Effect of the long-acting insulin analogues glargine and degludec on cardiomyocyte cell signalling and function
- PMID: 27422524
- PMCID: PMC4946153
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-016-0410-9
Effect of the long-acting insulin analogues glargine and degludec on cardiomyocyte cell signalling and function
Abstract
Background: The effects of insulin on cardiomyocytes, such as positive inotropic action and glucose uptake are well described. However, in vitro studies comparing long-acting insulin analogues with regard to cardiomyocyte signalling and function have not been systematically conducted.
Methods: Insulin receptor (IR) binding was assessed using membrane embedded and solubilised IR preparations. Insulin signalling was analysed in adult rat ventricular myocytes (ARVM) and HL-1 cardiac cells. Inotropic effects were examined in ARVM and the contribution of Akt to this effect was assessed by specific inhibition with triciribine. Furthermore, beating-rate in Cor.4U(®) human cardiomyocytes, glucose uptake in HL-1 cells, and prevention from H2O2 induced caspase 3/7 activation in cardiac cells overexpressing the human insulin receptor (H9c2-E2) were analysed. One-way ANOVA was performed to determine significance between conditions.
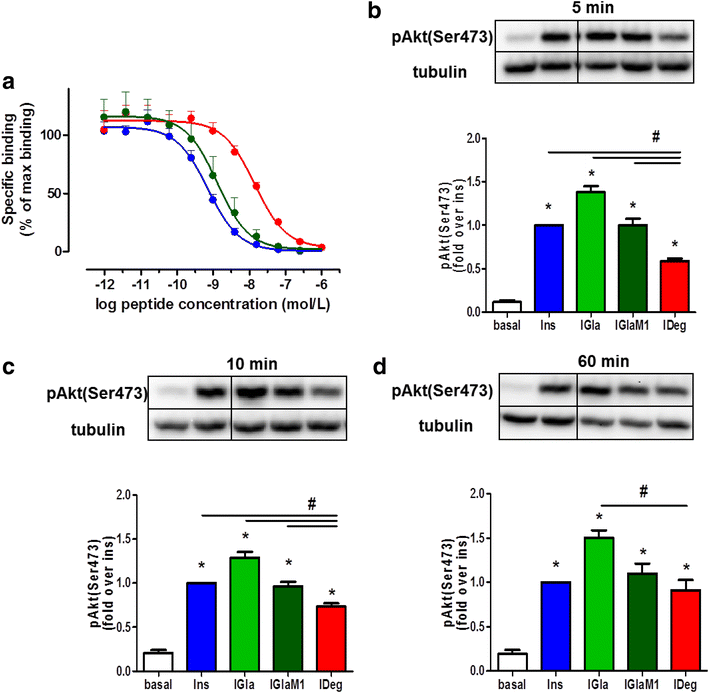
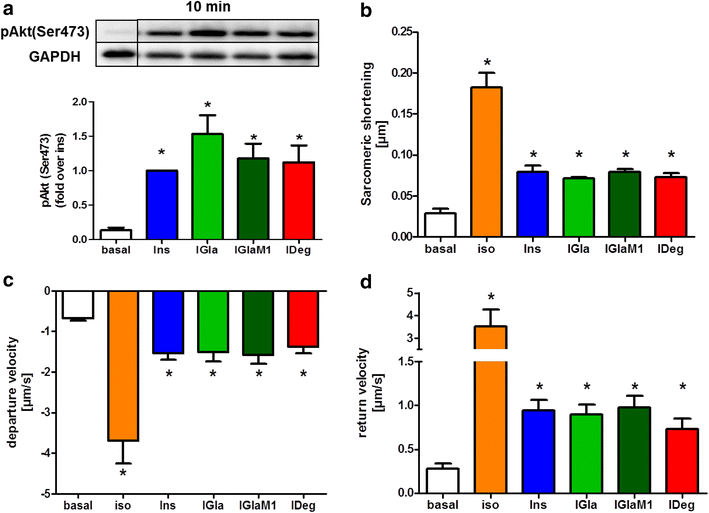
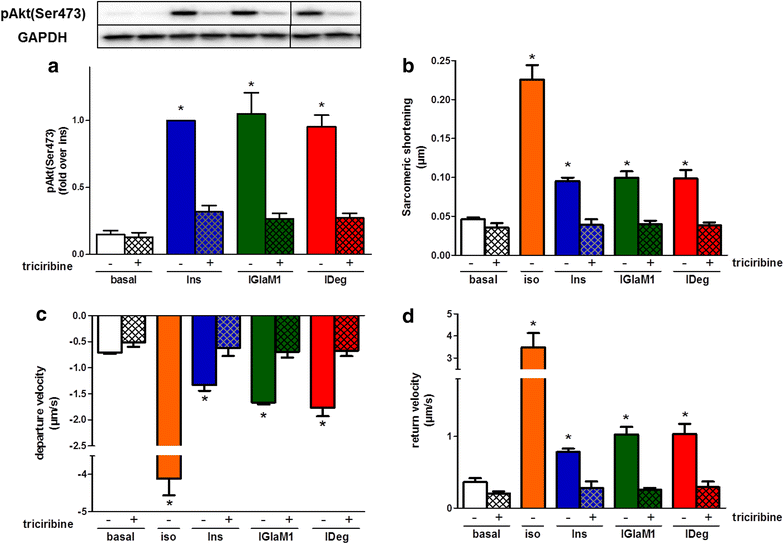
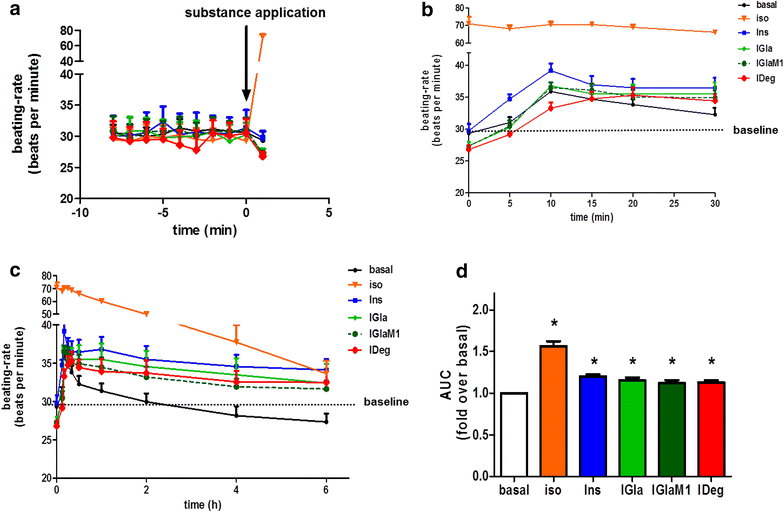
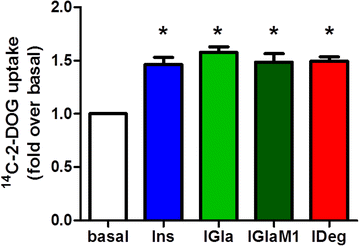
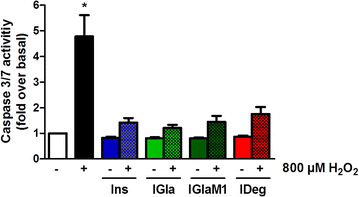
Results: Insulin degludec showed significant lower IR affinity in membrane embedded IR preparations. In HL-1 cardiomyocytes, stimulation with insulin degludec resulted in a lower Akt(Ser(473)) and Akt(Thr(308)) phosphorylation compared to insulin, insulin glargine and its active metabolite M1 after 5- and 10-min incubation. After 60-min treatment, phosphorylation of Akt was comparable for all insulin analogues. Stimulation of glucose uptake in HL-1 cells was increased by 40-60 %, with a similar result for all analogues. Incubation of electrically paced ARVM resulted for all insulins in a significantly increased sarcomere shortening, contractility- and relaxation-velocity. This positive inotropic effect of all insulins was Akt dependent. Additionally, in Cor.4U(®) cardiomyocytes a 10-20 % increased beating-rate was detected for all insulins, with slower onset of action in cells treated with insulin degludec. H9c2-E2 cells challenged with H2O2 showed a fivefold increase in caspase 3/7 activation, which could be abrogated by all insulins used.
Conclusions: In conclusion, we compared for the first time the signalling and functional impact of the long-acting insulin analogues insulin glargine and insulin degludec in cardiomyocyte cell models. We demonstrated similar efficacy under steady-state conditions relative to regular insulin in functional endpoint experiments. However, it remains to be shown how these results translate to the in vivo situation.
Keywords: Cardiac action; Insulin analogues; Insulin degludec; Insulin glargine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical relevance of pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles of insulin degludec (100, 200 U/mL) and insulin glargine (100, 300 U/mL) - a review of evidence and clinical interpretation.Diabetes Metab. 2019 Sep;45(4):330-340. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2018.11.004. Epub 2018 Nov 26. Diabetes Metab. 2019. PMID: 30496834 Review.
-
Long-acting insulin analogues elicit atypical signalling events mediated by the insulin receptor and insulin-like growth factor-I receptor.Diabetologia. 2010 Dec;53(12):2667-75. doi: 10.1007/s00125-010-1899-1. Epub 2010 Sep 12. Diabetologia. 2010. PMID: 20835859
-
Metabolic effect and receptor signalling profile of a non-metabolisable insulin glargine analogue.Arch Physiol Biochem. 2014 Oct;120(4):158-65. doi: 10.3109/13813455.2014.950589. Epub 2014 Aug 21. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2014. PMID: 25144413 Free PMC article.
-
Review of the Next Generation of Long-Acting Basal Insulins: Insulin Degludec and Insulin Glargine.Consult Pharm. 2017 Jan 1;32(1):42-46. doi: 10.4140/TCP.n.2017.42. Consult Pharm. 2017. PMID: 28077204 Review.
-
Degludec is superior to glargine in terms of daily glycemic variability in people with type 1 diabetes mellitus.Endocr J. 2016;63(1):53-60. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ15-0438. Epub 2015 Oct 31. Endocr J. 2016. PMID: 26522272 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Glucose transporters in cardiovascular system in health and disease.Pflugers Arch. 2020 Sep;472(9):1385-1399. doi: 10.1007/s00424-020-02444-8. Epub 2020 Aug 18. Pflugers Arch. 2020. PMID: 32809061 Review.
-
The signalling conformation of the insulin receptor ectodomain.Nat Commun. 2018 Oct 24;9(1):4420. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06826-6. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30356040 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ADA Standards of medical care in diabetes–2008. Diabetes Care. 2008;31(Suppl 1):S12–S54. - PubMed
-
- Rodbard HW, Gough S, Lane W, Korsholm L, Bretler DM, Handelsman Y. Reduced risk of hypoglycemia with insulin degludec versus insulin glargine in patients with type 2 diabetes requiring high doses of Basal insulin: a meta-analysis of 5 randomized begin trials. Endocr Pract. 2014;20(4):285–292. doi: 10.4158/EP13287.OR. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

