetry (DSF) and ion mobility-mass spectrometry (IM-MS) to evaluate effects of phosphorylation and structure on the ligand binding, dynamics and stability of components of heteromeric PKA protein complexes in vitro We uncover dynamic, conformationally distinct populations of the PKA catalytic subunit with distinct structural stability and susceptibility to the physiological protein inhibitor PKI. Native MS of reconstituted PKA R2C2 holoenzymes reveals variable subunit stoichiometry and holoenzyme ablation by PKI binding. Finally, we find that although a 'kinase-dead' PKA catalytic domain cannot bind to ATP in solution, it interacts with several prominent chemical kinase inhibitors. These data demonstrate the combined power of IM-MS and DSF to probe PKA dynamics and regulation, techniques that can be employed to evaluate other protein-ligand complexes, with broad implications for cellular signaling.
Keywords: complex; inhibitor; ion mobility; mass spectrometry; protein kinase A; protein structure.
© 2016 The Author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Probing cAMP-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme complexes I alpha and II beta by FT-IR and chemical protein footprinting.Biochemistry. 2004 Feb 24;43(7):1908-20. doi: 10.1021/bi0354435. Biochemistry. 2004. PMID: 14967031
-
Mapping intersubunit interactions of the regulatory subunit (RIalpha) in the type I holoenzyme of protein kinase A by amide hydrogen/deuterium exchange mass spectrometry (DXMS).J Mol Biol. 2004 Jul 23;340(5):1185-96. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.05.042. J Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15236976
-
Analysis of autophosphorylation sites in the recombinant catalytic subunit alpha of cAMP-dependent kinase by nano-UPLC-ESI-MS/MS.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2009 Nov;395(6):1713-20. doi: 10.1007/s00216-009-2932-4. Epub 2009 Jul 10. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2009. PMID: 19590856
-
A historical overview of protein kinases and their targeted small molecule inhibitors.Pharmacol Res. 2015 Oct;100:1-23. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2015.07.010. Epub 2015 Jul 21. Pharmacol Res. 2015. PMID: 26207888 Review.
-
PKA: a portrait of protein kinase dynamics.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Mar 11;1697(1-2):259-69. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2003.11.029. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 15023366 Review.
Cited by
-
Structure-based design of nucleoside-derived analogues as sulfotransferase inhibitors.RSC Adv. 2019 Oct 9;9(55):32165-32173. doi: 10.1039/c9ra07567d. eCollection 2019 Oct 7. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35530783 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical Analysis of AKAP-Anchored PKA Signaling Complexes.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2483:297-317. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2245-2_19. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35286684 Free PMC article.
-
Collision induced unfolding of isolated proteins in the gas phase: past, present, and future.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2018 Feb;42:93-100. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2017.11.010. Epub 2017 Dec 5. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2018. PMID: 29207278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ERK1/2 inhibitors act as monovalent degraders inducing ubiquitylation and proteasome-dependent turnover of ERK2, but not ERK1.Biochem J. 2023 May 15;480(9):587-605. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20220598. Biochem J. 2023. PMID: 37018014 Free PMC article.
-
Covalent inhibitors of EGFR family protein kinases induce degradation of human Tribbles 2 (TRIB2) pseudokinase in cancer cells.Sci Signal. 2018 Sep 25;11(549):eaat7951. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aat7951. Sci Signal. 2018. PMID: 30254057 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

