SARS Coronavirus Fusion Peptide-Derived Sequence Suppresses Collagen-Induced Arthritis in DBA/1J Mice
- PMID: 27349522
- PMCID: PMC4923882
- DOI: 10.1038/srep28672
SARS Coronavirus Fusion Peptide-Derived Sequence Suppresses Collagen-Induced Arthritis in DBA/1J Mice
Abstract
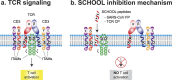
During the co-evolution of viruses and their hosts, the viruses have evolved numerous strategies to counter and evade host antiviral immune responses in order to establish a successful infection, replicate and persist in the host. Recently, based on our model of immune signaling, the Signaling Chain HOmoOLigomerization (SCHOOL) model, we suggested specific molecular mechanisms used by different viruses such as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) to modulate the host immune response mediated by members of the family of multichain immune recognition receptors (MIRRs). This family includes T cell receptor (TCR) that is critically involved in immune diseases such as autoimmune arthritis. In the present study, we provide compelling experimental in vivo evidence in support of our hypothesis. Using the SCHOOL approach and the SARS-CoV fusion peptide sequence, we rationally designed a novel immunomodulatory peptide that targets TCR. We showed that this peptide ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis in DBA/1J mice and protects against bone and cartilage damage. Incorporation of the peptide into self-assembling lipopeptide nanoparticles that mimic native human high density lipoproteins significantly increases peptide dosage efficacy. Together, our data further confirm that viral immune evasion strategies that target MIRRs can be transferred to therapeutic strategies that require similar functionalities.
Conflict of interest statement
Alexander B. Sigalov and Zu T. Shen are employees of SignaBlok, Inc. The funders provided support in the form of salaries for authors [ABS and ZTS], but did not have any additional role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. The specific roles of these authors are articulated in the ‘author contributions’ section.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of the Fusion Peptide-Containing Region in Betacoronavirus Spike Glycoproteins.J Virol. 2016 May 27;90(12):5586-5600. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00015-16. Print 2016 Jun 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27030273 Free PMC article.
-
Viral pathogenesis, modulation of immune receptor signaling and treatment.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;640:325-49. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-09789-3_22. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 19065800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction between heptad repeat 1 and 2 regions in spike protein of SARS-associated coronavirus: implications for virus fusogenic mechanism and identification of fusion inhibitors.Lancet. 2004 Mar 20;363(9413):938-47. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)15788-7. Lancet. 2004. PMID: 15043961 Free PMC article.
-
Fusion core structure of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV): in search of potent SARS-CoV entry inhibitors.J Cell Biochem. 2008 Aug 15;104(6):2335-47. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21790. J Cell Biochem. 2008. PMID: 18442051 Free PMC article.
-
SCHOOL model and new targeting strategies.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;640:268-311. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-09789-3_20. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 19065798 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Engineering self-assembled materials to study and direct immune function.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017 May 15;114:60-78. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2017.03.005. Epub 2017 Apr 6. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017. PMID: 28392305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel nano therapeutic materials for the effective treatment of rheumatoid arthritis-recent insights.Mater Today Commun. 2018 Dec;17:200-213. doi: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2018.09.011. Epub 2018 Sep 15. Mater Today Commun. 2018. PMID: 32289062 Free PMC article.
-
Rationally designed ligand-independent peptide inhibitors of TREM-1 ameliorate collagen-induced arthritis.J Cell Mol Med. 2017 Oct;21(10):2524-2534. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13173. Epub 2017 Apr 6. J Cell Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28382703 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of TREM-2 Markedly Suppresses Joint Inflammation and Damage in Experimental Arthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 9;23(16):8857. doi: 10.3390/ijms23168857. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012120 Free PMC article.
-
SCHOOL of nature: ligand-independent immunomodulatory peptides.Drug Discov Today. 2020 Aug;25(8):1298-1306. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2020.05.005. Epub 2020 May 12. Drug Discov Today. 2020. PMID: 32405248 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen J. & Subbarao K. The Immunobiology of SARS*. Annu Rev Immunol 25, 443–472 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Gallaher W. R., Ball J. M., Garry R. F., Griffin M. C. & Montelaro R. C. A general model for the transmembrane proteins of HIV and other retroviruses. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 5, 431–440 (1989). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

