Interleukin-27 as a Novel Biomarker for Early Cardiopulmonary Failure in Enterovirus 71-Infected Children with Central Nervous System Involvement
- PMID: 27403033
- PMCID: PMC4925946
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/4025167
Interleukin-27 as a Novel Biomarker for Early Cardiopulmonary Failure in Enterovirus 71-Infected Children with Central Nervous System Involvement
Abstract
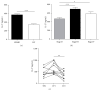
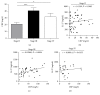
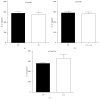
Enterovirus 71 (EV71) is a major pathogen for severe hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD), which leads to severe neurological complications and has high morbidity and mortality. Reliable biomarker for the prediction of deterioration in EV71-infected children with central nervous system (CNS) involvement may reduce the cardiopulmonary failure and mortality. Here, we found that serum IL-27 levels were significantly higher in stage III EV71-infected HFMD patients with early cardiopulmonary failure and strong correlation with CRP levels. IL27p28 polymorphisms (rs153109, rs17855750, and rs181206) did not influence IL-27 production, and these three SNPs were not associated with EV71 infection risk and clinical stage. IL-27 can be used as an prediction indicator for early cardiopulmonary failure in EV71-infected children with CNS involvement.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of clinical features between coxsackievirus A2 and enterovirus 71 during the enterovirus outbreak in Taiwan, 2008: a children's hospital experience.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2010 Apr;43(2):99-104. doi: 10.1016/S1684-1182(10)60016-3. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2010. PMID: 20457425
-
[The etiological and clinical characteristics of hospitalized children with hand, foot and mouth disease in Beijing in 2013].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2015 Jun;53(6):459-63. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26310558 Chinese.
-
Outbreak of central nervous system disease associated with hand, foot, and mouth disease in Japan during the summer of 2000: detection and molecular epidemiology of enterovirus 71.Microbiol Immunol. 2002;46(9):621-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.2002.tb02743.x. Microbiol Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12437029
-
Enterovirus-Associated Hand-Foot and Mouth Disease and Neurological Complications in Japan and the Rest of the World.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 20;20(20):5201. doi: 10.3390/ijms20205201. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31635198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Identification of P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 as one of the cellular receptors for enterovirus 71].Uirusu. 2009 Dec;59(2):195-203. doi: 10.2222/jsv.59.195. Uirusu. 2009. PMID: 20218328 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Exploring the role of interleukin-27 as a regulator of neuronal survival in central nervous system diseases.Neural Regen Res. 2022 Oct;17(10):2149-2152. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.336134. Neural Regen Res. 2022. PMID: 35259821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predicting Severe Enterovirus 71-Infected Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease: Cytokines and Chemokines.Mediators Inflamm. 2020 Jan 31;2020:9273241. doi: 10.1155/2020/9273241. eCollection 2020. Mediators Inflamm. 2020. PMID: 32089650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Entresto therapy effectively protects heart and lung against transverse aortic constriction induced cardiopulmonary syndrome injury in rat.Am J Transl Res. 2018 Aug 15;10(8):2290-2305. eCollection 2018. Am J Transl Res. 2018. PMID: 30210671 Free PMC article.
-
The upregulation of peripheral blood polyamine metabolites spermidine and spermine in children with hand, foot, mouth disease is related to enterovirus 71 capsid protein VP1, but not VP4.Transl Pediatr. 2023 Feb 28;12(2):194-207. doi: 10.21037/tp-23-41. Epub 2023 Feb 24. Transl Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 36891375 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic polymorphisms of IL-27 and risk of systemic lupus erythematosus disease in the Egyptian population.Clin Rheumatol. 2021 Dec;40(12):4899-4907. doi: 10.1007/s10067-021-05858-6. Epub 2021 Jul 29. Clin Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 34324143
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

