Chromatin remodelers: We are the drivers!!
- PMID: 27429206
- PMCID: PMC5039004
- DOI: 10.1080/19491034.2016.1211217
Chromatin remodelers: We are the drivers!!
Abstract
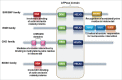
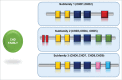
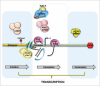
Chromatin is a highly dynamic structure that imparts structural organization to the genome and regulates the gene expression underneath. The decade long research in deciphering the significance of epigenetics in maintaining cellular integrity has embarked the focus on chromatin remodeling enzymes. These drivers have been categorized as readers, writers and erasers with each having significance of their own. Largely, on the basis of structure, ATP dependent chromatin remodelers have been grouped into 4 families; SWI/SNF, ISWI, IN080 and CHD. It is still unclear to what degree these enzymes are swayed by local DNA sequences when shifting a nucleosome to different positions. The ability of regulating active and repressive transcriptional state via open and close chromatin architecture has been well studied however, the significance of chromatin remodelers in regulating transcription at each step i.e. initiation, elongation and termination require further attention. The authors have highlighted the significance and role of different chromatin remodelers in transcription, DNA repair and histone variant deposition.
Keywords: Chromatin remodelers; histone variants; transcription.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The mechanisms of action of chromatin remodelers and implications in development and disease.Biochem Pharmacol. 2020 Oct;180:114200. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114200. Epub 2020 Aug 15. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32805211 Review.
-
Chromatin remodeling complexes: strength in diversity, precision through specialization.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2005 Apr;15(2):185-90. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2005.01.003. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2005. PMID: 15797201 Review.
-
Structure and Function of Chromatin Remodelers.J Mol Biol. 2021 Jul 9;433(14):166929. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.166929. Epub 2021 Mar 10. J Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33711345 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sophisticated Conversations between Chromatin and Chromatin Remodelers, and Dissonances in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 25;22(11):5578. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115578. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34070411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SWI/SNF Chromatin Remodelers: Structural, Functional and Mechanistic Implications.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2023 Jun;81(2):167-187. doi: 10.1007/s12013-023-01140-5. Epub 2023 Apr 29. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2023. PMID: 37119511 Review.
Cited by
-
CK2-Dependent Phosphorylation of the Brg1 Chromatin Remodeling Enzyme Occurs during Mitosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 30;21(3):923. doi: 10.3390/ijms21030923. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32019271 Free PMC article.
-
BAZ1B the Protean Protein.Genes (Basel). 2021 Sep 28;12(10):1541. doi: 10.3390/genes12101541. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34680936 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcription Factor SATB2 Regulates Skeletal Muscle Cell Proliferation and Migration via HDAC4 in Pigs.Genes (Basel). 2024 Jan 2;15(1):65. doi: 10.3390/genes15010065. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38254955 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Cell Transcriptomics Supports a Role of CHD8 in Autism.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 23;22(6):3261. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063261. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33806835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Histone Variant H2A.Z C-Terminal Domain Has Locus-Specific Differential Effects on H2A.Z Occupancy and Nucleosome Localization.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 23;11(2):e0255022. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02550-22. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36815792 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van Holde K, Zlatanova J. Chromatin fiber structure: Where is the problem now? Semin Cell Dev Biol 2007; 18:651-8; PMID:17905614; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2007.08.005 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Strahl BD, Allis CD. The language of covalent histone modifications. Nature 2000; 403:41-5; PMID:10638745; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/47412 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rippe K, Schrader A, Riede P, Strohner R, Lehmann E, Langst G. DNA sequence- and conformation-directed positioning of nucleosomes by chromatin-remodeling complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007; 104:15635-40; PMID:17893337; http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0702430104 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Clapier CR, Cairns BR. The biology of chromatin remodeling complexes. Ann Rev Biochem 2009; 78:273-304; PMID:19355820; http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.77.062706.153223 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Khorasanizadeh S. The nucleosome: from genomic organization to genomic regulation. Cell 2004; 116:259-72; PMID:14744436; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00044-3 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
