Thyroid hormone synthesis: a potential target of a Chinese herbal formula Haizao Yuhu Decoction acting on iodine-deficient goiter
- PMID: 27384475
- PMCID: PMC5239508
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.10329
Thyroid hormone synthesis: a potential target of a Chinese herbal formula Haizao Yuhu Decoction acting on iodine-deficient goiter
Abstract
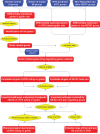
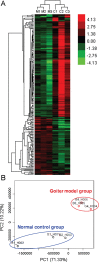
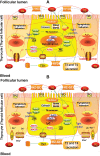
Haizao Yuhu Decoction (HYD), a famous multi-component herbal formula, has been widely used to treat various thyroid-related diseases, including iodine-deficient goiter. Herb pair Thallus Sargassi Pallidi (HZ) and Radix Glycyrrhizae (GC), one of the so-called "eighteen antagonistic medicaments", contains in HYD. To explore pharmacological mechanisms of HYD acting on iodine-deficient goiter and to provide evidence for potential roles of herb pair HZ and GC in HYD, our genome-wide microarray detection and network analysis identified a list of goiter-related genes, mainly involved into the alterations in hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid/gonad/growth axes. Then, the disease genes-drug genes interaction network illustrated the links between HYD regulating genes and goiter-related genes, and identified the candidate targets of HYD acting on goiter. Functionally, these candidate targets were closely correlated with thyroid hormone synthesis. Moreover, the potential regulating genes of herb pair HZ and GC were revealed to be crucial components in the pathway of thyroid hormone synthesis. The prediction results were all verified by following experiments based on goiter rats. Collectively, this integrative study combining microarray gene expression profiling, network analysis and experimental validations offers the convincing evidence that HYD may alleviate iodine-deficient goiter via regulating thyroid hormone synthesis, and explains the necessity of herb pair HZ and GC in HYD. Our work provides a novel and powerful means to clarify the mechanisms of action for multi-component drugs such as herbal formulae in a holistic way, which may improve drug development and applications.
Keywords: Chinese herbal formula; experimental validation; genome-wide microarray; goiter; network pharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not have any conflicts of interest with the content of the manuscript.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Exploring the effect and mechanism of Haizao Yuhu decoction containing three variants of glycyrrhiza on goiter using an integrated strategy of network pharmacology and RNA sequencing.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Nov 15;316:116750. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116750. Epub 2023 Jun 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37295576
-
Comparative Efficacy and Toxicity of Different Species of Sargassum in Haizao Yuhu Decoction in PTU-Induced Goiter Rats.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:3526186. doi: 10.1155/2017/3526186. Epub 2017 Jun 21. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017. PMID: 28713435 Free PMC article.
-
Haizao Yuhu decoctions including three species of glycyrrhiza protected against propylthiouracil-induced goiter with hypothyroidism in rats via the AMPK/mTOR pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Oct 5;296:115443. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115443. Epub 2022 Jun 6. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35680037
-
Two hundred years after discovery of iodine--less known functions of the element in human organism.Przegl Lek. 2012;69(12):1280-2. Przegl Lek. 2012. PMID: 23750439 Review.
-
[Network target: a starting point for traditional Chinese medicine network pharmacology].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2011 Aug;36(15):2017-20. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 22066431 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Prescription of Sageretia hamosa Brongn Relieved Goiter through Promoted Apoptosis of Thyroid Cells via miR-511-3p and PTEN/PI3K/Akt Pathway.J Healthc Eng. 2021 Sep 29;2021:3506559. doi: 10.1155/2021/3506559. eCollection 2021. J Healthc Eng. 2021. Retraction in: J Healthc Eng. 2023 Aug 2;2023:9878935. doi: 10.1155/2023/9878935. PMID: 34630982 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Uncovering the anticancer mechanism of Compound Kushen Injection against HCC by integrating quantitative analysis, network analysis and experimental validation.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 12;8(1):624. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-18325-7. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29330507 Free PMC article.
-
The Active Components of Fuzheng Huayu Formula and Their Potential Mechanism of Action in Inhibiting the Hepatic Stellate Cells Viability - A Network Pharmacology and Transcriptomics Approach.Front Pharmacol. 2018 May 24;9:525. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00525. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29881350 Free PMC article.
-
Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Experimental Validation to Unveil the Molecular Targets and Mechanisms of Compound Fuling Granule to Treat Ovarian Cancer.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Aug 23;2022:2896049. doi: 10.1155/2022/2896049. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. Retraction in: Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2023 Aug 2;2023:9867930. doi: 10.1155/2023/9867930. PMID: 36062197 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Molecular mechanisms of the analgesic action of Wu-tou Decoction on neuropathic pain in mice revealed using microarray and network analysis.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018 Jun;39(6):988-997. doi: 10.1038/aps.2017.110. Epub 2017 Aug 17. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018. PMID: 28816231 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Qureshi IA, Khabaz MN, Baig M, Begum B, Abdelrehaman AS, Hussain MB. Histopathological findings in goiter: A review of 624 thyroidectomies. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2015;36:48–52. - PubMed
-
- Anees M, Anis RA, Yousaf S, Murtaza I, Sultan A, Arslan M, Shahab M. Effect of maternal iodine supplementation on thyroid function and birth outcome in goiter endemic areas. Curr Med Res Opin. 2015;31:667–74. - PubMed
-
- Han Y, Gao L, Sun N, Zhang J, Zhang W, Zhou X, Zhang H, Zhao J. Effects of Kang-Jia-Wan, a Chinese medicinal herb officinal, on apoptosis induction in goiter of rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2009;122:533–40. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

