Protective Effects of Liquiritin on the Brain of Rats with Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 27399208
- PMCID: PMC4961333
- DOI: 10.7727/wimj.2016.058
Protective Effects of Liquiritin on the Brain of Rats with Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
Background: Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a sort of nerve degenerative disease with clinical manifestation of memory damage and cognitive dysfunction. Its typical pathological change is the abnormal deposition of amyloid-beta (Aβ).
Method: In this study, a rat AD model with liquiritin (LQ) interference was established to observe the effects of LQ on the AD rats' behavioural memory and primary hippocampus cells.
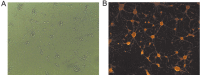
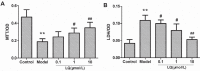
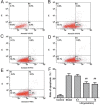
Results: Liquiritin had the effect of improving the rats' learning and memory ability, enhancing the activity of catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) in rats' brain tissues, increasing the antioxidant ability, protecting the primary cultured hippocampal neurons and inhibiting the apoptosis induced by Aβ25-35.
Conclusion: The protective effects of LQ can be related to the enhancement of antioxidase activity and clearance of oxygen radicals.
Antecedentes:: La enfermedad de Alzheimer (EA) es una especie de enfermedad degenerativa nerviosa con manifestaciones clínicas de daño de memoria y disfunción cognitiva. Su cambio patológico típico es el depósito anormal de beta-amiloide (Aβ).
Método:: En este estudio, se estableció un modelo de ratas con EA con interferencia de liquiritin (LQ) para observar los efectos de LQ en la memoria conductual y las células primarias del hipocampo de ratas con EA.
Resultados:: El liquiritin tuvo como efectos: mejorar la capacidad de la memoria y el aprendizaje de las ratas; aumentar la actividad de catalasa (CAT), el superóxido dismutasa (SOD) y el glutatión peroxidasa (GSH-Px) en los tejidos del cerebro de ratas; aumentar la capacidad antioxidante; proteger las neuronas primarias hipocámpicas de cultivo; e inhibir la apoptosis inducida por Aβ25-35.
Conclusión:: Los efectos protectores de LQ pueden atribuirse a la mejora de la actividad antioxidasa y la depuración de los radicales de oxígeno.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective effects of liquiritin on cognitive deficits induced by soluble amyloid-β1-42 oligomers injected into the hippocampus.J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2016 Dec;18(12):1186-1199. doi: 10.1080/10286020.2016.1201811. Epub 2016 Sep 2. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2016. PMID: 27589374
-
[Neuroprotection and neurotrophism effects of liquiritin on primary cultured hippocampal cells].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2008 Apr;33(8):931-5. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2008. PMID: 18619356 Chinese.
-
[Effects of Electroacupuncture Intervention on Oxygen Free Radicals and Expression of Apoptosis-related Proteins in Rats with Ischemic Learning and Memory Disorder].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2015 Dec;40(6):431-8. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2015. PMID: 26887202 Chinese.
-
Ginsenoside Rd attenuates Aβ25-35-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in primary cultured hippocampal neurons.Chem Biol Interact. 2015 Sep 5;239:12-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2015.06.030. Epub 2015 Jun 22. Chem Biol Interact. 2015. PMID: 26111763
-
Nanoparticles as potential clinical therapeutic agents in Alzheimer's disease: focus on selenium nanoparticles.Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2017 Jul;10(7):773-782. doi: 10.1080/17512433.2017.1324781. Epub 2017 May 16. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28463572 Review.
Cited by
-
Xiaochaihutang Improves the Cortical Astrocyte Edema in Thioacetamide-Induced Rat Acute Hepatic Encephalopathy by Activating NRF2 Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Apr 16;11:382. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00382. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32372950 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease and therapeutic strategies involving traditional Chinese medicine.RSC Med Chem. 2024 Oct 3;15(12):3950-69. doi: 10.1039/d4md00660g. Online ahead of print. RSC Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39430949 Review.
-
Demaghi, a polyherbal formulation, mitigates aluminum chloride-induced neurological impairment in mice: Insights from phytochemical analysis and behavioral assessment.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 27;9(11):e21234. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21234. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38027790 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of NF-κB as Determinant of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder and Its Inhibition by the Chinese Herbal Remedy Free and Easy Wanderer.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Apr 6;8:181. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00181. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28428751 Free PMC article.
-
Liquiritin Protects Against Cardiac Fibrosis After Myocardial Infarction by Inhibiting CCL5 Expression and the NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022 Dec 2;16:4111-4125. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S386805. eCollection 2022. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022. PMID: 36483459 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Braidy N, Muñoz P, Palacios AG, Castellano-Gonzalez G, Inestrosa NC, Chung RS, et al. Recent models for Alzheimer's disease: clinical implications and basic research. J Neural Transm. 2012;119:173–195. - PubMed
-
- Casal C, Serratosa J, Tusell JM. Effects of beta-AP peptides on activation of the transcription factor NF-kappa B and in cell proliferation in glial cell cultures. J Neurosci Res. 2004;48:315–323. - PubMed
-
- Newman M, Musgrave IF, Lardelli M. Alzheimer disease: amyloidogenesis, the presenilins and animal models. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1772:285–297. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

