A short CD3/CD28 costimulation combined with IL-21 enhance the generation of human memory stem T cells for adoptive immunotherapy
- PMID: 27435312
- PMCID: PMC4952071
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-016-0973-y
A short CD3/CD28 costimulation combined with IL-21 enhance the generation of human memory stem T cells for adoptive immunotherapy
Abstract
Background: Immunotherapy based on the adoptive transfer of gene modified T cells is an emerging approach for the induction of tumor-specific immune responses. Memory stem T cells, due to their enhanced antitumor and self-renewal capacity, have become potential candidate for adoptive T cell therapy of cancer. Methods to generate memory stem T cells ex vivo rely on CD3/CD28 costimulation and the use of cytokines such as IL-7 and IL-15 during the entire culture period. However, a strong costimulation may induce differentiation of memory stem T cells to effector memory T cells. Here we show that manipulation of the length of the costimulation and addition of IL-21 enhance the ex vivo expansion of memory stem T cells.
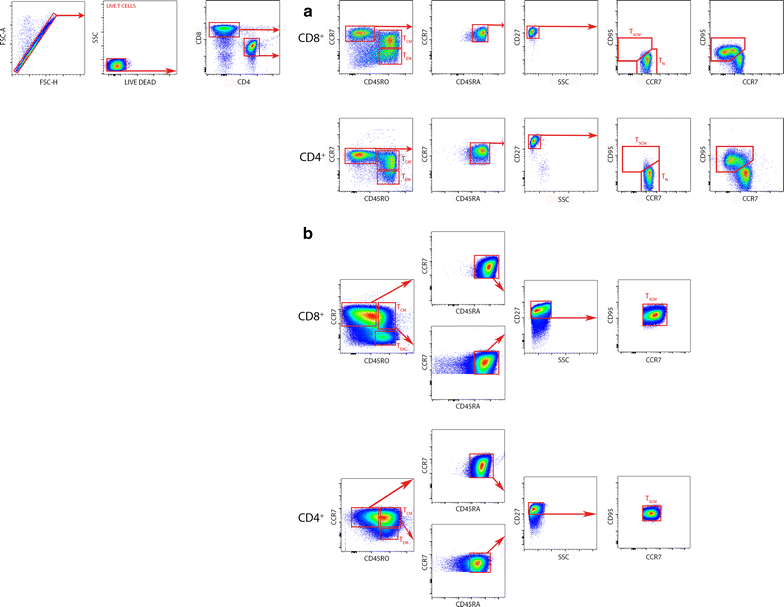
Methods: Purified naïve T cells from healthy donors were cultured in the presence of anti-CD3/CD28 coated beads, IL-7, IL-15 and/or IL-21 (25 ng/ml). T cells phenotype from the different memory and effector subpopulations were analyzed by multiparametric flow cytometry.
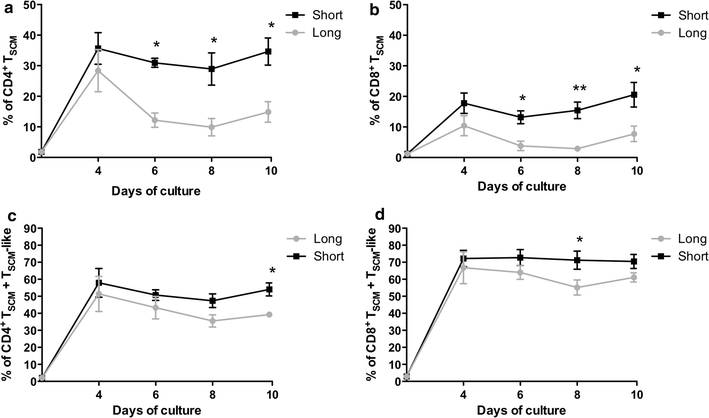
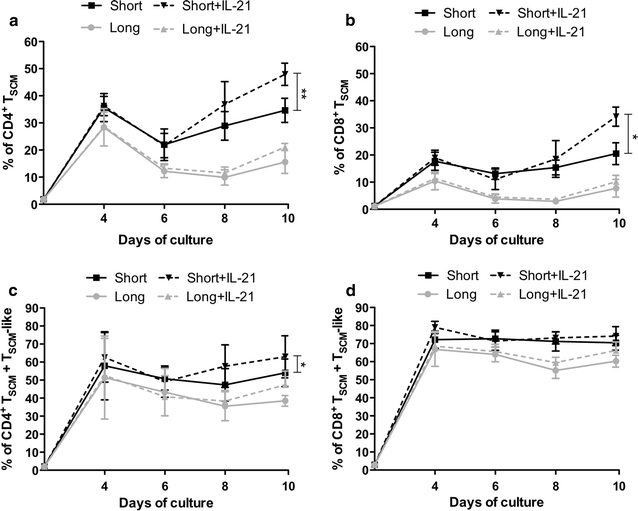
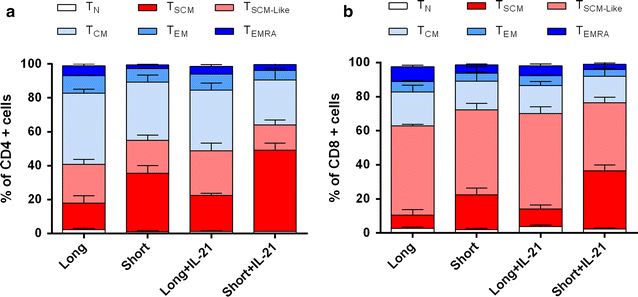
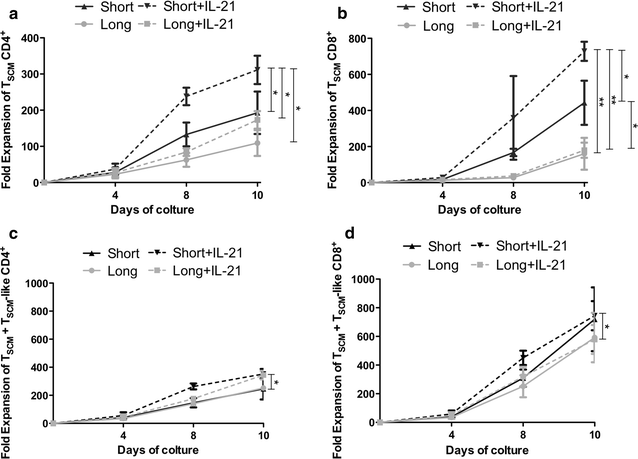
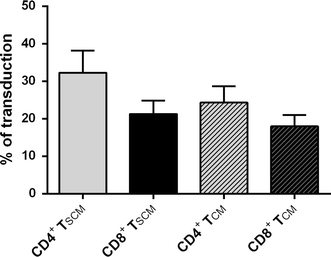
Results: A short anti-CD3/CD28 costimulation of naïve T cells, combined with IL-7 and IL-15 significantly increased the frequencies of CD4(+) and CD8(+) memory stem T cells ex vivo, compared to a prolonged costimulation (34.6 ± 4.4 % vs 15.6 ± 4.24 % in CD4(+); p = 0.008, and 20.5 ± 4.00 % vs 7.7 ± 2.53 % in CD8(+); p = 0.02). Moreover, the addition of IL-21 to this condition further enhanced the enrichment and expansion of CD4(+) and CD8(+) memory stem T cells with an increase in the absolute numbers (0.7 × 10(6) ± 0.1 vs 0.26 × 10(6) ± 0.1 cells for CD4(+); p = 0.002 and 1.1 × 10(6) ± 0.1 vs 0.27 × 10(6) ± 0.1 cells for CD8(+); p = 0.0002; short + IL-21 vs long).
Conclusions: These new in vitro conditions increase the frequencies and expansion of memory stem T cells and may have relevant clinical implications for the generation of this memory T cell subset for adoptive cell therapy of patients with cancer.
Keywords: IL-21; Immunotherapy; Memory stem T cell.
Figures
Similar articles
-
4-1BB is superior to CD28 costimulation for generating CD8+ cytotoxic lymphocytes for adoptive immunotherapy.J Immunol. 2007 Oct 1;179(7):4910-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.7.4910. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17878391 Free PMC article.
-
Ex vivo expansion of dendritic-cell-activated antigen-specific CD4+ T cells with anti-CD3/CD28, interleukin-7, and interleukin-15: potential for adoptive T cell immunotherapy.Clin Immunol. 2006 Apr;119(1):21-31. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2005.11.003. Epub 2006 Jan 9. Clin Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16406844
-
Transient stimulation expands superior antitumor T cells for adoptive therapy.JCI Insight. 2017 Jan 26;2(2):e89580. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.89580. JCI Insight. 2017. PMID: 28138559 Free PMC article.
-
Memory T cells need CD28 costimulation to remember.Semin Immunol. 2009 Apr;21(2):69-77. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2009.02.005. Epub 2009 Mar 5. Semin Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19268606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-15 is a growth factor and an activator of CD8 memory T cells.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002 Dec;975:46-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb05940.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002. PMID: 12538153 Review.
Cited by
-
Model-informed drug development of autologous CAR-T cell therapy: Strategies to optimize CAR-T cell exposure leveraging cell kinetic/dynamic modeling.CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2023 Nov;12(11):1577-1590. doi: 10.1002/psp4.13011. Epub 2023 Jul 28. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37448343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adoptive Transfer of Interleukin-21-stimulated Human CD8+ T Memory Stem Cells Efficiently Inhibits Tumor Growth.J Immunother. 2018 Jul/Aug;41(6):274-283. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0000000000000229. J Immunother. 2018. PMID: 29864078 Free PMC article.
-
Generation and application of human induced-stem cell memory T cells for adoptive immunotherapy.Cancer Sci. 2018 Jul;109(7):2130-2140. doi: 10.1111/cas.13648. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Cancer Sci. 2018. PMID: 29790621 Free PMC article.
-
Improving Adoptive T Cell Therapy: The Particular Role of T Cell Costimulation, Cytokines, and Post-Transfer Vaccination.Front Immunol. 2016 Sep 6;7:345. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00345. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27656185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The S enantiomer of 2-hydroxyglutarate increases central memory CD8 populations and improves CAR-T therapy outcome.Blood Adv. 2020 Sep 22;4(18):4483-4493. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020002309. Blood Adv. 2020. PMID: 32941648 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hinrichs CS, Borman ZA, Cassard L, Gattinoni L, Spolski R, Yu Z, Sanchez-Perez L, Muranski P, Kern SJ, Logun C, et al. Adoptively transferred effector cells derived from naive rather than central memory CD8+ T cells mediate superior antitumor immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:17469–17474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0907448106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhou X, Cui Y, Huang X, Yu Z, Thomas AM, Ye Z, Pardoll DM, Jaffee EM, Cheng L. Lentivirus-mediated gene transfer and expression in established human tumor antigen-specific cytotoxic T cells and primary unstimulated T cells. Hum Gene Ther. 2003;14:1089–1105. doi: 10.1089/104303403322124800. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

