Therapeutic Elimination of the Type 1 Interferon Receptor for Treating Psoriatic Skin Inflammation
- PMID: 27369778
- PMCID: PMC5035634
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jid.2016.06.608
Therapeutic Elimination of the Type 1 Interferon Receptor for Treating Psoriatic Skin Inflammation
Abstract
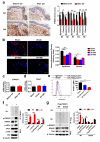
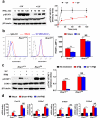
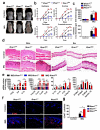
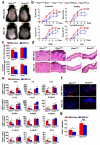
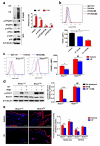
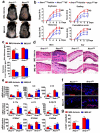
Phototherapy with UV light is a standard treatment for psoriasis, yet the mechanisms underlying the therapeutic effects are not well understood. Studies in human and mouse keratinocytes and in the skin tissues from human patients and mice showed that UV treatment triggers ubiquitination and downregulation of the type I IFN receptor chain IFNAR1, leading to suppression of IFN signaling and an ensuing decrease in the expression of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. The severity of imiquimod-induced psoriasiform inflammation was greatly exacerbated in skin of mice deficient in IFNAR1 ubiquitination (Ifnar1(SA)). Furthermore, these mice did not benefit from UV phototherapy. Pharmacologic induction of IFNAR1 ubiquitination and degradation by an antiprotozoal agent halofuginone also relieved psoriasiform inflammation in wild-type but not in Ifnar1(SA) mice. These data identify downregulation of IFNAR1 by UV as a major mechanism of the UV therapeutic effects against the psoriatic inflammation and provide a proof of principle for future development of agents capable of inducing IFNAR1 ubiquitination and downregulation for the treatment of psoriasis.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Triggering ubiquitination of IFNAR1 protects tissues from inflammatory injury.EMBO Mol Med. 2014 Mar;6(3):384-97. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201303236. Epub 2014 Jan 30. EMBO Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24480543 Free PMC article.
-
Dual Inhibition of TNFR1 and IFNAR1 in Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasiform Skin Inflammation in Mice.J Immunol. 2015 Jun 1;194(11):5094-102. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1403015. Epub 2015 Apr 24. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25911755 Free PMC article.
-
Role of p38 protein kinase in the ligand-independent ubiquitination and down-regulation of the IFNAR1 chain of type I interferon receptor.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jun 24;286(25):22069-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.238766. Epub 2011 May 3. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21540188 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the IFNAR1 chain of type 1 interferon receptor in benign cells protects against progression of acute leukemia.Leuk Lymphoma. 2018 Jan;59(1):171-177. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2017.1319053. Epub 2017 May 15. Leuk Lymphoma. 2018. PMID: 28503979 Free PMC article.
-
Type1 Interferons Potential Initiating Factors Linking Skin Wounds With Psoriasis Pathogenesis.Front Immunol. 2019 Jun 25;10:1440. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01440. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31293591 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
OTULIN maintains skin homeostasis by controlling keratinocyte death and stem cell identity.Nat Commun. 2021 Oct 8;12(1):5913. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25944-2. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34625556 Free PMC article.
-
Orchestrated Cytokines Mediated by Biologics in Psoriasis and Its Mechanisms of Action.Biomedicines. 2022 Feb 20;10(2):498. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10020498. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35203707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signs of innate immune activation and premature immunosenescence in psoriasis patients.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 8;7(1):7553. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07975-2. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28790368 Free PMC article.
-
A peptide derived from phage-display limits psoriasis-like lesions in mice.Heliyon. 2020 Jun 17;6(6):e04162. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04162. eCollection 2020 Jun. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 32577560 Free PMC article.
-
Differentially expressed genes and miRNAs in female osteoporosis patients.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Jul 15;101(28):e29856. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000029856. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 35839011 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baechler EC, Batliwalla FM, Reed AM, Peterson EJ, Gaffney PM, Moser KL, Gregersen PK, Behrens TW. Immunol Rev. 2006;210:120–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

