The vital role of citrate buffer in acetone-butanol-ethanol (ABE) fermentation using corn stover and high-efficient product recovery by vapor stripping-vapor permeation (VSVP) process
- PMID: 27441040
- PMCID: PMC4952226
- DOI: 10.1186/s13068-016-0566-2
The vital role of citrate buffer in acetone-butanol-ethanol (ABE) fermentation using corn stover and high-efficient product recovery by vapor stripping-vapor permeation (VSVP) process
Abstract
Background: Butanol is not only an important solvent and chemical intermediate in food and pharmaceutical industries, but also considered as an advanced biofuel. Recently, there have been resurging interests in producing biobutanol especially using low-cost lignocellulosic biomass, but the process still suffers from low titer and productivity. The challenge for the bioconversion approach is to find an effective way of degrading materials into simple sugars that can then be converted into fuels by microorganisms. The pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass is the great important process in influencing butanol production and recovery, finally determining its eco-feasibility in commercialization.
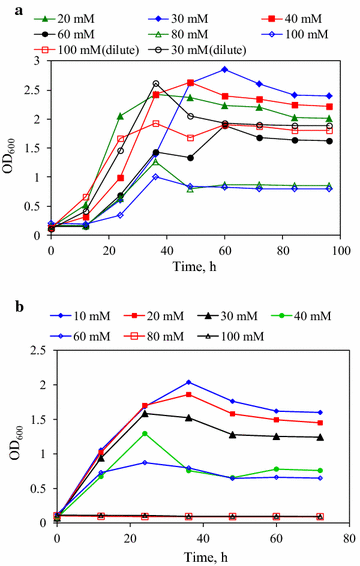
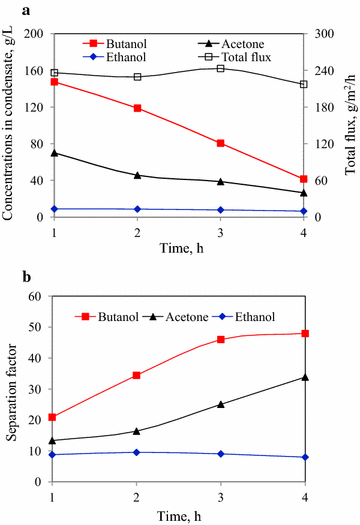
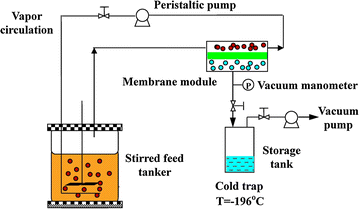
Results: The effects of various strengths of citrate buffer on enzymatic hydrolysis and acetone-butanol-ethanol fermentation using corn stover or glucose as feedstock were investigated. The strengths of citrate buffer in the range of 20-100 mM had no effect on enzymatic hydrolysis, but greatly influenced the performance of ABE fermentation using corn stover hydrolysate. When 30 mM citrate buffer was used for enzymatic hydrolysis, the fermentation broth with the maximum butanol and ABE concentrations of 11.2 and 19.8 g/L were obtained from 30.9 g/L glucose and 9.7 g/L xylose, respectively, which was concentrated to 100.4 g/L butanol and 153.5 g/L ABE by vapor stripping-vapor permeation process. Furthermore, using glucose as sole carbon source, there were no cell growth and ABE production in the P2 medium with 80 or 100 mM citrate buffer, indicating that higher concentrations of citrate buffer had deleterious effect on cell growth and metabolism due to the variation of cells internal pH and cell membrane permeability. To mimic in situ product recovery for ABE fermentation, the VSVP process produced the condensate containing 212.0-232.0 g/L butanol (306.6-356.1 g/L ABE) from fermentation broth containing ~10 g/L butanol (~17 g/L ABE), the performance of which was more effective than pervaporation and gas stripping.
Conclusions: As it has significant impact on butanol fermentation, the strength of citrate buffer is of great importance in lignocellulosic butanol fermentation. Compared with pervaporation and gas stripping, the VSVP process has great potential for efficient butanol recovery in biobutanol production.
Keywords: ABE fermentation; Butanol recovery; Corn stover; Vapor stripping–vapor permeation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The advanced strategy for enhancing biobutanol production and high-efficient product recovery with reduced wastewater generation.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2017 Jun 10;10:148. doi: 10.1186/s13068-017-0836-7. eCollection 2017. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2017. PMID: 28616072 Free PMC article.
-
A novel in situ gas stripping-pervaporation process integrated with acetone-butanol-ethanol fermentation for hyper n-butanol production.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2016 Jan;113(1):120-9. doi: 10.1002/bit.25666. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2016. PMID: 26032697
-
A novel close-circulating vapor stripping-vapor permeation technique for boosting biobutanol production and recovery.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2018 May 4;11:128. doi: 10.1186/s13068-018-1129-5. eCollection 2018. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2018. PMID: 29755587 Free PMC article.
-
Acetone-butanol-ethanol fermentation of corn stover: current production methods, economic viability and commercial use.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2016 Mar;363(6):fnw033. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnw033. Epub 2016 Feb 11. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2016. PMID: 26872494 Review.
-
Applied in situ product recovery in ABE fermentation.Biotechnol Prog. 2017 May;33(3):563-579. doi: 10.1002/btpr.2446. Epub 2017 Mar 10. Biotechnol Prog. 2017. PMID: 28188696 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of high-titer lactic acid fermentation from NaOH- and NH3-H2O2-pretreated corncob by Bacillus coagulans using simultaneous saccharification and fermentation.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 17;6:37245. doi: 10.1038/srep37245. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27853308 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional analysis of degenerate strain Clostridium beijerinckii DG-8052 reveals a pleiotropic response to CaCO3-associated recovery of solvent production.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 14;6:38818. doi: 10.1038/srep38818. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27966599 Free PMC article.
-
Biobutanol production from coffee silverskin.Microb Cell Fact. 2018 Sep 27;17(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s12934-018-1002-z. Microb Cell Fact. 2018. PMID: 30261894 Free PMC article.
-
Pleiotropic regulation of a glucose-specific PTS in Clostridium acetobutylicum for high-efficient butanol production from corn stover without detoxification.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2019 Nov 7;12:264. doi: 10.1186/s13068-019-1604-7. eCollection 2019. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2019. PMID: 31709013 Free PMC article.
-
The advanced strategy for enhancing biobutanol production and high-efficient product recovery with reduced wastewater generation.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2017 Jun 10;10:148. doi: 10.1186/s13068-017-0836-7. eCollection 2017. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2017. PMID: 28616072 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hudiburg TW, Wang WW, Khanna M, Long SP, Dwivedi P, Parton WJ, Hartman M, DeLucia EH. Impacts of a 32-billion-gallon bioenergy landscape on land and fossil fuel use in the US. Nat Energy. 2016;1:15005. doi: 10.1038/nenergy.2015.5. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

