Inhibition of Bromodomain and Extraterminal Domain Family Proteins Ameliorates Experimental Renal Damage
- PMID: 27436852
- PMCID: PMC5280004
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2015080910
Inhibition of Bromodomain and Extraterminal Domain Family Proteins Ameliorates Experimental Renal Damage
Abstract
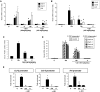
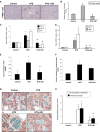
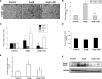
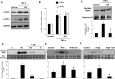
Renal inflammation has a key role in the onset and progression of immune- and nonimmune-mediated renal diseases. Therefore, the search for novel anti-inflammatory pharmacologic targets is of great interest in renal pathology. JQ1, a small molecule inhibitor of bromodomain and extraterminal (BET) proteins, was previously found to preserve renal function in experimental polycystic kidney disease. We report here that JQ1-induced BET inhibition modulated the in vitro expression of genes involved in several biologic processes, including inflammation and immune responses. Gene silencing of BRD4, an important BET protein, and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays showed that JQ1 alters the direct association of BRD4 with acetylated histone-packaged promoters and reduces the transcription of proinflammatory genes (IL-6, CCL-2, and CCL-5). In vivo, JQ1 abrogated experimental renal inflammation in murine models of unilateral ureteral obstruction, antimembrane basal GN, and infusion of Angiotensin II. Notably, JQ1 downregulated the expression of several genes controlled by the NF-κB pathway, a key inflammatory signaling pathway. The RelA NF-κB subunit is activated by acetylation of lysine 310. In damaged kidneys and cytokine-stimulated renal cells, JQ1 reduced the nuclear levels of RelA NF-κB. Additionally, JQ1 dampened the activation of the Th17 immune response in experimental renal damage. Our results show that inhibition of BET proteins reduces renal inflammation by several mechanisms: chromatin remodeling in promoter regions of specific genes, blockade of NF-κB pathway activation, and modulation of the Th17 immune response. These results suggest that inhibitors of BET proteins could have important therapeutic applications in inflammatory renal diseases.
Keywords: Cell Signaling; chemokine; transcription factors.
Copyright © 2017 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bromodomain and extraterminal (BET) protein inhibition suppresses human T cell leukemia virus 1 (HTLV-1) Tax protein-mediated tumorigenesis by inhibiting nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) signaling.J Biol Chem. 2013 Dec 13;288(50):36094-105. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.485029. Epub 2013 Nov 4. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24189064 Free PMC article.
-
SF2523: Dual PI3K/BRD4 Inhibitor Blocks Tumor Immunosuppression and Promotes Adaptive Immune Responses in Cancer.Mol Cancer Ther. 2019 Jun;18(6):1036-1044. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-18-1206. Epub 2019 Apr 24. Mol Cancer Ther. 2019. PMID: 31018997 Free PMC article.
-
BET protein function is required for inflammation: Brd2 genetic disruption and BET inhibitor JQ1 impair mouse macrophage inflammatory responses.J Immunol. 2013 Apr 1;190(7):3670-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1202838. Epub 2013 Feb 18. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23420887 Free PMC article.
-
BET bromodomain inhibitors--a novel epigenetic approach in castration-resistant prostate cancer.Cancer Biol Ther. 2014;15(12):1583-5. doi: 10.4161/15384047.2014.962297. Cancer Biol Ther. 2014. PMID: 25535892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bromodomain and extraterminal domain inhibitors (BETi) for cancer therapy: chemical modulation of chromatin structure.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014 Dec 1;6(12):a018663. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a018663. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014. PMID: 25452384 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacologic Targeting of BET Proteins Attenuates Hyperuricemic Nephropathy in Rats.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Feb 16;12:636154. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.636154. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33664670 Free PMC article.
-
BRD4: an effective target for organ fibrosis.Biomark Res. 2024 Aug 30;12(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s40364-024-00641-6. Biomark Res. 2024. PMID: 39215370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Modulation of Gremlin-1/NOTCH Pathway in Experimental Crescentic Immune-Mediated Glomerulonephritis.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Jan 20;15(2):121. doi: 10.3390/ph15020121. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35215234 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting BRD4: Potential therapeutic strategy for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (Review).Oncol Rep. 2024 Jun;51(6):74. doi: 10.3892/or.2024.8733. Epub 2024 Apr 12. Oncol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38606512 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological targeting of BET proteins inhibits renal fibroblast activation and alleviates renal fibrosis.Oncotarget. 2016 Oct 25;7(43):69291-69308. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12498. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27732564 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

