APOBEC3DE Inhibits LINE-1 Retrotransposition by Interacting with ORF1p and Influencing LINE Reverse Transcriptase Activity
- PMID: 27428332
- PMCID: PMC4948907
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157220
APOBEC3DE Inhibits LINE-1 Retrotransposition by Interacting with ORF1p and Influencing LINE Reverse Transcriptase Activity
Abstract
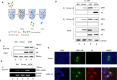
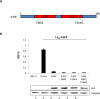
Human long interspersed elements 1 (LINE-1 or L1) is the only autonomous non-LTR retroelement in humans and has been associated with genome instability, inherited genetic diseases, and the development of cancer. Certain human APOBEC3 family proteins are known to have LINE-1 restriction activity. The mechanisms by which APOBEC3 affects LINE-1 retrotransposition are not all well characterized; here, we confirm that both A3B and A3DE have a strong ability to inhibit LINE-1 retrotransposition. A3DE interacts with LINE-1 ORF1p to target LINE-1 ribonucleoprotein particles in an RNA-dependent manner. Moreover, A3DE binds to LINE-1 RNA and ORF1 protein in cell culture system. Fluorescence microscopy demonstrated that A3DE co-localizes with ORF1p in cytoplasm. Furthermore, A3DE inhibits LINE-1 reverse transcriptase activity in LINE-1 ribonucleoprotein particles in a cytidine deaminase-independent manner. In contrast, A3B has less inhibitory effects on LINE-1 reverse transcriptase activity despite its strong inhibition of LINE-1 retrotransposition. This study demonstrates that different A3 proteins have been evolved to inhibit LINE-1 activity through distinct mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Human LINE-1 restriction by APOBEC3C is deaminase independent and mediated by an ORF1p interaction that affects LINE reverse transcriptase activity.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jan;42(1):396-416. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt898. Epub 2013 Oct 7. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24101588 Free PMC article.
-
Ribonucleoprotein particle formation is necessary but not sufficient for LINE-1 retrotransposition.Hum Mol Genet. 2005 Nov 1;14(21):3237-48. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddi354. Epub 2005 Sep 23. Hum Mol Genet. 2005. PMID: 16183655
-
APOBEC3 proteins inhibit LINE-1 retrotransposition in the absence of ORF1p binding.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009 Oct;1178:268-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05006.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009. PMID: 19845642 Free PMC article.
-
Protein-nucleic acid interactions of LINE-1 ORF1p.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Feb;86:140-149. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2018.03.019. Epub 2018 Mar 31. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 29596909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleic acid chaperone properties of ORF1p from the non-LTR retrotransposon, LINE-1.RNA Biol. 2010 Nov-Dec;7(6):706-11. doi: 10.4161/rna.7.6.13766. Epub 2010 Nov 1. RNA Biol. 2010. PMID: 21045547 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recurrent evolution of an inhibitor of ESCRT-dependent virus budding and LINE-1 retrotransposition in primates.Curr Biol. 2022 Apr 11;32(7):1511-1522.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2022.02.018. Epub 2022 Mar 3. Curr Biol. 2022. PMID: 35245459 Free PMC article.
-
A Possible Role for Long Interspersed Nuclear Elements-1 (LINE-1) in Huntington's Disease Progression.Med Sci Monit. 2018 May 31;24:3644-3652. doi: 10.12659/MSM.907328. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 29851926 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress of LINE-1 in the diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of gynecologic tumors.Front Oncol. 2023 Jul 20;13:1201568. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1201568. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37546391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enterovirus Infection Restricts Long Interspersed Element 1 Retrotransposition.Front Microbiol. 2021 Oct 18;12:706241. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.706241. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34733242 Free PMC article.
-
Factors Regulating the Activity of LINE1 Retrotransposons.Genes (Basel). 2021 Sep 30;12(10):1562. doi: 10.3390/genes12101562. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34680956 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chiu YL, Witkowska HE, Hall SC, Santiago M, Soros VB, Esnault C, et al. High-molecular-mass APOBEC3G complexes restrict Alu retrotransposition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. [Journal Article; Research Support, N.I.H., Extramural; Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't]. 2006 2006-October-17;103(42):15588–93. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Malim MH. Natural resistance to HIV infection: The Vif-APOBEC interaction. C R Biol. [Journal Article; Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't]. 2006 2006-November-01;329(11):871–5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

