Tiliroside, the major component of Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb ethanol extract, inhibits MAPK/JNK/p38-mediated inflammation in lipopolysaccharide-activated RAW 264.7 macrophages
- PMID: 27347085
- PMCID: PMC4906937
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2016.3305
Tiliroside, the major component of Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb ethanol extract, inhibits MAPK/JNK/p38-mediated inflammation in lipopolysaccharide-activated RAW 264.7 macrophages
Abstract
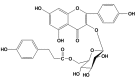
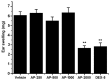
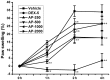
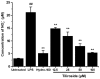
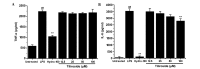
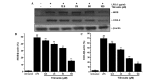
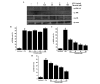
In the present study, the in vivo anti-inflammatory activity of Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb (AP) ethanol extract was confirmed in experimental animal models, including xylene-induced ear edema in mice and carrageenan-induced paw edema in rats. Tiliroside, the major component of AP extract, was isolated and purified by high-performance liquid chromatography. The anti-inflammatory mechanism of tiliroside was then examined using lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. An MTT assay was used to determine cytotoxicity and a Griess assay was used to determine nitric oxide (NO) production. Concentration levels of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Protein expression levels of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), phosphorylated (p)-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2, p-c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNK), p-p38 and inhibitor of κB-α were detected by western blot analysis. AP ethanol extract was revealed to inhibit xylene-induced ear edema in mice and carrageenan-induced paw edema in rats. Tiliroside significantly suppressed the overproduction of NO (P<0.01), but revealed no notable inhibition of the release of TNF-α and IL-6. In addition, tiliroside significantly downregulated the elevated expression levels of iNOS and COX-2 induced by LPS (P<0.01). The phosphorylation of JNK and p38 proteins were also significantly inhibited (P<0.01), however, tiliroside exhibited no obvious inhibition on the phosphorylation of ERK 1/2 and the degradation of IκB-α protein. In conclusion, the anti-inflammatory molecular mechanism of tiliroside may involve the downregulation of iNOS and COX-2 protein expression levels, and the inactivation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/JNK, in addition to the MAPK/p38 signaling pathway.
Keywords: Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb; cyclooxygenase-2; inducible nitric oxide synthase; mitogen-activated protein kinase; tiliroside.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In vivo and in vitro anti-inflammatory effects of ethanol fraction from Periploca forrestii Schltr.Chin J Integr Med. 2017 Jul;23(7):528-534. doi: 10.1007/s11655-017-2803-3. Epub 2017 Mar 10. Chin J Integr Med. 2017. PMID: 28283936
-
11-O-acetylcyathatriol inhibits MAPK/p38-mediated inflammation in LPS-activated RAW 264.7 macrophages and has a protective effect on ethanol-induced gastric injury.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Jul;14(1):874-80. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5305. Epub 2016 May 18. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27222252
-
Anti-inflammatory activity of 4-methoxyhonokiol is a function of the inhibition of iNOS and COX-2 expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages via NF-kappaB, JNK and p38 MAPK inactivation.Eur J Pharmacol. 2008 May 31;586(1-3):340-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.02.044. Epub 2008 Feb 26. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18378223
-
Agrimonia pilosa: A Phytochemical and Pharmacological Review.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Apr 29;2022:3742208. doi: 10.1155/2022/3742208. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35529922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Progress and Outlook for Agrimonolide: A Promising Bioactive Compound from Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Jan 19;16(2):150. doi: 10.3390/ph16020150. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37259301 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tiliroside as a CAXII inhibitor suppresses liver cancer development and modulates E2Fs/Caspase-3 axis.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 21;11(1):8626. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-88133-7. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33883691 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of β-carboline and canthinone alkaloids as anti-inflammatory agents but with different inhibitory profile on the expression of iNOS and COX-2 in lipopolysaccharide-activated RAW 264.7 macrophages.J Nat Med. 2019 Jan;73(1):124-130. doi: 10.1007/s11418-018-1251-5. Epub 2018 Oct 15. J Nat Med. 2019. PMID: 30324332 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the p-Coumaroyl Moiety in the Antioxidant and Cytoprotective Effects of Flavonoid Glycosides: Comparison of Astragalin and Tiliroside.Molecules. 2017 Jul 12;22(7):1165. doi: 10.3390/molecules22071165. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28704976 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Flavonoids from Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb: Focusing on Activity-Guided Isolation.Molecules. 2024 Jan 5;29(2):283. doi: 10.3390/molecules29020283. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38257196 Free PMC article.
-
Tiliroside Protects against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Kidney Injury via Intrarenal Renin-Angiotensin System in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 25;24(21):15556. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115556. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958538 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
