Running-Induced Systemic Cathepsin B Secretion Is Associated with Memory Function
- PMID: 27345423
- PMCID: PMC6029441
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.05.025
Running-Induced Systemic Cathepsin B Secretion Is Associated with Memory Function
Abstract
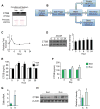
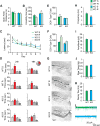
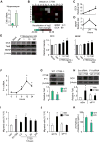
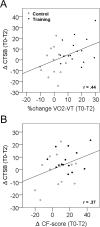
Peripheral processes that mediate beneficial effects of exercise on the brain remain sparsely explored. Here, we show that a muscle secretory factor, cathepsin B (CTSB) protein, is important for the cognitive and neurogenic benefits of running. Proteomic analysis revealed elevated levels of CTSB in conditioned medium derived from skeletal muscle cell cultures treated with AMP-kinase agonist AICAR. Consistently, running increased CTSB levels in mouse gastrocnemius muscle and plasma. Furthermore, recombinant CTSB application enhanced expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and doublecortin (DCX) in adult hippocampal progenitor cells through a mechanism dependent on the multifunctional protein P11. In vivo, in CTSB knockout (KO) mice, running did not enhance adult hippocampal neurogenesis and spatial memory function. Interestingly, in Rhesus monkeys and humans, treadmill exercise elevated CTSB in plasma. In humans, changes in CTSB levels correlated with fitness and hippocampus-dependent memory function. Our findings suggest CTSB as a mediator of effects of exercise on cognition.
Keywords: cathepsin B; exercise; hippocampus; humans; memory; mice; muscle.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
Comment in
-
How Body Affects Brain.Cell Metab. 2016 Aug 9;24(2):192-3. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.07.022. Cell Metab. 2016. PMID: 27508865
Similar articles
-
Glucocorticoid signaling and exercise-induced downregulation of the mineralocorticoid receptor in the induction of adult mouse dentate neurogenesis by treadmill running.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2008 Oct;33(9):1173-82. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2008.05.014. Epub 2008 Aug 28. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2008. PMID: 18760539
-
Voluntary exercise induces anxiety-like behavior in adult C57BL/6J mice correlating with hippocampal neurogenesis.Hippocampus. 2010 Mar;20(3):364-76. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20634. Hippocampus. 2010. PMID: 19452518
-
Voluntary resistance running with short distance enhances spatial memory related to hippocampal BDNF signaling.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2012 Oct 15;113(8):1260-6. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00869.2012. Epub 2012 Aug 30. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2012. PMID: 22936723
-
Cathepsin B Gene Knockout Improves Behavioral Deficits and Reduces Pathology in Models of Neurologic Disorders.Pharmacol Rev. 2022 Jul;74(3):600-629. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.121.000527. Pharmacol Rev. 2022. PMID: 35710131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Mild Exercise Results in Robust Brain Activation and Increased Memory Function].Brain Nerve. 2018 Jul;70(7):745-752. doi: 10.11477/mf.1416201075. Brain Nerve. 2018. PMID: 29997270 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Major Depressive Disorder and Gut Microbiota: Role of Physical Exercise.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 28;24(23):16870. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316870. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Milk Fat Globule Membrane-Containing Protein Powder Promotes Fitness in Caenorhabditis elegans.Nutrients. 2024 Jul 17;16(14):2290. doi: 10.3390/nu16142290. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39064733 Free PMC article.
-
Research trends and hotspot evolution of exercise-regulated myokines: a bibliometric analysis from 2003 to 2023.Front Physiol. 2024 Aug 1;15:1410068. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1410068. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39148743 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic communication during exercise.Nat Metab. 2020 Sep;2(9):805-816. doi: 10.1038/s42255-020-0258-x. Epub 2020 Aug 3. Nat Metab. 2020. PMID: 32747791 Review.
-
Musclin prevents depression-like behavior in male mice by activating urocortin 2 signaling in the hypothalamus.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Dec 5;14:1288282. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1288282. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38116320 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agudelo LZ, Femenia T, Orhan F, Porsmyr-Palmertz M, Goiny M, Martinez-Redondo V, Correia JC, Izadi M, Bhat M, Schuppe-Koistinen I, et al. Skeletal muscle PGC-1alpha1 modulates kynurenine metabolism and mediates resilience to stress-induced depression. Cell. 2014;159:33–45. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee M, Sasse VA, Wang Y, Maulik M, Kar S. Increased levels and activity of cathepsins B and D in kainate-induced toxicity. Neuroscience. 2015;284:360–373. - PubMed
-
- Bednarski E, Lauterborn JC, Gall CM, Lynch G. Lysosomal dysfunction reduces brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression. Exp. Neurol. 1998;150:128–135. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

