Human Cytomegalovirus Immediate-Early 1 Protein Rewires Upstream STAT3 to Downstream STAT1 Signaling Switching an IL6-Type to an IFNγ-Like Response
- PMID: 27387064
- PMCID: PMC4936752
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005748
Human Cytomegalovirus Immediate-Early 1 Protein Rewires Upstream STAT3 to Downstream STAT1 Signaling Switching an IL6-Type to an IFNγ-Like Response
Abstract
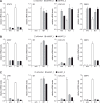
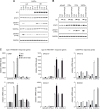
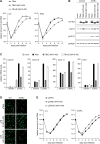
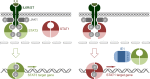
The human cytomegalovirus (hCMV) major immediate-early 1 protein (IE1) is best known for activating transcription to facilitate viral replication. Here we present transcriptome data indicating that IE1 is as significant a repressor as it is an activator of host gene expression. Human cells induced to express IE1 exhibit global repression of IL6- and oncostatin M-responsive STAT3 target genes. This repression is followed by STAT1 phosphorylation and activation of STAT1 target genes normally induced by IFNγ. The observed repression and subsequent activation are both mediated through the same region (amino acids 410 to 445) in the C-terminal domain of IE1, and this region serves as a binding site for STAT3. Depletion of STAT3 phenocopies the STAT1-dependent IFNγ-like response to IE1. In contrast, depletion of the IL6 receptor (IL6ST) or the STAT kinase JAK1 prevents this response. Accordingly, treatment with IL6 leads to prolonged STAT1 instead of STAT3 activation in wild-type IE1 expressing cells, but not in cells expressing a mutant protein (IE1dl410-420) deficient for STAT3 binding. A very similar STAT1-directed response to IL6 is also present in cells infected with a wild-type or revertant hCMV, but not an IE1dl410-420 mutant virus, and this response results in restricted viral replication. We conclude that IE1 is sufficient and necessary to rewire upstream IL6-type to downstream IFNγ-like signaling, two pathways linked to opposing actions, resulting in repressed STAT3- and activated STAT1-responsive genes. These findings relate transcriptional repressor and activator functions of IE1 and suggest unexpected outcomes relevant to viral pathogenesis in response to cytokines or growth factors that signal through the IL6ST-JAK1-STAT3 axis in hCMV-infected cells. Our results also reveal that IE1, a protein considered to be a key activator of the hCMV productive cycle, has an unanticipated role in tempering viral replication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Human cytomegalovirus IE1 protein elicits a type II interferon-like host cell response that depends on activated STAT1 but not interferon-γ.PLoS Pathog. 2011 Apr;7(4):e1002016. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002016. Epub 2011 Apr 14. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 21533215 Free PMC article.
-
Human cytomegalovirus IE1 protein disrupts interleukin-6 signaling by sequestering STAT3 in the nucleus.J Virol. 2013 Oct;87(19):10763-76. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01197-13. Epub 2013 Jul 31. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23903834 Free PMC article.
-
"Activated" STAT proteins: a paradoxical consequence of inhibited JAK-STAT signaling in cytomegalovirus-infected cells.J Immunol. 2014 Jan 1;192(1):447-58. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1203516. Epub 2013 Dec 6. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24319264
-
The functions of signal transducers and activators of transcriptions 1 and 3 as cytokine-inducible proteins.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011 Jan;31(1):33-40. doi: 10.1089/jir.2010.0100. Epub 2010 Dec 19. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011. PMID: 21166594 Free PMC article. Review.
-
STAT1 and pathogens, not a friendly relationship.Biochimie. 2010 May;92(5):425-44. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2010.02.009. Epub 2010 Feb 13. Biochimie. 2010. PMID: 20159032 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Human cytomegalovirus UL23 inhibits transcription of interferon-γ stimulated genes and blocks antiviral interferon-γ responses by interacting with human N-myc interactor protein.PLoS Pathog. 2018 Jan 29;14(1):e1006867. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006867. eCollection 2018 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29377960 Free PMC article.
-
Human Cytomegalovirus Utilizes a Nontraditional Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 1 Activation Cascade via Signaling through Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and Integrins To Efficiently Promote the Motility, Differentiation, and Polarization of Infected Monocytes.J Virol. 2017 Nov 30;91(24):e00622-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00622-17. Print 2017 Dec 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 29021395 Free PMC article.
-
CCR4-NOT differentially controls host versus virus poly(a)-tail length and regulates HCMV infection.EMBO Rep. 2023 Dec 6;24(12):e56327. doi: 10.15252/embr.202256327. Epub 2023 Oct 17. EMBO Rep. 2023. PMID: 37846490 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for Tethering of Human Cytomegalovirus Genomes to Host Chromosomes.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Sep 30;10:577428. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.577428. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33117732 Free PMC article.
-
PRD-Class Homeobox Genes in Bovine Early Embryos: Function, Evolution, and Overlapping Roles.Mol Biol Evol. 2022 May 3;39(5):msac098. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msac098. Mol Biol Evol. 2022. PMID: 35512670 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rodig SJ, Meraz MA, White JM, Lampe PA, Riley JK, Arthur CD, et al. Disruption of the Jak1 gene demonstrates obligatory and nonredundant roles of the Jaks in cytokine-induced biologic responses. Cell. 1998;93(3):373–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

