World Health Organization Group I Pulmonary Hypertension: Epidemiology and Pathophysiology
- PMID: 27443134
- PMCID: PMC4959804
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccl.2016.04.001
World Health Organization Group I Pulmonary Hypertension: Epidemiology and Pathophysiology
Abstract
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a debilitating disease characterized by pathologic remodeling of the resistance pulmonary arteries, ultimately leading to right ventricular (RV) failure and death. In this article we discuss the definition of PAH, the initial epidemiology based on the National Institutes of Health Registry, and the updated epidemiology gleaned from contemporary registries, pathogenesis of pulmonary vascular dysfunction and proliferation, and RV failure in PAH.
Keywords: Epidemiology; Pathophysiology; Pulmonary arterial hypertension; Pulmonary vasculature; Right ventricle.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
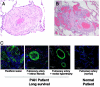

Similar articles
-
Current Trends and Future Perspectives in the Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension: WHO Group II-V.Curr Probl Cardiol. 2018 May;43(5):217-231. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2017.10.003. Epub 2017 Oct 31. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29153390 Review.
-
Right ventricular dyssynchrony in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension: determinants and impact on pump function.J Heart Lung Transplant. 2015 Mar;34(3):381-9. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2014.06.010. Epub 2014 Jun 21. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2015. PMID: 25087105
-
Group 2 Pulmonary Hypertension: Pulmonary Venous Hypertension: Epidemiology and Pathophysiology.Cardiol Clin. 2016 Aug;34(3):401-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ccl.2016.04.010. Cardiol Clin. 2016. PMID: 27443137 Review.
-
Right ventricular remodeling in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension: adaptive versus maladaptive morphology.J Heart Lung Transplant. 2015 Mar;34(3):395-403. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2014.11.002. Epub 2014 Nov 8. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2015. PMID: 25499139
-
The changing picture of patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension in the United States: how REVEAL differs from historic and non-US Contemporary Registries.Chest. 2011 Jan;139(1):128-37. doi: 10.1378/chest.10-0075. Epub 2010 Jun 17. Chest. 2011. PMID: 20558556 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Emerging Roles of Extracellular Non-Coding RNAs in Vascular Diseases.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2022 Jun;15(3):492-499. doi: 10.1007/s12265-022-10237-w. Epub 2022 Apr 22. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 35460016 Review.
-
Incidence and Risk Factors of Pulmonary Hypertension After Venous Thromboembolism: An Analysis of a Large Health Care Database.J Am Heart Assoc. 2022 Jul 19;11(14):e024358. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.024358. Epub 2022 Jul 15. J Am Heart Assoc. 2022. PMID: 35861839 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary hypertension and insulin resistance: a mechanistic overview.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jan 4;14:1283233. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1283233. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38239990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Echocardiographic Evaluation of Initial Ambrisentan Plus Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitor on Right Ventricular Pulmonary Artery Coupling in Severe Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Patients.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 May 3;9:843606. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.843606. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35592406 Free PMC article.
-
Echocardiographic determination of pulmonary arterial capacitance.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019 Sep;35(9):1581-1586. doi: 10.1007/s10554-019-01595-9. Epub 2019 Apr 9. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30968263 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Farber HW, Loscalzo J. Pulmonary arterial hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(16):1655–65. - PubMed
-
- Rich S, et al. Primary pulmonary hypertension. A national prospective study. Ann Intern Med. 1987;107(2):216–23. - PubMed
-
- D'Alonzo GE, et al. Survival in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension. Results from a national prospective registry. Ann Intern Med. 1991;115(5):343–9. - PubMed
-
- Galiè N, et al. Updated treatment algorithm of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62(25 Suppl):D60–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

