Evaluation of Antibiotics Active against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Based on Activity in an Established Biofilm
- PMID: 27401574
- PMCID: PMC5038242
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01251-16
Evaluation of Antibiotics Active against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Based on Activity in an Established Biofilm
Abstract
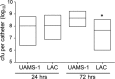
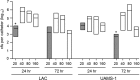
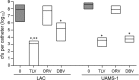
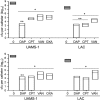
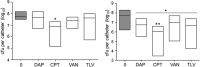
We used in vitro and in vivo models of catheter-associated biofilm formation to compare the relative activity of antibiotics effective against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in the specific context of an established biofilm. The results demonstrated that, under in vitro conditions, daptomycin and ceftaroline exhibited comparable activity relative to each other and greater activity than vancomycin, telavancin, oritavancin, dalbavancin, or tigecycline. This was true when assessed using established biofilms formed by the USA300 methicillin-resistant strain LAC and the USA200 methicillin-sensitive strain UAMS-1. Oxacillin exhibited greater activity against UAMS-1 than LAC, as would be expected, since LAC is an MRSA strain. However, the activity of oxacillin was less than that of daptomycin and ceftaroline even against UAMS-1. Among the lipoglycopeptides, telavancin exhibited the greatest overall activity. Specifically, telavancin exhibited greater activity than oritavancin or dalbavancin when tested against biofilms formed by LAC and was the only lipoglycopeptide capable of reducing the number of viable bacteria below the limit of detection. With biofilms formed by UAMS-1, telavancin and dalbavancin exhibited comparable activity relative to each other and greater activity than oritavancin. Importantly, ceftaroline was the only antibiotic that exhibited greater activity than vancomycin when tested in vivo in a murine model of catheter-associated biofilm formation. These results emphasize the need to consider antibiotics other than vancomycin, most notably, ceftaroline, for the treatment of biofilm-associated S. aureus infections, including by the matrix-based antibiotic delivery methods often employed for local antibiotic delivery in the treatment of these infections.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
New lipoglycopeptides: a comparative review of dalbavancin, oritavancin and telavancin.Drugs. 2010 May 7;70(7):859-86. doi: 10.2165/11534440-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20426497 Review.
-
Emergence of dalbavancin non-susceptible, vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus (VISA) after treatment of MRSA central line-associated bloodstream infection with a dalbavancin- and vancomycin-containing regimen.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2018 Apr;24(4):429.e1-429.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2017.07.028. Epub 2017 Aug 3. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2018. PMID: 28782651
-
Comparative In Vitro Activities of Oritavancin, Dalbavancin, and Vancomycin against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolates in a Nondividing State.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Jun 20;60(7):4342-5. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00169-16. Print 2016 Jul. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27067327 Free PMC article.
-
Dalbavancin Alone and in Combination with Ceftaroline against Four Different Phenotypes of Staphylococcus aureus in a Simulated Pharmacodynamic/Pharmacokinetic Model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019 Mar 27;63(4):e01743-18. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01743-18. Print 2019 Apr. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019. PMID: 30670436 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative review of the lipoglycopeptides: oritavancin, dalbavancin, and telavancin.Pharmacotherapy. 2010 Jan;30(1):80-94. doi: 10.1592/phco.30.1.80. Pharmacotherapy. 2010. PMID: 20030476 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis and antimicrobial studies of hydrazone derivatives of 4-[3-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-4-formyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl]benzoic acid and 4-[3-(3,4-difluorophenyl)-4-formyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl]benzoic acid.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2018 Sep 15;28(17):2914-2919. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2018.07.016. Epub 2018 Jul 10. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2018. PMID: 30017319 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Study of Antibiotic Elution Profiles From Alternative Formulations of Polymethylmethacrylate Bone Cement.J Arthroplasty. 2019 Jul;34(7):1458-1461. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2019.03.008. Epub 2019 Mar 12. J Arthroplasty. 2019. PMID: 30935799 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of the Elution Capacity of Dalbavancin in Bone Cements: New Alternative for the Treatment of Biofilm-Related Peri-Prosthetic Joint Infections Based on an In Vitro Study.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Sep 23;11(10):1300. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11101300. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36289958 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Staphylococcus aureus Antibiotic Tolerance Using Kill Curve Assays.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2341:45-54. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1550-8_7. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34264460
-
Evaluation of a bone filler scaffold for local antibiotic delivery to prevent Staphylococcus aureus infection in a contaminated bone defect.Sci Rep. 2021 May 13;11(1):10254. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-89830-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33986462 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

